Abstract
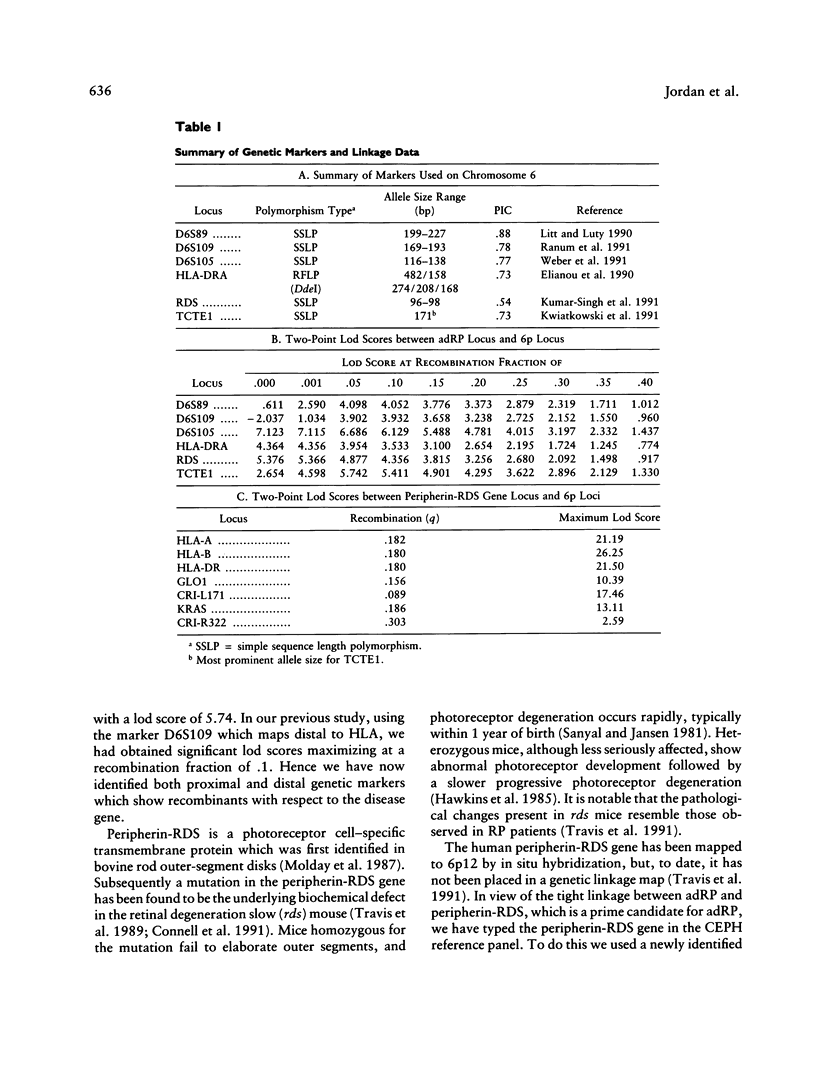
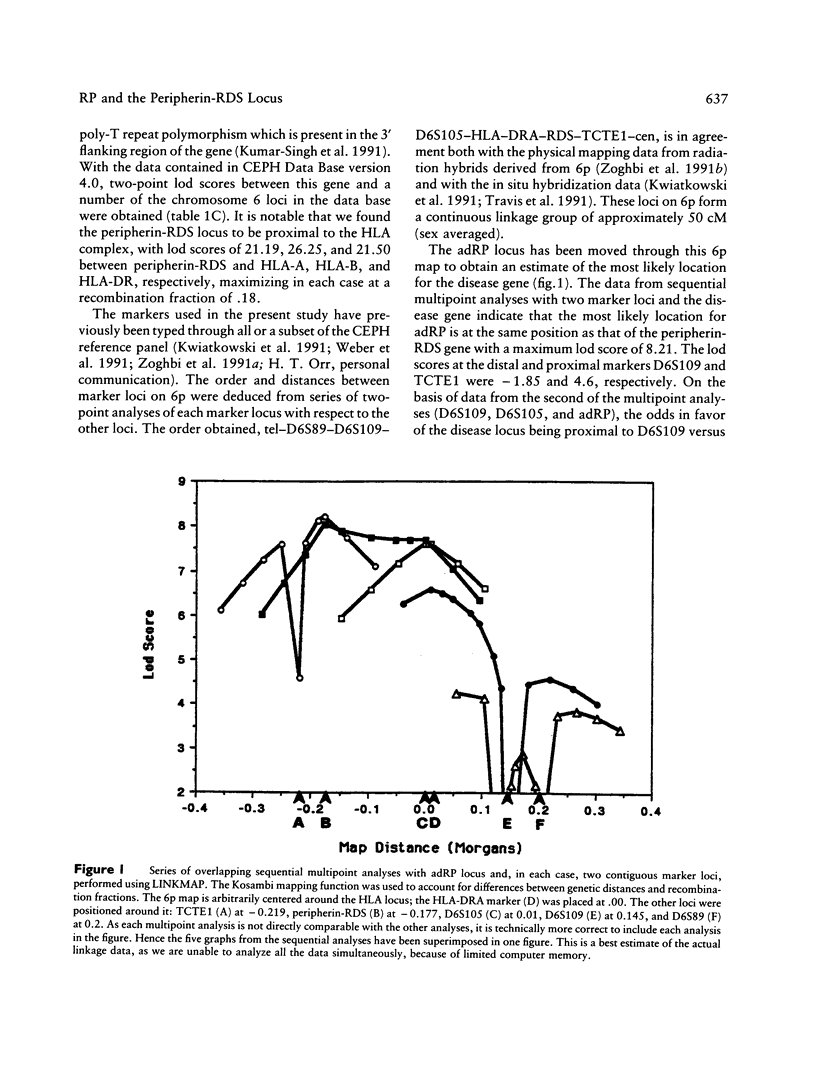
We recently reported the localization of a gene for late-onset autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP; RP6), on the short arm of chromosome 6, by linkage analysis in a large family of Irish origin. It is notable that the gene encoding peripherin-RDS, a photoreceptor-specific protein, recently has been physically mapped on 6p. In our own analysis, an intrageneic marker derived from this gene cosegregated with the adRP disease locus with zero recombination (lod score 5.46 at q = .00). Using the CEPH reference panel, we now report the mapping of the peripherin-RDS gene relative to other 6p markers in the CEPH data base. Incorporation of these data into a multipoint analysis produced a lod score for adRP of 8.21, maximizing at the peripherin-RDS locus. This study provides strong evidence suggesting a role for peripherin-RDS in the etiology of one form of adRP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attwood J., Bryant S. A computer program to make linkage analysis with LIPED and LINKAGE easier to perform and less prone to input errors. Ann Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;52(Pt 3):259–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1988.tb01103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton S. H., Heckenlively J. R., Cottingham A. W., Friedman J., Sadler L. A., Wagner M., Friedman L. H., Daiger S. P. Linkage mapping of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (RP1) to the pericentric region of human chromosome 8. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):857–869. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Crews S. J. A study of retinitis pigmentosa in the City of Birmingham. I Prevalence. J Med Genet. 1984 Dec;21(6):417–420. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.6.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunker C. H., Berson E. L., Bromley W. C., Hayes R. P., Roderick T. H. Prevalence of retinitis pigmentosa in Maine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Mar;97(3):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(84)90636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell G., Bascom R., Molday L., Reid D., McInnes R. R., Molday R. S. Photoreceptor peripherin is the normal product of the gene responsible for retinal degeneration in the rds mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):723–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J., Cann H., Cohen D., Lathrop M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Centre d'etude du polymorphisme humain (CEPH): collaborative genetic mapping of the human genome. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):575–577. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90491-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Olsson J. E., Reichel E., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. Mutations within the rhodopsin gene in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 8;323(19):1302–1307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011083231903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Reichel E., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Yandell D. W., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):364–366. doi: 10.1038/343364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliaou J. F., Pinet V., Clot J. DdeI polymorphism in the HLA-DRA regulatory region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7195–7195. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., Jordan S. A., Kenna P., Humphries M. M., Kumar-Singh R., McWilliam P., Allamand V., Sharp E., Humphries P. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: localization of a disease gene (RP6) to the short arm of chromosome 6. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):870–874. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., Kenna P., Jordan S. A., Kumar-Singh R., Humphries M. M., Sharp E. M., Sheils D. M., Humphries P. A three-base-pair deletion in the peripherin-RDS gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):478–480. doi: 10.1038/354478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., Kenna P., Redmond R., Shiels D., McWilliam P., Humphries M. M., Sharp E. M., Jordan S., Kumar-Singh R., Humphries P. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: a mutation in codon 178 of the rhodopsin gene in two families of Celtic origin. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):1170–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., McWilliam P., Bradley D. G., Kenna P., Lawler M., Sharp E. M., Humphries M. M., Eiberg H., Conneally P. M., Trofatter J. A. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: linkage to rhodopsin and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90223-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery J. G., Farber D. B., Bird A. C., Bok D. Degenerative changes in a retina affected with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Feb;30(2):191–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. K., Jansen H. G., Sanyal S. Development and degeneration of retina in rds mutant mice: photoreceptor abnormalities in the heterozygotes. Exp Eye Res. 1985 Dec;41(6):701–720. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(85)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglehearn C. F., Bashir R., Lester D. H., Jay M., Bird A. C., Bhattacharya S. S. A 3-bp deletion in the rhodopsin gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):26–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglehearn C. F., Jay M., Lester D. H., Bashir R., Jay B., Bird A. C., Wright A. F., Evans H. J., Papiha S. S., Bhattacharya S. S. No evidence for linkage between late onset autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and chromosome 3 locus D3S47 (C17): evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90462-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar-Singh R., Jordan S. A., Farrar G. J., Humphries P. Poly (T/A) polymorphism at the human retinal degeneration slow (RDS) locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5800–5800. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski T. J., Jr, Beaudet A. L., Trask B. J., Zoghbi H. Y. Linkage mapping and fluorescence in situ hybridization of TCTE1 on human chromosome 6p: analysis of dinucleotide polymorphisms on native gels. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):921–926. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90180-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S89 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4301–4301. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massof R. W., Finkelstein D. Two forms of autosomal dominant primary retinitis pigmentosa. Doc Ophthalmol. 1981 Nov;51(4):289–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00143336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliam P., Farrar G. J., Kenna P., Bradley D. G., Humphries M. M., Sharp E. M., McConnell D. J., Lawler M., Sheils D., Ryan C. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (ADRP): localization of an ADRP gene to the long arm of chromosome 3. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., Hicks D., Molday L. Peripherin. A rim-specific membrane protein of rod outer segment discs. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Jan;28(1):50–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranum L. P., Chung M. Y., Duvick L. A., Zoghbi H. Y., Orr H. T. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S109 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1171–1171. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1171-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S., Jansen H. G. Absence of receptor outer segments in the retina of rds mutant mice. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 1;21(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard for clinical electroretinography. International Standardization Committee. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Jun;107(6):816–819. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070010838024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Brennan M. B., Danielson P. E., Kozak C. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Identification of a photoreceptor-specific mRNA encoded by the gene responsible for retinal degeneration slow (rds). Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):70–73. doi: 10.1038/338070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Christerson L., Danielson P. E., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Hahn L. B., Dryja T. P., Sutcliffe J. G. The human retinal degeneration slow (RDS) gene: chromosome assignment and structure of the mRNA. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90457-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Zoghbi H. Y. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D6S105 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):968–968. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., Jodice C., Sandkuijl L. A., Kwiatkowski T. J., Jr, McCall A. E., Huntoon S. A., Lulli P., Spadaro M., Litt M., Cann H. M. The gene for autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA1) maps telomeric to the HLA complex and is closely linked to the D6S89 locus in three large kindreds. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., McCall A. E., LeBorgne-Demarquoy F. Sixty-five radiation hybrids for the short arm of human chromosome 6: their value as a mapping panel and as a source for rapid isolation of new probes using repeat element-mediated PCR. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):713–720. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90365-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


