Abstract
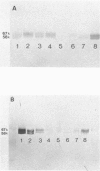
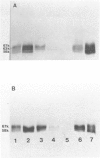
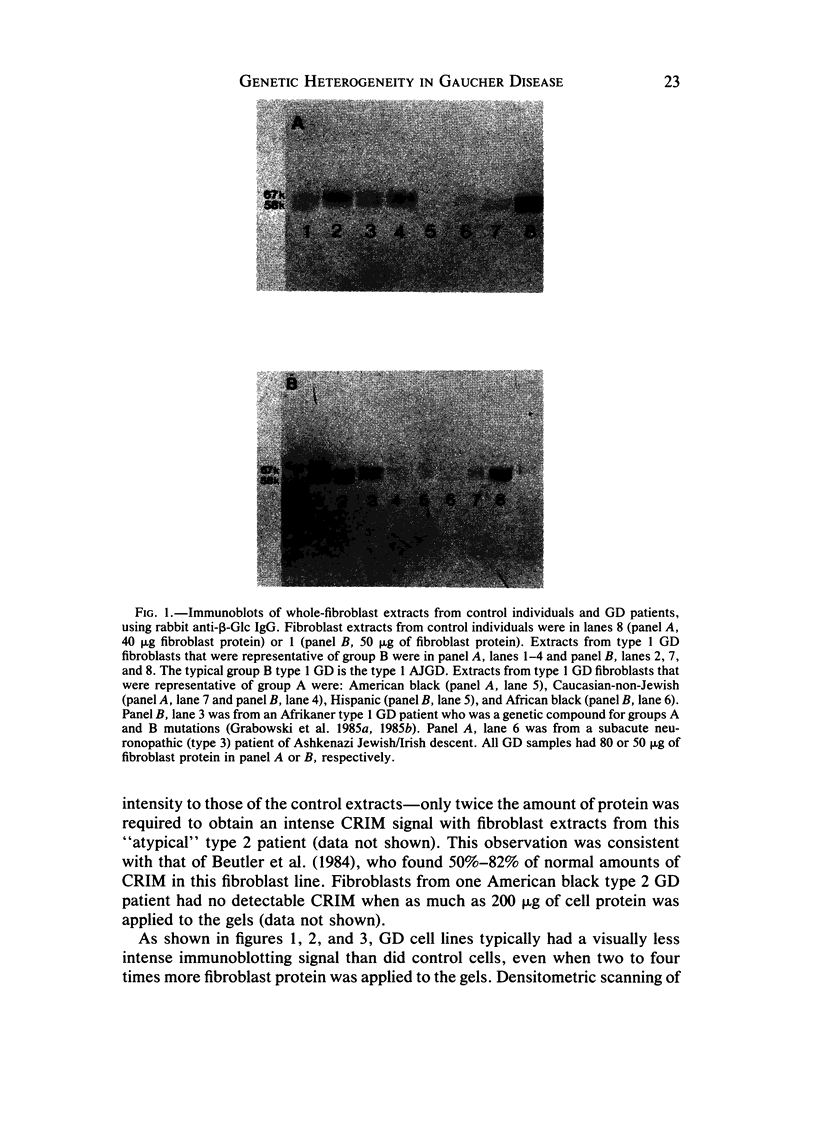
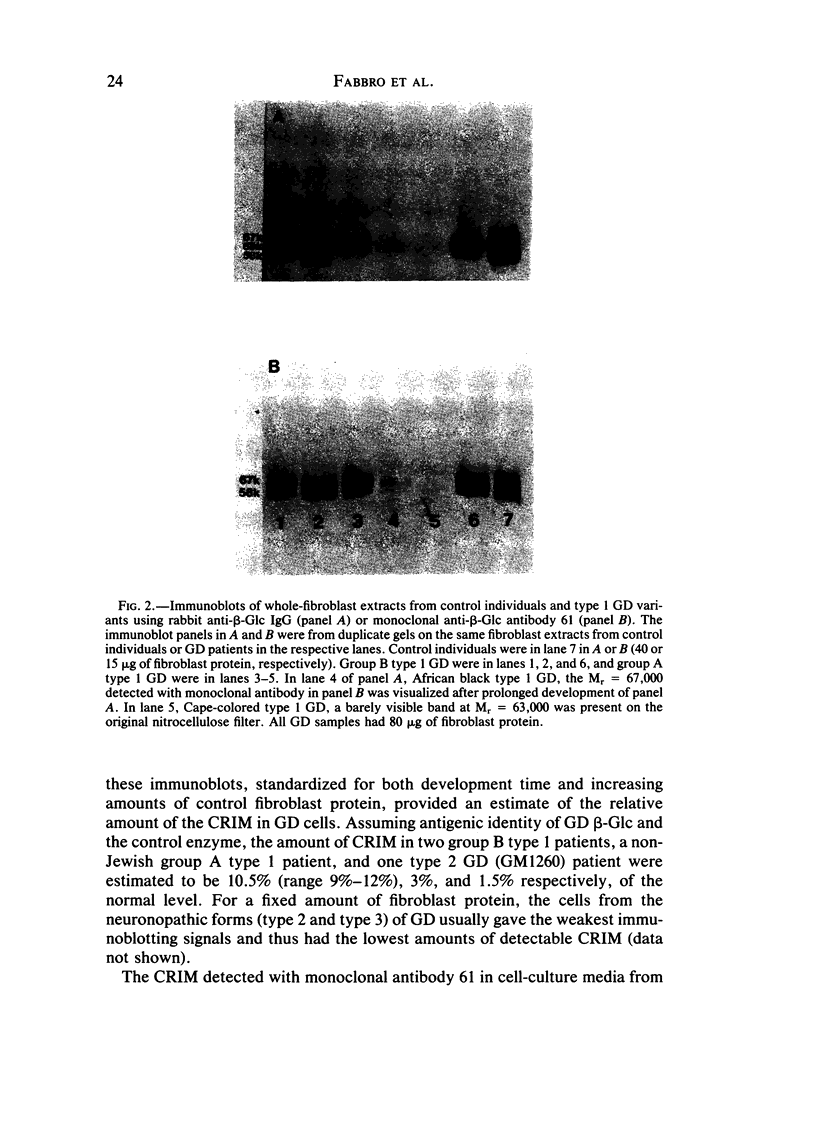
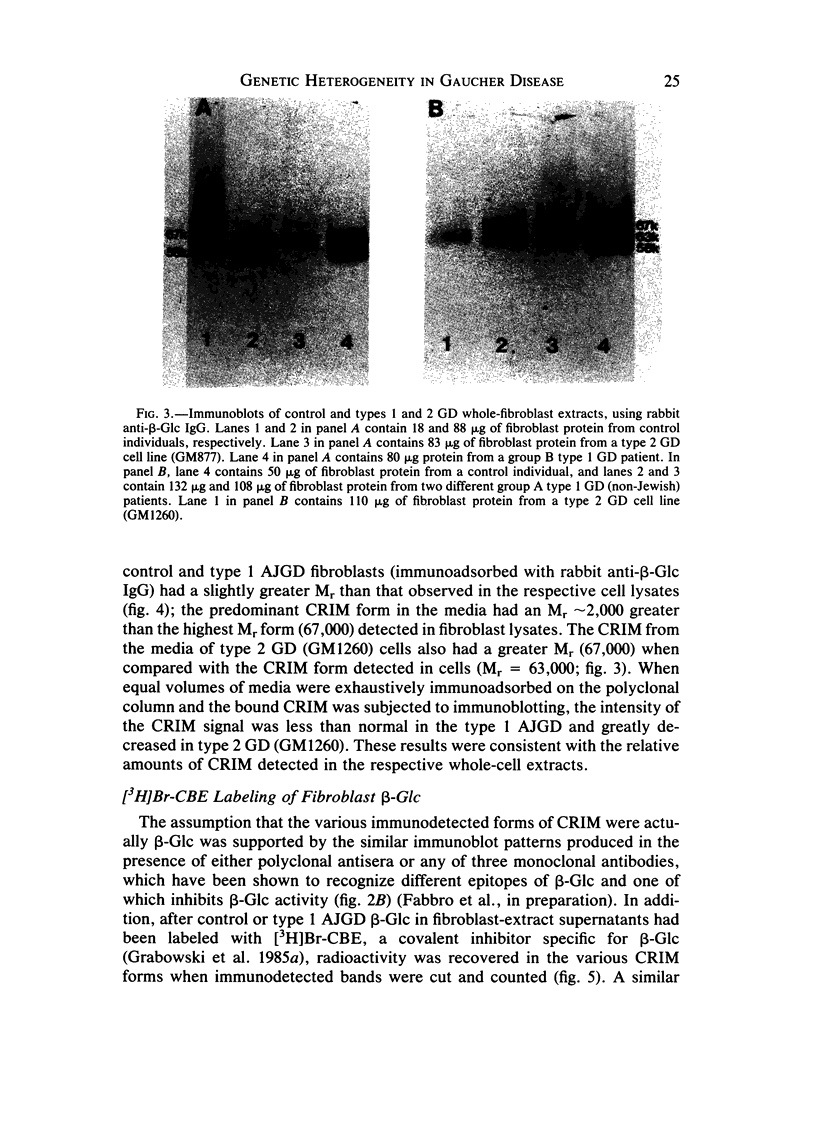
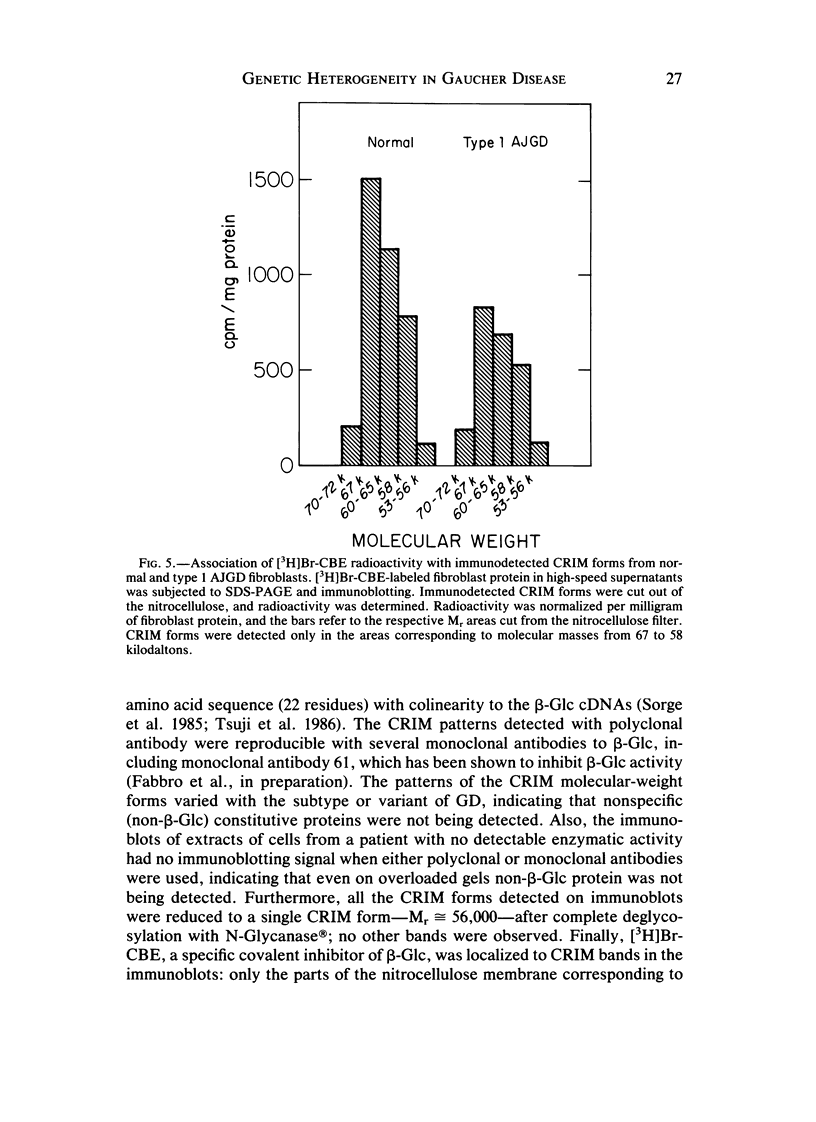
The genetic heterogeneity of Gaucher disease subtypes and variants was investigated by immunoblotting of fibroblast extracts. For these studies polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies were raised to acid beta-glucosidase preparations containing a single N-terminal amino acid sequence that was colinear with that encoded by the beta-Glc cDNAs. Three forms (Mr approximately equal to 67,000, 64,000-61,000, and 58,000) of cross-reacting immunologic material (CRIM) were observed in control individuals. Decreased amounts of the same CRIM forms were detected in most type 1 Gaucher disease patients, but single CRIM forms of variable molecular weight were observed in several non-Jewish type 1 variants. One or two CRIM forms of variable molecular weight were found in neuronopathic (type 2 and type 3) patients. The amount of CRIM was severely decreased in the majority of the type 2 and type 3 patients; one American black type 2 patient was CRIM negative. With this one exception, one CRIM form was detected in the cell-free culture media from all normal or Gaucher disease fibroblasts that had an Mr approximately 2,000 greater than the highest respective intracellular molecular-weight form. All intra- or extracellular CRIM forms were reduced to a single form after deglycosylation with N-Glycanase. In addition, the radioactivity from [3H]Br-conduritol B epoxide, a specific covalent inhibitor of beta-Glc, localized to the CRIM forms of beta-Glc on immunoblots. These results indicate that all subtypes and variants of Gaucher disease result from mutations that alter the stability and/or processing of beta-Glc. