Abstract
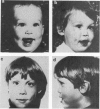
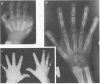
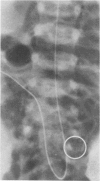
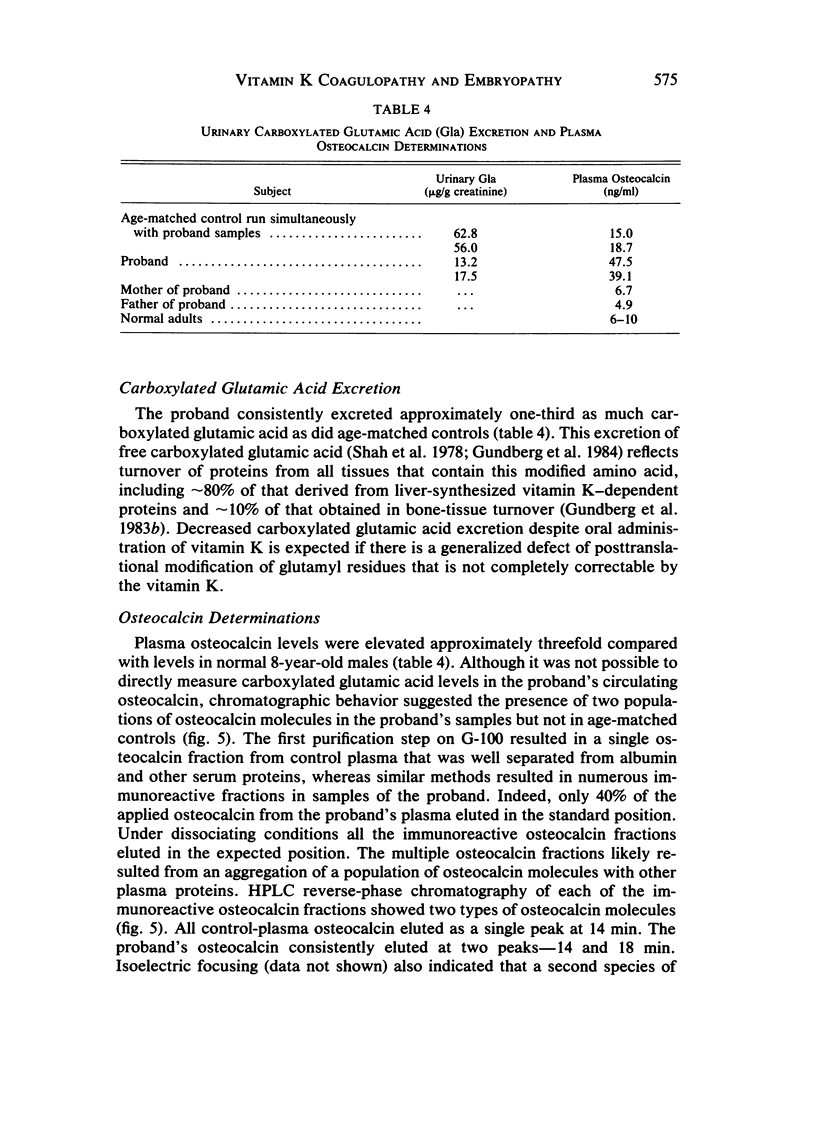
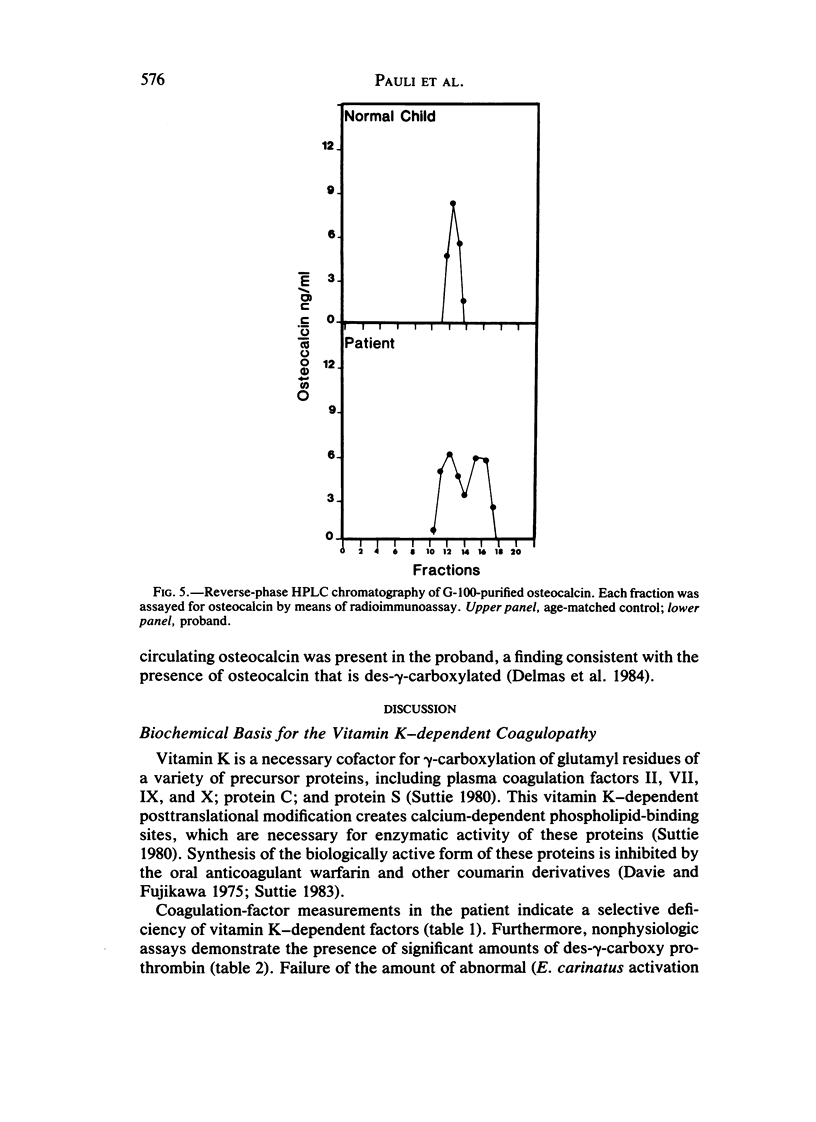
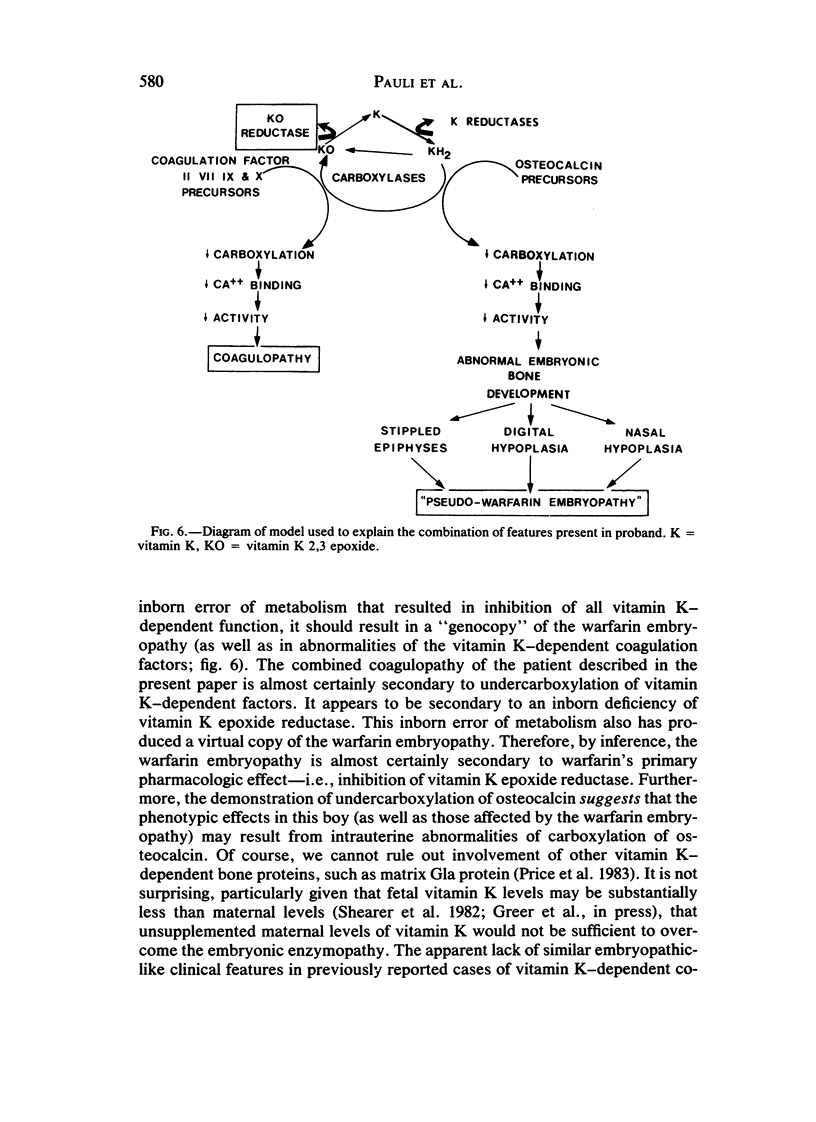
We have evaluated a boy who had excessive bleeding and bruising from birth and showed markedly prolonged prothrombin times, partially correctable by oral vitamin K administration. Additional laboratory studies demonstrated decreased activities of plasma factors II, VII, IX, and X; near normal levels of immunologically detected and calcium binding-independent prothrombin; undercarboxylation of prothrombin; excess circulating vitamin K epoxide; decreased excretion of carboxylated glutamic acid residues; and abnormal circulating osteocalcin. These results all are consistent with effects resulting from decreased posttranslational carboxylation secondary to an inborn deficiency of vitamin K epoxide reductase. This individual also had nasal hypoplasia, distal digital hypoplasia, and epiphyseal stippling on infant radiographs, all of which are virtually identical to features seen secondary to first-trimester exposure to coumarin derivatives. Therefore, by inference, the warfarin embryopathy is probably secondary to warfarin's primary pharmacologic effect (interference with vitamin K-dependent posttranslational carboxylation of glutamyl residues of various proteins) and may result from undercarboxylation of osteocalcin or other vitamin K-dependent bone proteins.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechtold H., Trenk D., Jähnchen E., Meinertz T. Plasma vitamin K1-2,3-epoxide as diagnostic aid to detect surreptitious ingestion of oral anticoagulant drug. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):596–597. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92852-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M. H., Genieser N. B., Finegold M., Miranda D., Spackman T. Chondrodysplasis punctata: is maternal warfarin therapy a factor? Am J Dis Child. 1975 Mar;129(3):356–359. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120400056013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard R. A., Furie B. C., Jorgensen M., Kruger S. F., Furie B. Acquired vitamin K-dependent carboxylation deficiency in liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 30;305(5):242–248. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107303050502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard R. A., Furie B. C., Kruger S. F., Waneck G., Jorgensen M. J., Furie B. Immunoassays of human prothrombin species which correlate with functional coagulant activities. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Feb;101(2):242–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleyer W. A., Hakami N., Shepard T. H. The development of hemostasis in the human fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1971 Nov;79(5):838–853. