Abstract
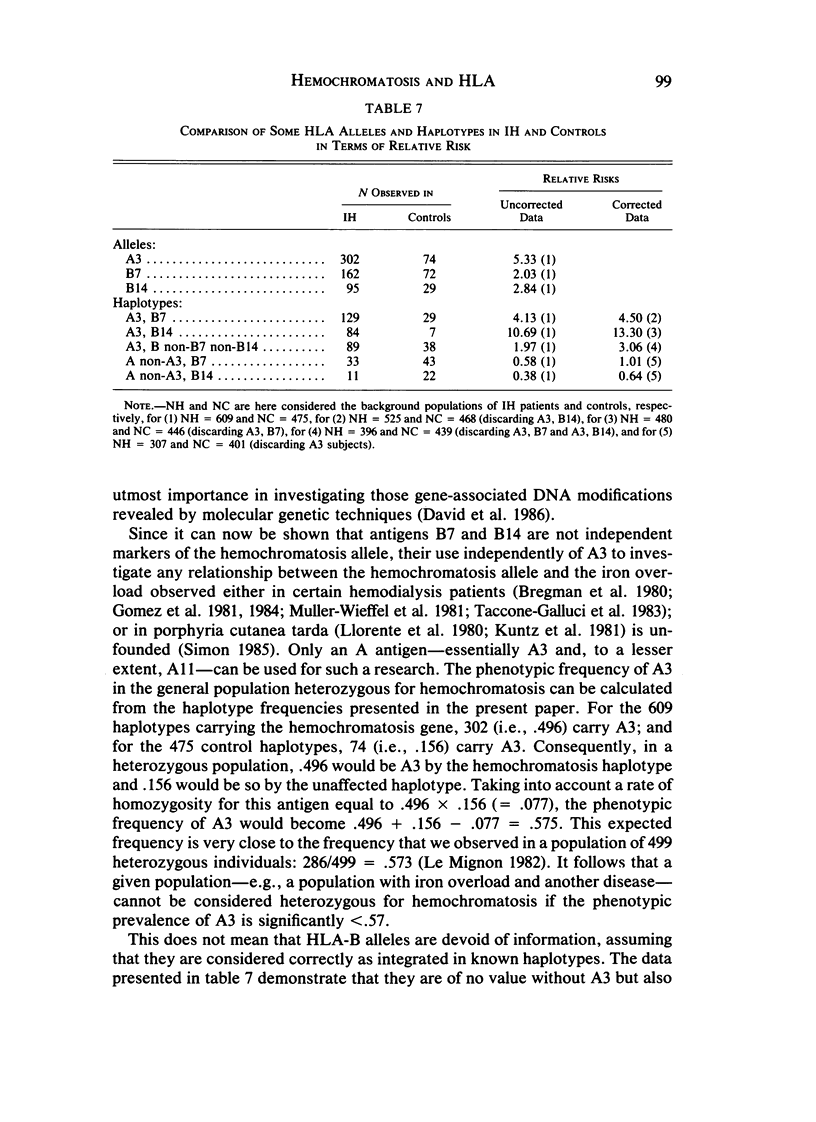
We compared 609 haplotypes carrying the idiopathic hemochromatosis allele with 475 control haplotypes. Four haplotypes were more frequent in hemochromatosis: A3, B7 (actually A3, CW., B7, Bfs, DR2); A3, B14 (actually A3, CW., B14, BfF, DRW6); A11, B35; and A11, B5. The linkage disequilibrium for A3, B7 and A3, B14 (and probably also for A11, B5) was undeniably stronger in hemochromatosis than in controls. Two haplotypes--A3, B12 and A3, B15--were more frequent in hemochromatosis, without linkage disequilibrium. Four haplotypes in linkage disequilibrium in hemochromatosis--i.e., A2, B12; A1, B8; A9, B7; and A29, B12--were also found to have the same frequency and strength of linkage in controls. The dual observation (1) that haplotypes carrying A3 without either B7 or B14 were highly significantly more frequent in hemochromatosis than in controls and (2) that haplotypes carrying B7 or B14 but not A3 had the same frequency in hemochromatosis and controls led to the formal conclusion that only A3 is an independent marker for the hemochromatosis allele, B7 and B14 being involved only owing to the haplotypic mode of marking; the hemochromatosis allele can thus be mapped closer to locus A than to locus B. Our findings fit well with the hypothesis that the hemochromatosis mutation was a rare if not unique event that produced an ancestral HLA marking that was subsequently modified by recombinations and geographical scattering due to migrations.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford A., Eddleston A. L., Kennedy L. A., Batchelor J. R., Williams R. Histocompatibility antigens as markers of abnormal iron metabolism in patients with idiopathic haemochromatosis and their relatives. Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):327–329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman H., Gelfand M. C., Winchester J. F., Manz H. J., Knepshield J. H., Schreiner G. E. iron-overload-associated myopathy in patients on maintenance haemodialysis: a histocompatibility-linked disorder. Lancet. 1980 Oct 25;2(8200):882–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M., Annoni G., Donato M. F., Fargion S., Tiribelli C., Dioguardi N. Serum marker of type III procollagen in patients with idiopathic hemochromatosis and its relationship to hepatic fibrosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4):499–502. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadone M. M., Kushner J. P., Edwards C. Q., Bishop D. T., Skolnick M. H. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Analysis of laboratory expression of the disease by genotype in 18 pedigrees. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Aug;78(2):196–207. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J., Legrand L., Lepage V., Contu L., Marcelli-Barge A., Wildloecher I., Benajam A., Meo T., Degos L. A haplotype study of HLA complex with special reference to the HLA-DR series and to Bf. C2 and glyoxalase I polymorphisms. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Oct;12(4):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David V., Paul P., Simon M., Le Gall J. Y., Fauchet R., Gicquel I., Dugast I., Le Mignon L., Yaouanq J., Cohen D. DNA polymorphism related to the idiopathic hemochromatosis gene: evidence in a recombinant family. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):113–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00282073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Miguel E., Benito S., Gijon J., Vesga J. C. Idiopathic hemochromatosis and HLA antigens. J Rheumatol. 