Abstract
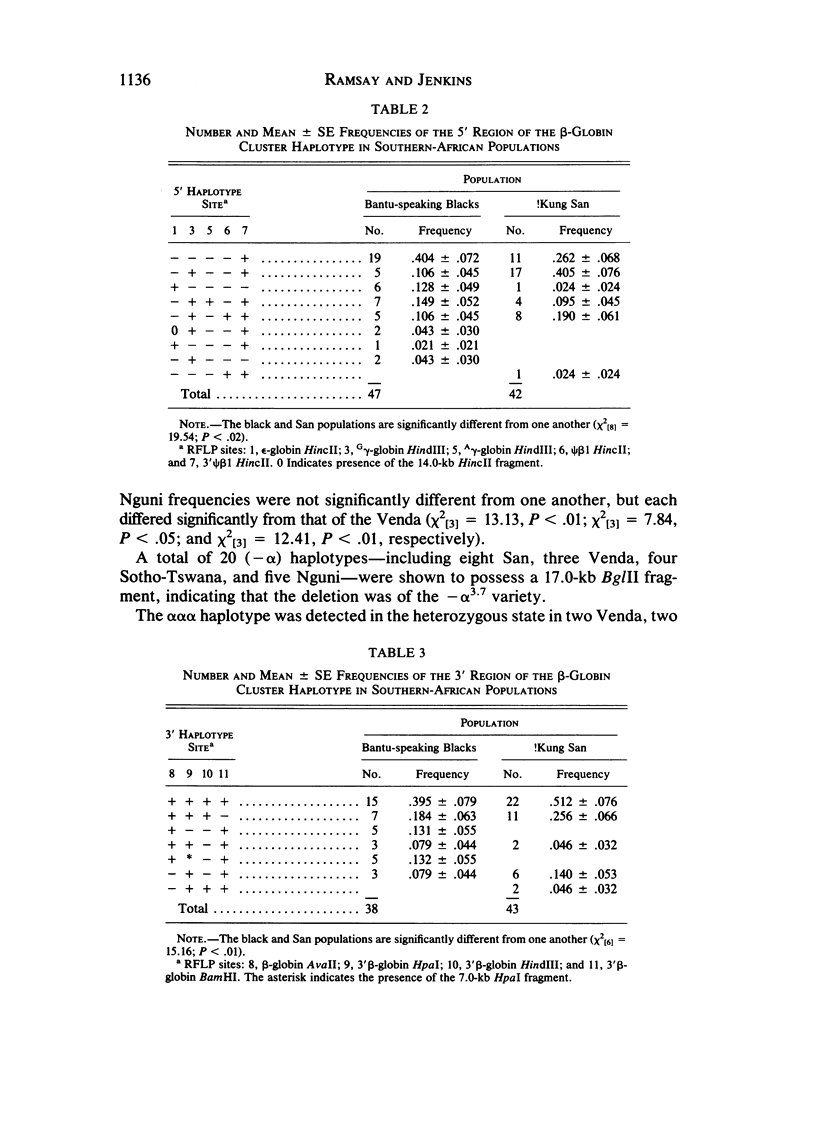
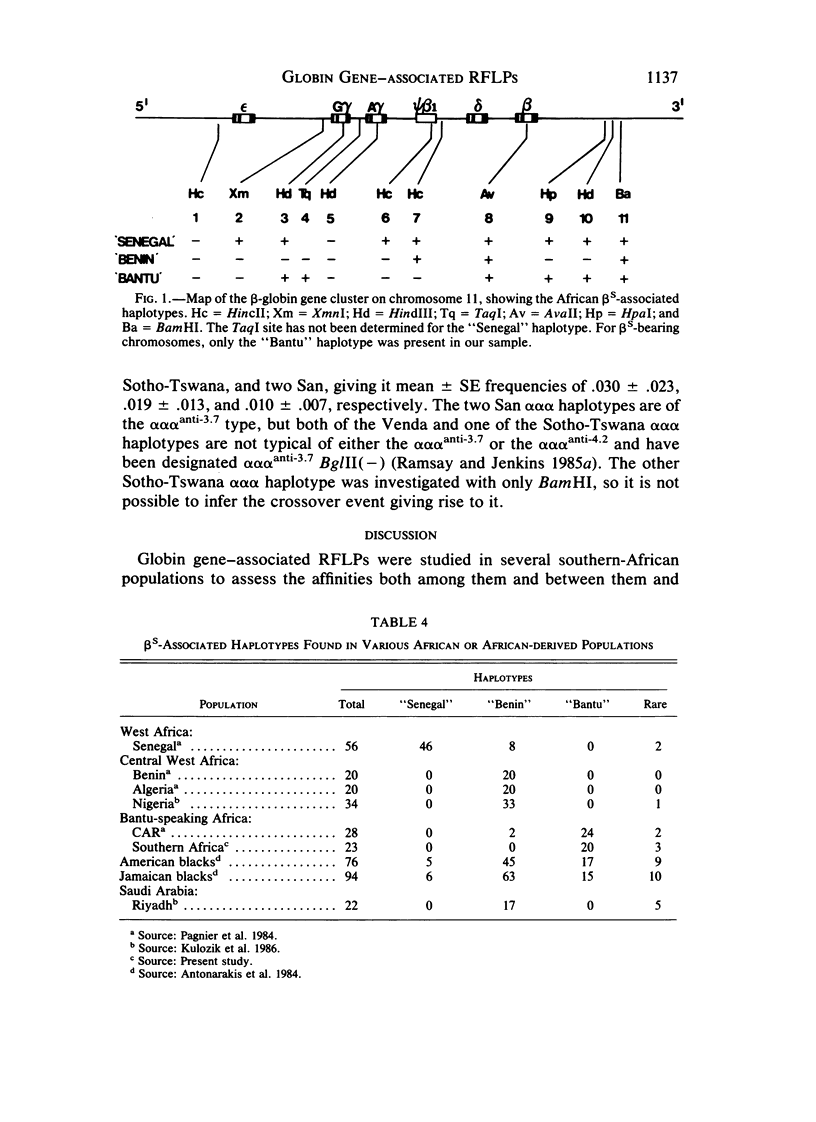
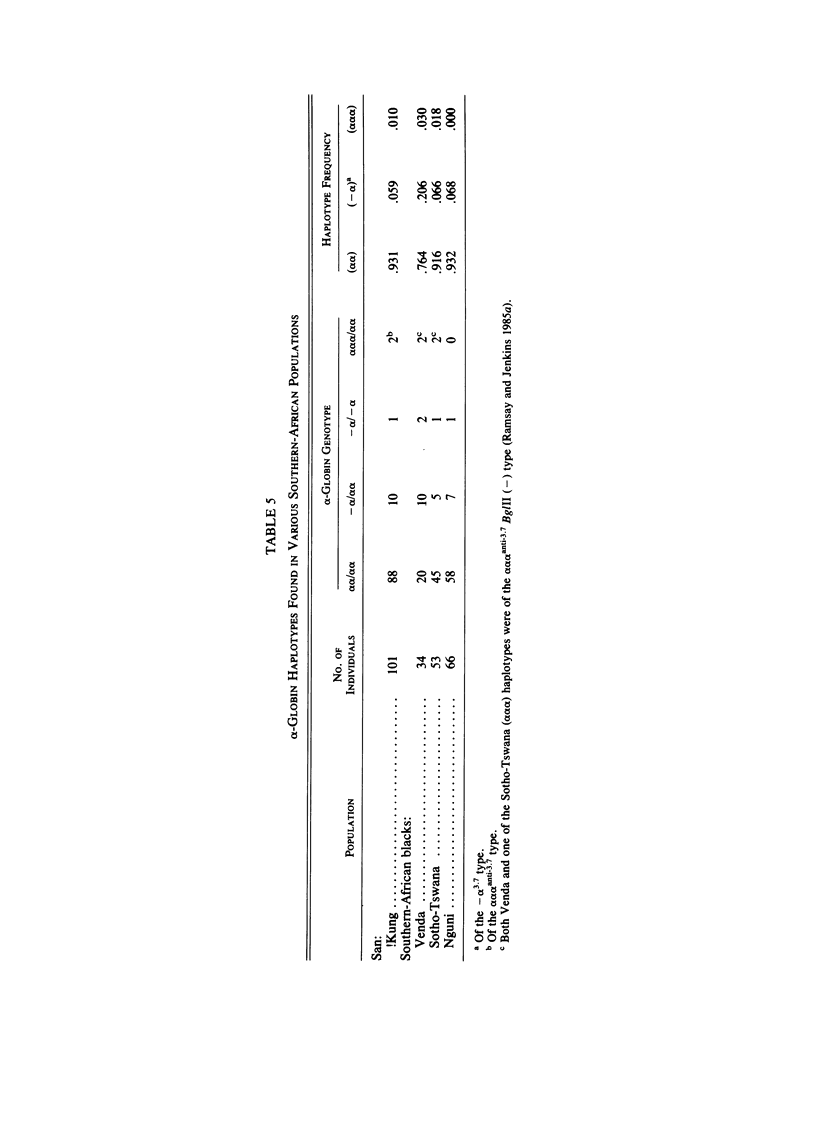
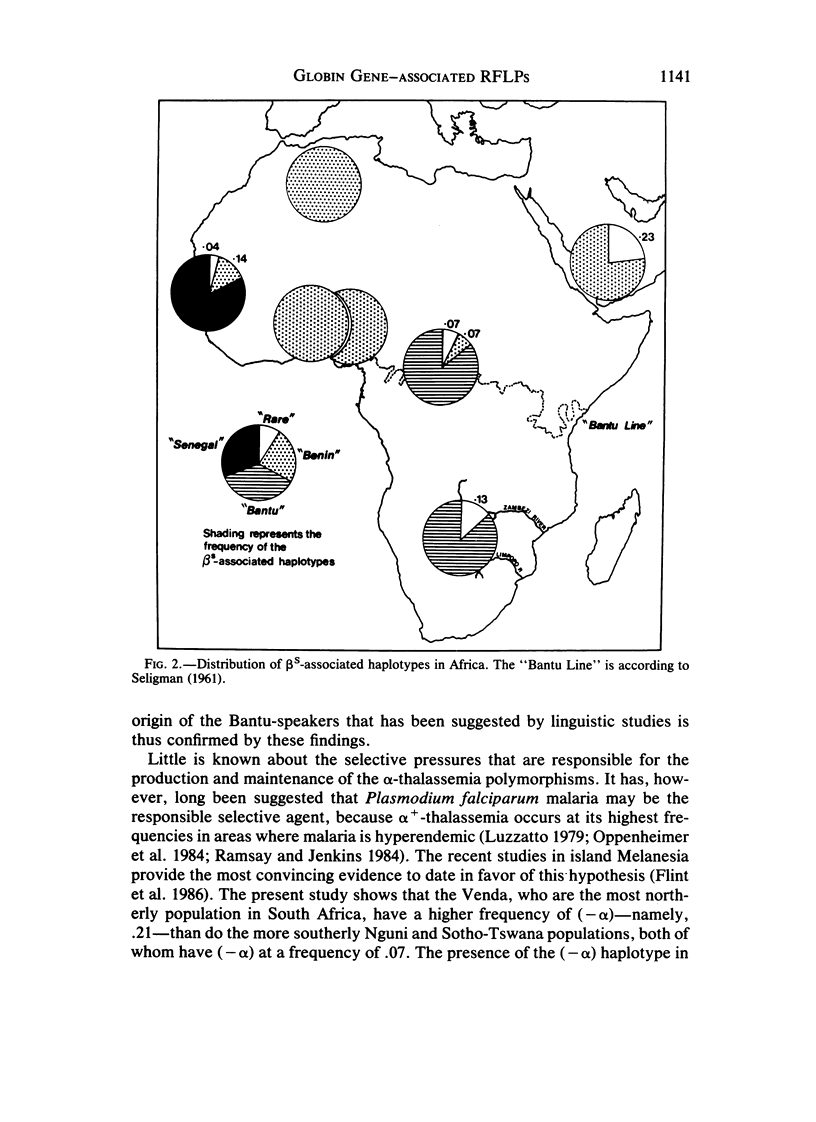
The combination of polymorphic restriction-enzyme sites in the 3' region of the beta-globin gene cluster shows very little variation in southern-African Bantu-speaking black and Kalahari !Kung San populations. The sites of the 5' region, on the other hand, show marked variation, and two common haplotypes are present--the "Negro" type (- - - - +) and the "San" type (- + - - +)--in frequencies of .404 and .106, respectively, in the Bantu-speakers and .262 and .405, respectively, in the San. Twenty of 23 beta s-associated haplotypes in southern-African Bantu-speaking black subjects were the same as that found commonly in the Central African Republic (CAR)--i.e., the "Bantu" type--a finding providing the first convincing biological evidence for the common ancestry of geographically widely separated speakers of languages belonging to the Bantu family. The (-alpha) haplotype has a frequency of .21 in the Venda, .07 in both the Sotho-Tswana and the Nguni, and .06 among the !Kung San. These data are interpreted in the light of Plasmodium falciparum malaria selection and population movements in the African subcontinent.