Abstract
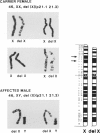
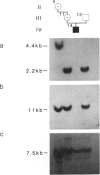
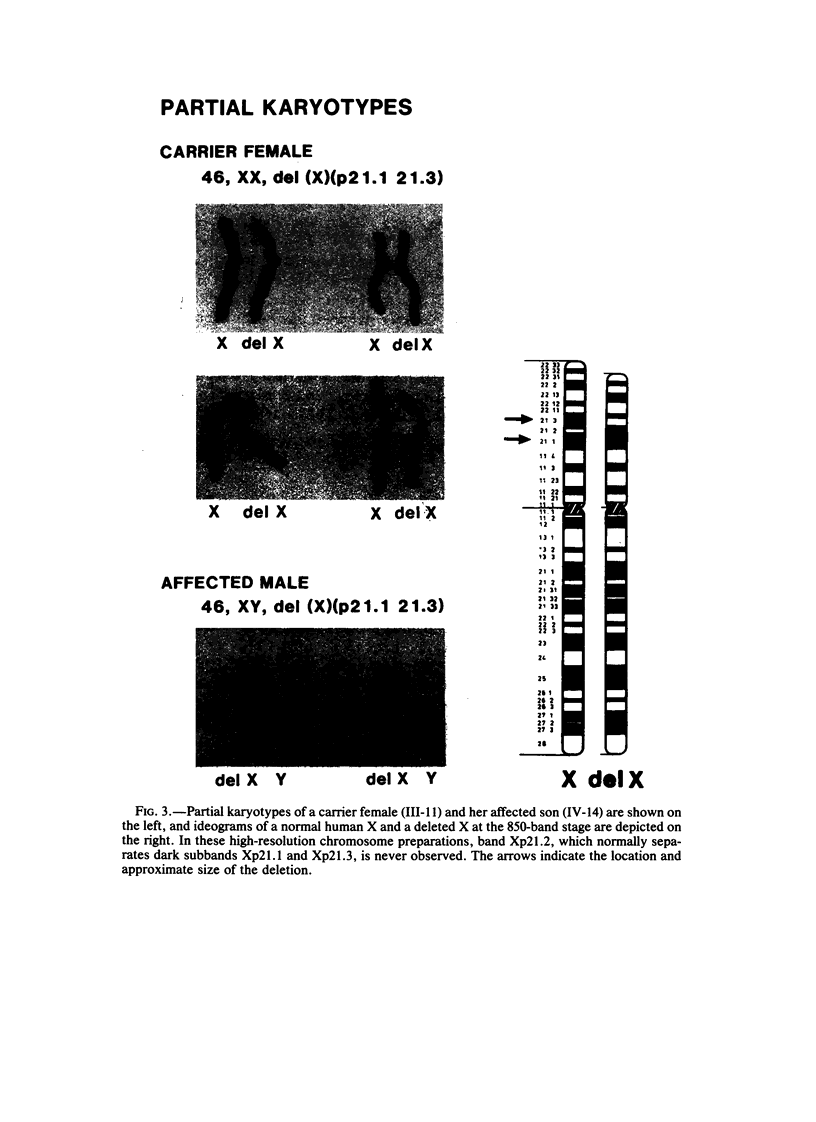
We have performed Southern blot analysis on a large, four-generation kindred with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Probes 754 (DXS 84), pERT87-1, pERT87-8, pERT87-15 (DXS164), and pXJ-1.1 did not hybridize to digested genomic DNA of affected males. Obligate-carrier mothers and unaffected brothers showed signals of a single X-chromosome copy intensity, and suspected noncarrier sisters demonstrated either a single band of two-copy intensity or informative polymorphisms. Uniform hybridization was seen with probes C7 (DXS28) and D2 (DXS43), which map distal to the DMD locus, and with OTC, which maps proximally. This deletion was present in six affected individuals and has been transmitted through 3 generations to date. On high-resolution chromosome analysis, a deletion within band Xp21 was consistently observed in one affected male studied and in one of the two X chromosomes in obligate carriers. This large molecular and cytogenetically visible deletion in affected DMD individuals without glycerol kinase deficiency, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa (RP), or ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency is a very rare finding and should prove useful in specifically cloning additional probes within and flanking the DMD locus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorkins H., Junien C., Mandel J. L., Wrogemann K., Moison J. P., Martinez M., Old J. M., Bundey S., Schwartz M., Carpenter N. Segregation analysis of a marker localised Xp21.2-Xp21.3 in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):103–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00283362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V. X;autosome translocations in females with Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):291–292. doi: 10.1038/322291b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunger D. B., Davies K. E., Pembrey M., Lake B., Pearson P., Williams D., Whitfield A., Dillon M. J. Deletion on the X chromosome detected by direct DNA analysis in one of two unrelated boys with glycerol kinase deficiency, adrenal hypoplasia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1986 Mar 15;1(8481):585–587. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Ochs H. D., de Martinville B., Giacalone J., Lindgren V., Distèche C., Pagon R. A., Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa, and McLeod syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):250–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goussault Y., Turpin E., Neel D., Dreux C., Chanu B., Bakir R., Rouffy J. 'Pseudohypertriglyceridemia' caused by hyperglycerolemia due to congenital enzyme deficiency. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Aug 18;123(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Williams K. R., Kalousek F., Kraus J. P., Doolittle R. F., Konigsberg W., Rosenberg L. E. Structure and expression of a complementary DNA for the nuclear coded precursor of human mitochondrial ornithine transcarbamylase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1068–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.6372096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Hunt P. A., Mayer M., Bart R. D. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in a female with an X/autosome translocation: further evidence that the DMD locus is at Xp21. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):513–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T., Speer A., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Colletti C. A., Bertelson C., Müller U., Bresnan M. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):73–77. doi: 10.1038/322073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Eisenhard M., Latt S. A. Regional localization on the human X of DNA segments cloned from flow sorted chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1557–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Belfall B., Duff C., Logan C., Kean V., Thompson M. W., Sylvester J. E., Gorski J. L., Schmickel R. D., Worton R. G. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):672–675. doi: 10.1038/318672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell D. C., Wang H. S., Beckett J., Chan A., Holden J. J., Mulligan L. M., Phillips M. A., Simpson N. E., Wrogemann K., Hamerton J. L. Regional localization of 18 human X-linked DNA sequences. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;42(3):123–128. doi: 10.1159/000132264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hustinx T., Scheres J., Renier W., ter Haar B. Complex glycerol kinase deficiency syndrome explained as X-chromosomal deletion. Clin Genet. 1985 May;27(5):522–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. E., Cooke A., Colgan J., Boyd E., Aitken D. A., Sinclair L., Glasgow L., Stephenson J. B., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to familial Xp21 deletion detectable by DNA analysis and flow cytometry. Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;73(2):175–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00291610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., Poon R., Riddell D. C., Royle N. J., Hamerton J. L. A DNA marker for human chromosome 8 that detects alleles of differing sizes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;42(3):113–118. doi: 10.1159/000132262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]