1985 Jun;12(3):634–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. J., Bashir H. V., Trejaut J., Bassett M. L., Halliday J. W., Powell L. W. Idiopathic haemochromatosis in the Australian population: HLA linkage and recessivity. Hum Immunol. 1981 May;2(3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrszka H., Eberhardt G., Eckert G. HLA-phenotype and hemochromatosis in Germany. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):555–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. Q., Dadone M. M., Skolnick M. H., Kushner J. P. Hereditary haemochromatosis. Clin Haematol. 1982 Jun;11(2):411–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. Q., Skolnick M. H., Kushner J. P. Hereditary hemochromatosis: contributions of genetic analyses. Prog Hematol. 1981;12:43–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez E., Ortega F., Morales J. M., Gago E., Comas A., Alvarez J. Serum ferritin and HLA antigens in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Lancet. 1981 Apr 11;1(8224):836–837. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92708-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez E., Ortega F., Peces R., Gago E., Marín R., Alvarez Grande J. Serum ferritin in haemodialysis patients: role of blood transfusions and 'haemochromatosis alleles' HLA A3, B7 and B14. Nephron. 1984;36(2):106–110. doi: 10.1159/000183127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke J., Ungar W. HLA-antigens in idiopathic haemochromatosis (i.h.). preliminary report. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1978;154(1):41–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravitz K., Skolnick M., Cannings C., Carmelli D., Baty B., Amos B., Johnson A., Mendell N., Edwards C., Cartwright G. Genetic linkage between hereditary hemochromatosis and HLA. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;31(5):601–619. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz B. M., Goerz G., Soneborg H. H., Lissner R. HLA-types in porphyria cutanea tarda. Lancet. 1981 Jan 17;1(8212):155–155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90739-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnl P., Kaltwasser J. P., Seidl S. HLA antigens in patients with idiopathic hemochromatosis (IH). Tissue Antigens. 1978 Nov;12(5):398–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Le Mignon L., Simon M., Fauchet R., Bourel M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E. Genetic analysis of idiopathic hemochromatosis using both qualitative (disease status) and quantitative (serum iron) information. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):700–718. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laukens P., Versieck J., De Potter E., Barbier F. Association of HLA antigens with idopathic hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1351–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Mignon L., Simon M., Fauchet R., Edan G., Le Reun M., Brissot P., Genetet B., Bourel M. An HLA-All association with the hemochromatosis allele? Clin Genet. 1983 Sep;24(3):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeSage G. D., Baldus W. P., Fairbanks V. F., Baggenstoss A. H., McCall J. T., Moore S. B., Taswell H. F., Gordon H. Hemochromatosis: genetic or alcohol-induced? Gastroenterology. 1983 Jun;84(6):1471–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M., Hors J., Saleun J. P., Saddi R., Passa P., Lafaurie S., Feingold N., Dausset J. Idiopathic hemochromatosis: linkage with HLA. Tissue Antigens. 