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of the CRIM patterns within and among the variants of Gaucher disease cause the diagnostic usefulness of immunoblotting to be restricted to those families in which the phenotype has been well established.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINN L., GLABMAN S. Gaucher's disease without splenomegaly. Oldest patient on record, with review. N Y State J Med. 1962 Jul 15;62:2346–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Sorge J. Cross-reacting material in Gaucher disease fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6506–6510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. K., Rees D. C. Molecular basis for the alpha1-protease inhibitor deficiency. Nature. 1975 May 15;255(5505):240–241. doi: 10.1038/255240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy F. Y. Gaucher disease: the effects of phosphatidylserine on glucocerebrosidase from normal and Gaucher fibroblasts. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):432–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00291405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L. B., Glew R. H. beta-Glucosidase assays in the diagnosis of Gaucher's disease. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 1):569–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreborg S., Erikson A., Hagberg B. Gaucher disease--Norrbottnian type. I. General clinical description. Eur J Pediatr. 1980 Mar;133(2):107–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00441578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Ginns E. I., Barranger J. A. Biosynthesis of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14319–14324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Brady R. O., Pirruccello S., Moore C., Sorrell S., Furbish F. S., Murray G. J., Tager J., Barranger J. A. Mutations of glucocerebrosidase: discrimination of neurologic and non-neurologic phenotypes of Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5607–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Tegelaers F. P., Barneveld R., Galjaard H., Reuser A. J., Brady R. O., Tager J. M., Barranger J. A. Determination of Gaucher's disease phenotypes with monoclonal antibody. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jul 15;131(3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Daniels L. B., Clark L. S., Hoyer S. W. Enzymic differentiation of neurologic and nonneurologic forms of Gaucher's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 Nov;41(6):630–641. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198211000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski G. A., Dinur T., Osiecki K. M., Kruse J. R., Legler G., Gatt S. Gaucher disease types 1, 2, and 3: differential mutations of the acid beta-glucosidase active site identified with conduritol B epoxide derivatives and sphingosine. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):499–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski G. A., Gatt S., Kruse J., Desnick R. J. Human lysosomal beta-glucosidase: kinetic characterization of the catalytic, aglycon, and hydrophobic binding sites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 15;231(1):144–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
