Abstract
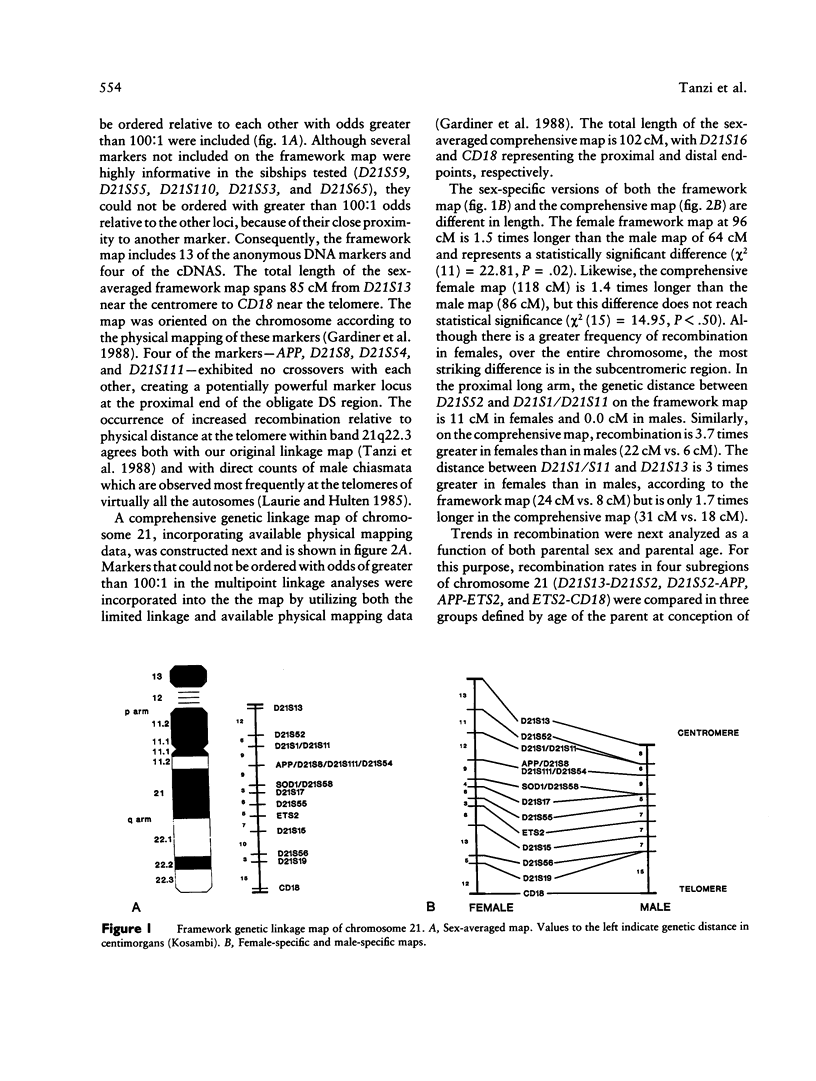
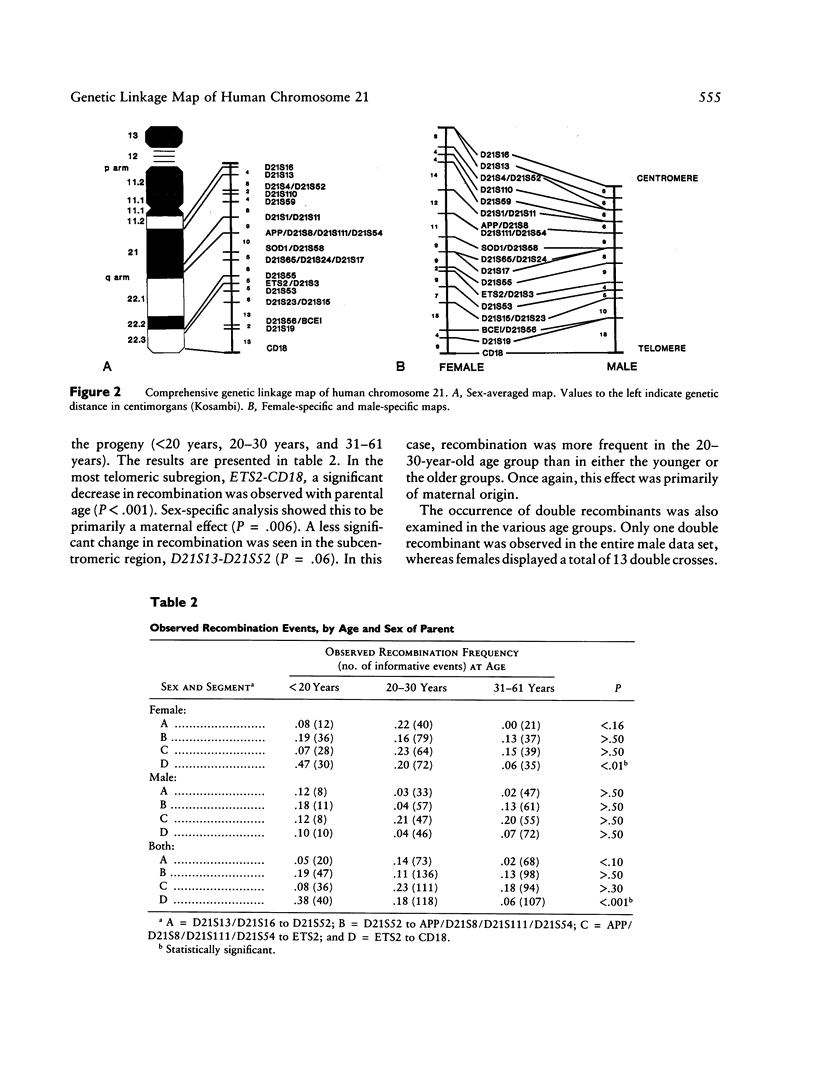
A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21 has been constructed using 22 anonymous DNA markers and five complementary DNAs (cDNAs) encoding the amyloid beta protein precursor (APP), superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), the ets-2 proto-oncogene (ETS2), the estrogen inducible breast cancer locus (BCEI), and the leukocyte antigen, CD18 (CD18). Segregation of RFLPs detected by these DNA markers was traced in the Venezuelan Reference Pedigree (VRP). A comprehensive genetic linkage map consisting of the 27 DNA markers spans 102 cM on the long arm of chromosome 21. We have confirmed our initial findings of a dramatically increased rate of recombination at the telomere in both females and males and of significantly higher recombination in females in the pericentromeric region. By comparing patterns of recombination in specific regions of chromosome 21 with regard to both parental sex and age, we have now identified a statistically significant downward trend in the frequency of crossovers in the most telomeric portion of chromosome 21 with increasing maternal age. A less significant decrease in recombination with increasing maternal age was observed in the pericentromeric region of the chromosome. These results may help in ultimately understanding the physical relationship between recombination and nondisjunction in the occurrence of trisomy 21.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. A., Gusella J. F. Use of cyclosporin A in establishing Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoblastoid cell lines. In Vitro. 1984 Nov;20(11):856–858. doi: 10.1007/BF02619631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Watkins P., Münke M., Drabkin H., Jones C., Patterson D. Partial physical map of human chromosome 21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):623–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines J. L., Ozelius L. J., McFarlane H., Menon A., Tzall S., Martiniuk F., Hirschhorn R., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of chromosome 17. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90218-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallewell R. A., Masiarz F. R., Najarian R. C., Puma J. P., Quiroga M. R., Randolph A., Sanchez-Pescador R., Scandella C. J., Smith B., Steimer K. S. Human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase cDNA: isolation of clones synthesising high levels of active or inactive enzyme from an expression library. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2017–2034. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Hultén M. A. Further studies on bivalent chiasma frequency in human males with normal karyotypes. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;49(Pt 3):189–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Sistonen P., Miao J., Hästbacka J., Norio R., de la Chapelle A. Localization of a gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy to chromosome 21q22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3696–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Morton C. C., Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. LFA-1 immunodeficiency disease. Definition of the genetic defect and chromosomal mapping of alpha and beta subunits of the lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) by complementation in hybrid cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):855–867. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Breathnach R., Bloch J., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hormone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7895–7903. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Gardiner K., Kao F. T., Tanzi R., Watkins P., Gusella J. F. Mapping of the gene encoding the beta-amyloid precursor protein and its relationship to the Down syndrome region of chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8266–8270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Watson D. K., Guerts van Kessel A. H., Hagemeijer A., Kersey J., Drabkin H. D., Patterson D., Papas T. S. Hu-ets-1 and Hu-ets-2 genes are transposed in acute leukemias with (4;11) and (8;21) translocations. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.3941901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Figlewicz D. A., Pericak-Vance M. A., Haines J. L., Rouleau G., Jeffers A. J., Sapp P., Hung W. Y., Bebout J., McKenna-Yasek D. Linkage of a gene causing familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to chromosome 21 and evidence of genetic-locus heterogeneity. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., Warren S. T. The biology of Down syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;450:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb21478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Haines J. L., Farrer L. A., Polinsky R., Van Broeckhoven C., Goate A., McLachlan D. R., Orr H., Bruni A. C., Sorbi S. Genetic linkage studies suggest that Alzheimer's disease is not a single homogeneous disorder. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):194–197. doi: 10.1038/347194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Haines J. L., Nee L., Watkins P. C., Myers R. H., Feldman R. G., Pollen D., Drachman D. The genetic defect causing familial Alzheimer's disease maps on chromosome 21. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):885–890. doi: 10.1126/science.2880399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E. Genetic linkage studies of human neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Oct;1(3):455–461. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90069-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., George-Hyslop P. S., Gusella J. F. Molecular genetics of Alzheimer disease amyloid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20579–20582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., St George-Hyslop P. H., Haines J. L., Polinsky R. J., Nee L., Foncin J. F., Neve R. L., McClatchey A. I., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. The genetic defect in familial Alzheimer's disease is not tightly linked to the amyloid beta-protein gene. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):156–157. doi: 10.1038/329156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Genthe A. M., Vandenberghe A., Horsthemke B., Backhovens H., Raeymaekers P., Van Hul W., Wehnert A., Gheuens J., Cras P. Failure of familial Alzheimer's disease to segregate with the A4-amyloid gene in several European families. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):153–155. doi: 10.1038/329153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Wong C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Halloran S. L., Watkins P. C., Metaxotou C., Antonarakis S. E. Evidence for reduced recombination on the nondisjoined chromosomes 21 in Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.2955519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 17 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