1978 May;11(5):471–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorente L., Enríquez de Salamanca R., Campillo F., Peña M. L. HLA and porphyria cutanea tarda. Arch Dermatol Res. 1980;269(2):209–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00406542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D., Fitzgerald G. A., O'Connell L. G., Waters J. M., Watt D. W., Stevens F. M., McCarthy C. F., Drury M. I. Histocompatibility antigens and haemochromatosis in Ireland. Ir J Med Sci. 1979 May-Jun;148(5-6):168–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Doppert B. A. Rapid detection of glyoxalase I (GLO) on cellulose acetate gel and the distribution of GLO variants in a Dutch population. Hum Genet. 1976 Sep 10;34(1):53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00284434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman N., Graudal N., Nielsen L. S., Sørensen S. A. HLA determinants in idiopathic haemochromatosis. Dan Med Bull. 1985 Oct;32(5):262–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Wiefel D. E., Lenhard V., Schärer K. Body iron stores in children with chronic renal failure in relation to HLA phenotypes. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc. 1981;18:524–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno A., Fargion S., Panaiotopoulos N., Del Ninno E., Taddei M. T., Fiorelli G. Idiopathic haemochromatosis and HLA antigens in Italy: is A3 Bw35 HLA haplotype a marker for idiopathic haemochromatosis gene in north east regions? J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;39(2):125–128. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter B., Säfwenberg J., Olsson K. S. HLA as a marker of the hemochromatosis gene in Sweden. Hum Genet. 1984;68(1):62–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00293874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saddi R., Muller J. Y., Pouliquen A., Kaplan C., Sylvestre R. HLA-A3, B7 linkage disequilibrium in hemochromatotic patients with or without insulin dependent diabetes. Tissue Antigens. 1981 May;17(5):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattenkirchner M., Fischbacher L., Giebner-Fischbacher U., Albert E. D. Arthropathie bei der idiopathischen Hämochromatose. Klin Wochenschr. 1983 Dec 1;61(23):1199–1207. doi: 10.1007/BF01537431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewan W. G., Mouat S. A., Allan T. M. Letter: HLA antigens in haemochromatosis. Br Med J. 1976 Jan 31;1(6004):281–282. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6004.281-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Alexandre J. L., Fauchet R., Genetet B., Bourel M. The genetics of hemochromatosis. Prog Med Genet. 1980;4:135–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Bourel M., Fauchet R., Genetet B. Association of HLA-A3 and HLA-B14 antigens with idiopathic haemochromatosis. Gut. 1976 May;17(5):332–334. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.5.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Bourel M., Genetet B., Fauchet R. Idiopathic hemochromatosis. Demonstration of recessive transmission and early detection by family HLA typing. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 10;297(19):1017–1021. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711102971901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Pawlotsky Y., Bourel M., Fauchet R., Genetet B. Hémochromatose idiopathique Maladie associée à l'antigène tissulaire HL-A 3. Nouv Presse Med. 1975 May 10;4(19):1432–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. Secondary iron overload and the haemochromatosis allele. Br J Haematol. 1985 May;60(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. M., Watt D. W., Stevens F. M., McCarthy C. F. Letter: HLA antigens in haemochromatosis. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 29;4(5995):520–520. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5995.520-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