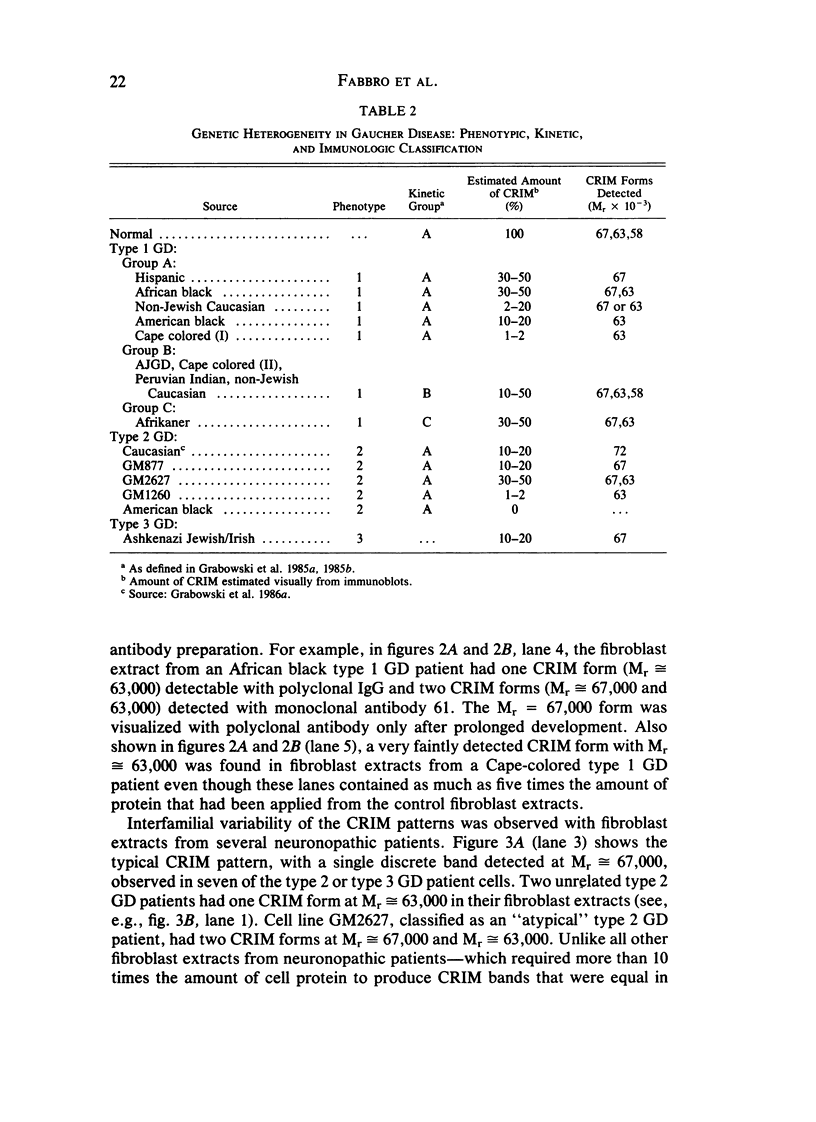
- Grabowski G. A., Goldblatt J., Dinur T., Kruse J., Svennerholm L., Gatt S., Desnick R. J. Genetic heterogeneity in Gaucher disease: physicokinetic and immunologic studies of the residual enzyme in cultured fibroblasts from non-neuronopathic and neuronopathic patients. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jul;21(3):529–549. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski G. A., Osiecki-Newman K., Dinur T., Fabbro D., Legler G., Gatt S., Desnick R. J. Human acid beta-glucosidase. Use of conduritol B epoxide derivatives to investigate the catalytically active normal and Gaucher disease enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8263–8269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson P., Goldblatt J., Beighton P. Non-neuropathic Gaucher disease presenting in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Sep;54(9):707–709. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.9.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALONEY A. F., CUMINGS J. N. A case of juvenile Gaucher's disease with intraneuronal lipid storage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Aug;23:207–213. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDOFF A. S., BAYRD E. D. Gaucher's disease in 29 cases: hematologic complications and effect of splenectomy. Ann Intern Med. 1954 Mar;40(3):481–492. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-40-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osiecki-Newman K. M., Fabbro D., Dinur T., Boas S., Gatt S., Legler G., Desnick R. J., Grabowski G. A. Human acid beta-glucosidase: affinity purification of the normal placental and Gaucher disease splenic enzymes on N-alkyl-deoxynojirimycin-sepharose. Enzyme. 1986;35(3):147–153. doi: 10.1159/000469336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin J. L., Brunning R. D. Pathology of the Gaucher cell. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;95:151–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Neumeyer B., Svennerholm L., Groth C. G., Brady R. O. Immunological and catalytic quantitation of splenic glucocerebrosidase from the three clinical forms of Gaucher disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;35(4):621–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirruccello S., Barranger J. A., Barton N. W., Brady R. O., Ginns E. I. Molecular weight characterization of beta-D-glucocerebrosidase in mononuclear white blood cells in Gaucher's disease. Biochem Med. 1984 Feb;31(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(84)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., West C., Westwood B., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of human glucocerebrosidase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7289–7293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Winfield S., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA containing the complete coding sequence for human lysosomal glucocerebrosidase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Roth S. Homozygote and heterozygote identification. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;95:551–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]