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong M. K., Harvey D., de Swiet M. Follow-up study of children whose mothers were treated with warfarin during pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 Nov;91(11):1070–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1984.tb15077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. S., Bezeaud A., Goldsmith J. C., McMillan C. W., Ménaché D., Roberts H. R. Congenital deficiency of blood clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):776–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K. Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:799–829. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas P. D., Tracy R. P., Riggs B. L., Mann K. G. Identification of the noncollagenous proteins of bovine bone by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984 May;36(3):308–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02405335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasco M. J., Hildebrandt E. F., Suttie J. W. Evidence that warfarin anticoagulant action involves two distinct reductase activities. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11210–11212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallop P. M., Lian J. B., Hauschka P. V. Carboxylated calcium-binding proteins and vitamin K. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 26;302(26):1460–1466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006263022608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O., Niléhn J. E. Plasma prothrombin during treatment with Dicumarol. II. Demonstration of an abnormal prothrombin fraction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;22(1):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Pence R. E., Ratnoff O. D., Adelstein D. J., Furie B. Studies on a family with combined functional deficiencies of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1253–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI110564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Hauschka P. V., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M. Osteocalcin: isolation, characterization, and detection. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:516–544. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M. Measurements of gamma-carboxyglutamate and circulating osteocalcin in normal children and adults. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Feb 28;128(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M., Steinberg J. J. Urinary gamma-carboxyglutamic acid and serum osteocalcin as bone markers: studies in osteoporosis and Paget's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1221–1225. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Pauli R. M., Wilson K. M. Maternal and fetal sequelae of anticoagulation during pregnancy. Am J Med. 1980 Jan;68(1):122–140. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M. Direct identification of the calcium-binding amino acid, gamma-carboxyglutamate, in mineralized tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3925–3929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Reid M. L. Timed appearance of a calcium-binding protein containing gamma-carboxyglutamic acid in developing chick bone. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. A., Chung K. S., McGrath K. M., Bean P. E., Roberts H. R. Characterization of a variant prothrombin in a patient congenitally deficient in factors II, VII, IX and X. Br J Haematol. 1980 Mar;44(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb05916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort H. I., Cassel G. A. An appraisal of warfarin therapy during pregnancy. S Afr Med J. 1981 Oct 10;60(15):578–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. J., Lian J. B. gamma-Carboxyglutamate excretion and warfarin therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 May;25(5 Pt 1):562–570. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979255part1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian J. B., Roufosse A. H., Reit B., Glimcher M. J. Concentrations of osteocalcin and phosphoprotein as a function of mineral content and age in cortical bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 1982;34 (Suppl 2):S82–S87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan C. W., Roberts H. R. Congenital combined deficiency of coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X. Report of a case. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 9;274(23):1313–1315. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606092742309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melick R. A., Farrugia W., Quelch K. J. Plasma osteocalcin in man. Aust N Z J Med. 1985 Aug;15(4):410–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1985.tb02761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWCOMB T., MATTER M., CONROY L., DEMARSH Q. B., FINCH C. A. Congenital hemorrhagic diathesis of the prothrombin complex. Am J Med. 1956 May;20(5):798–805. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto S. K., Price P. A. Secretion of the vitamin K-dependent protein of bone by rat osteosarcoma cells. Evidence for an intracellular precursor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6579–6583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill H., Blake S., Sugrue D., Macdonald D. Problems in the management of patients with artificial valves during pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1982 Nov;89(11):940–943. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1982.tb05062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley C. Pregnancy in patients with prosthetic heart valves. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 28;286(6379):1680–1682. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6379.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli R. M., Madden J. D., Kranzler K. J., Culpepper W., Port R. Warfarin therapy initiated during pregnancy and phenotypic chondrodysplasia punctata. J Pediatr. 1976 Mar;88(3):506–508. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettifor J. M., Benson R. Congenital malformations associated with the administration of oral anticoagulants during pregnancy. J Pediatr. 1975 Mar;86(3):459–462. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Nishimoto S. K. Radioimmunoassay for the vitamin K-dependent protein of bone and its discovery in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Otsuka A. A., Poser J. W., Kristaponis J., Raman N. Characterization of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Urist M. R., Otawara Y. Matrix Gla protein, a new gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein which is associated with the organic matrix of bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91663-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A., Williamson M. K. Effects of warfarin on bone. Studies on the vitamin K-dependent protein of rat bone. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12754–12759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs B. L., Tsai K. S., Mann K. G. Effect of acute increases in bone matrix degradation on circulating levels of bone-Gla protein. J Bone Miner Res. 1986 Dec;1(6):539–542. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650010608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. V., Swanson J. C., Suttie J. W. Abnormal prothrombin in the vitamin K-deficient rat. Thromb Res. 1984 Aug 15;35(4):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. V., Tews J. K., Harper A. E., Suttie J. W. Metabolism and transport of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 1;539(2):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul W. L., Emery H., Hall J. G. Chondrodysplasia punctata and maternal warfarin use during pregnancy. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Mar;129(3):360–362. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120400060014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer M. J., Rahim S., Barkhan P., Stimmler L. Plasma vitamin K1 in mothers and their newborn babies. Lancet. 1982 Aug 28;2(8296):460–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield L. J., Danks D. M., Mayne V., Hutchinson A. L. Chondrodysplasia punctata-23 cases of a mild and relatively common variety. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):916–923. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soff G. A., Levin J. Familial multiple coagulation factor deficiencies. I. Review of the literature: Differentiation of single hereditary disorders associated with multiple factor deficiencies from coincidental concurrence of single factor deficiency states. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1981 Fall;7(2):112–148. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno T., Suttie J. W. High-pressure liquid chromatographic-reductive electrochemical detection analysis of serum trans-phylloquinone. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):62–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]