Abstract
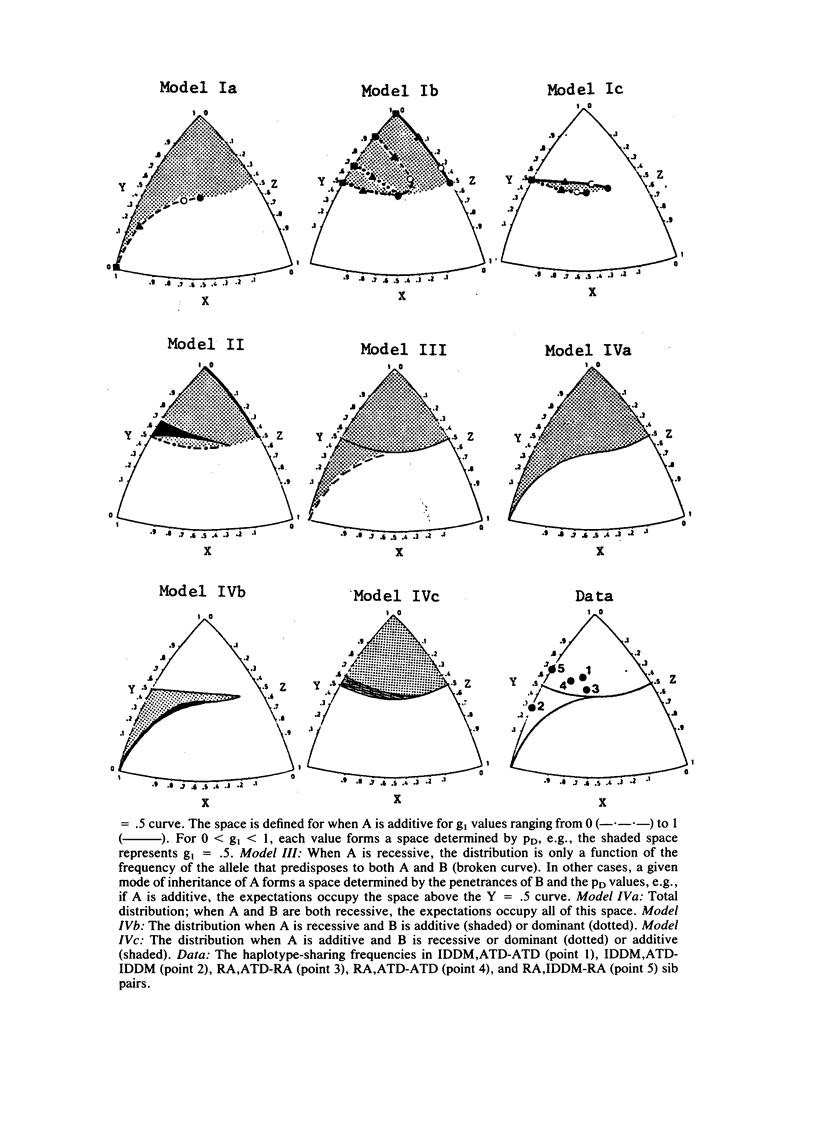
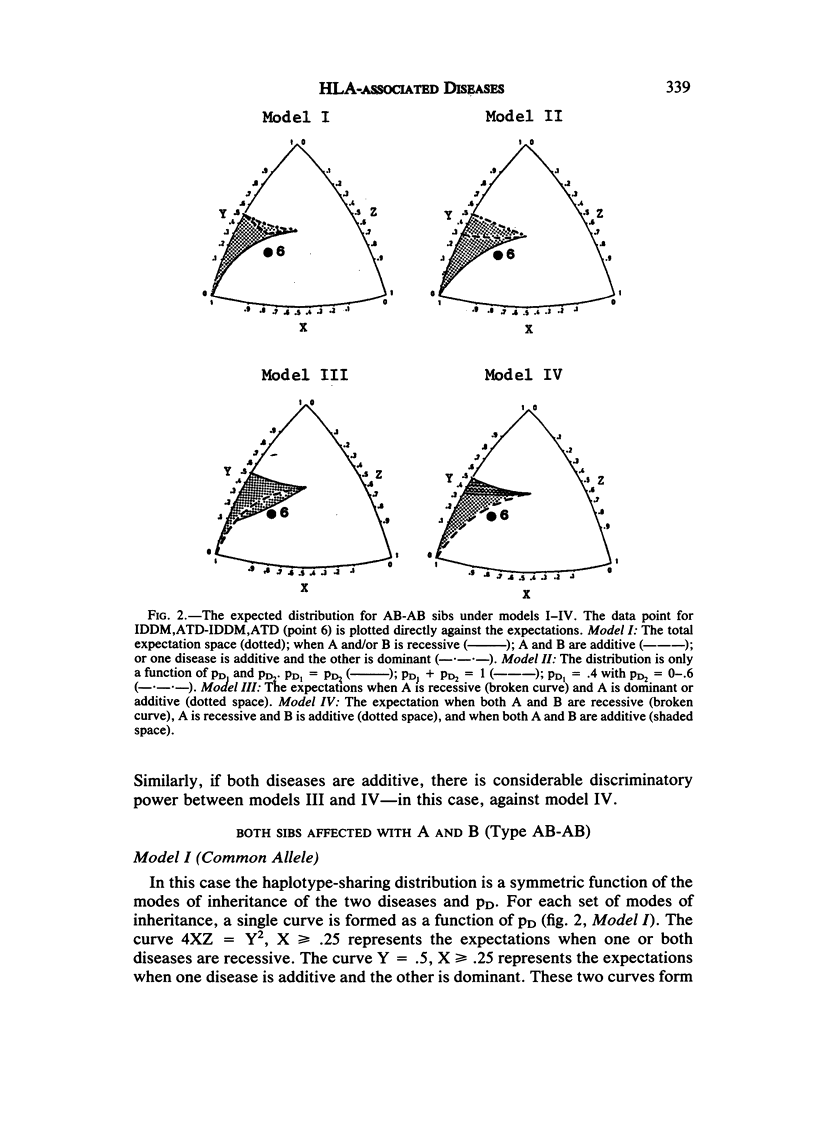
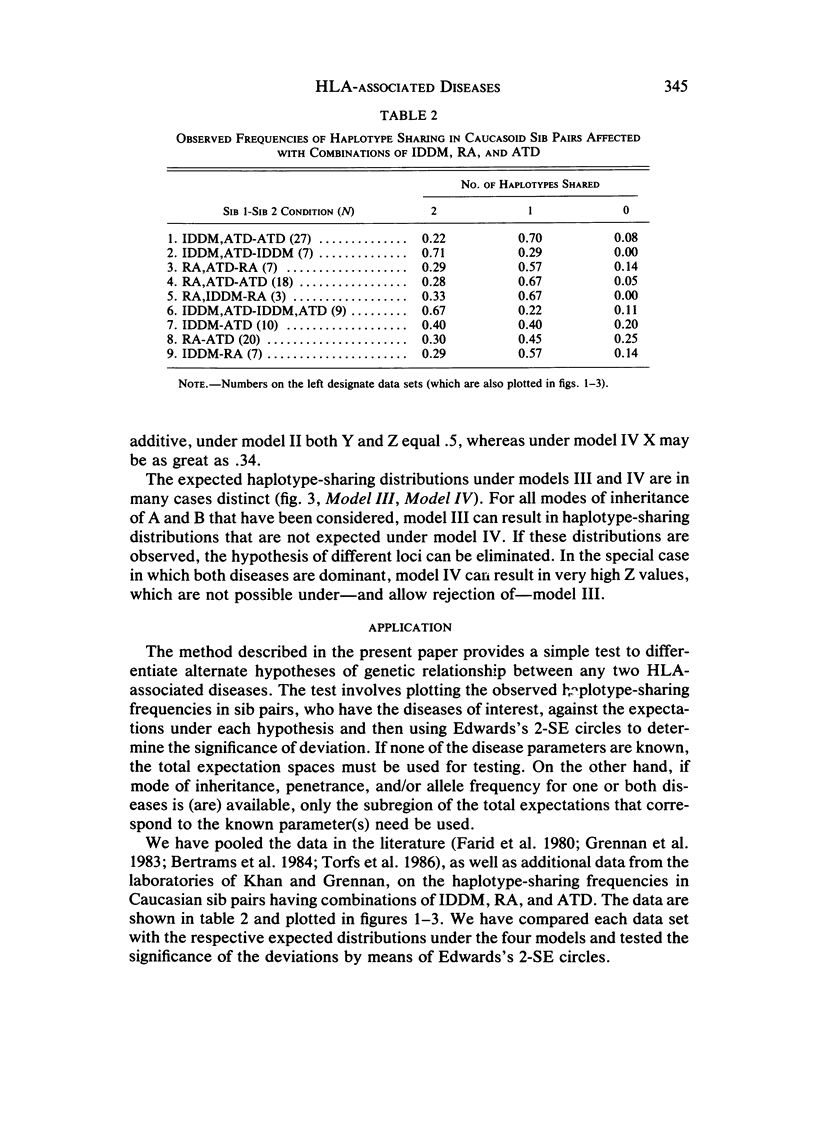
We have developed a method to study the genetic relationship between any two HLA-associated diseases. We have considered the following hypotheses: (1) both diseases are caused by a common allele; (2) different alleles at the same locus predispose to the two diseases; (3) one disease is predisposed by two alleles, one of which can also lead to the second disease; and (4) different HLA-linked loci are involved in the etiology of each disease. For each hypothesis, we have derived the expected HLA haplotype-sharing distribution in sib pairs who are affected with two diseases. The comparison of the expectations indicate that, in many cases, the alternate hypotheses can be distinguished, if the sample size is appropriately large. The knowledge of the mode of inheritance of each disease is not usually necessary; however, it can greatly increase the power of the test. Analyses of data on pairwise combinations of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), autoimmune thyroid disease (ATD), and insulin-dependent (type I) diabetes mellitus (IDDM) suggest that (a) IDDM is predisposed by two HLA-linked alleles, one of which also predisposes to ATD, (b) one of the IDDM alleles also confers susceptibility to RA, and (c) although the HLA-linked susceptibilities to RA and ATD appear to be primarily due to distinct alleles, the ATD allele may also have a minor role in predisposition to RA.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewerton D. A. Inherited susceptibility to rheumatic disease. J R Soc Med. 1978 May;71(5):331–338. doi: 10.1177/014107687807100505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. W. Distances between populations on the basis of gene frequencies. Biometrics. 1971 Dec;27(4):873–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Moens H., Larsen B., Payne R., Saltman K., Fifield F., Ingram D. W. HLA haplotypes in familial Graves' disease. Tissue Antigens. 1980 May;15(5):492–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Dyer P. A., Clague R., Dodds W., Smeaton I., Harris R. Family studies in RA - the importance of HLA-DR4 and of genes for autoimmune thyroid disease. J Rheumatol. 1983 Aug;10(4):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Sanders P. A., Dyer P. A., Harris R. HLA haplotype sharing by siblings with rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Feb;45(2):126–129. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Thomson G., Payami H. The affected sib method. II. The intermediate model. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;47(Pt 3):225–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Thomson G., Khan M. A., Grennan D. M., Sanders P., Dyer P., Dostal C. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Feb;27(2):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb01499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Thomson G., Motro U., Louis E. J., Hudes E. The affected sib method. IV. Sib trios. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Oct;49(Pt 4):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait B. D., Boyle A., Solty S., Cunningham T., Mandel T., Martin F. I., Doran T. DR4 related antisera pattern differences in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1984 Oct;24(4):228–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1984.tb02131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfs C. P., King M. C., Huey B., Malmgren J., Grumet F. C. Genetic interrelationship between insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, the autoimmune thyroid diseases, and rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):170–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