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Boehm C. D., Giardina P. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Nonrandom association of polymorphic restriction sites in the beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Boehm C. D., Serjeant G. R., Theisen C. E., Dover G. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Origin of the beta S-globin gene in blacks: the contribution of recurrent mutation or gene conversion or both. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):853–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird M., Driscoll C., Schreiner H., Sciarratta G. V., Sansone G., Niazi G., Ramirez F., Bank A. A nucleotide change at a splice junction in the human beta-globin gene is associated with beta 0-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4218–4221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Hill A. V., Bowden D. K., Oppenheimer S. J., Sill P. R., Serjeantson S. W., Bana-Koiri J., Bhatia K., Alpers M. P., Boyce A. J. High frequencies of alpha-thalassaemia are the result of natural selection by malaria. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):744–750. doi: 10.1038/321744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human beta-like globin gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):959–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geever R. F., Wilson L. B., Nallaseth F. S., Milner P. F., Bittner M., Wilson J. T. Direct identification of sickle cell anemia by blot hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5081–5085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wainscoat J. S., Flint J., Hill A. V., Thein S. L., Nicholls R. D., Teal H., Ayyub H., Peto T. E., Falusi A. G. Analysis of the human alpha-globin gene cluster reveals a highly informative genetic locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Rouhani S. Human evolution. How small was the bottleneck? Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):449–450. doi: 10.1038/319449b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Genetics of red cells and susceptibility to malaria. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):961–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio A., Acuto S., Lo Gioco P., Di Marzo R., Giambona A., Sammarco P., Caronia F. Beta A and beta thal DNA haplotypes in Sicily. Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;72(3):229–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00291883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old J. M., Petrou M., Modell B., Weatherall D. J. Feasibility of antenatal diagnosis of beta thalassaemia by DNA polymorphisms in Asian Indian and Cypriot populations. Br J Haematol. 1984 Jun;57(2):255–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer S. J., Higgs D. R., Weatherall D. J., Barker J., Spark R. A. Alpha thalassaemia in Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 1984 Feb 25;1(8374):424–426. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnier J., Mears J. G., Dunda-Belkhodja O., Schaefer-Rego K. E., Beldjord C., Nagel R. L., Labie D. Evidence for the multicentric origin of the sickle cell hemoglobin gene in Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1771–1773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay M., Jenkins T. Alpha-thalassaemia in Africa: the oldest malaria protective trait? Lancet. 1984 Aug 18;2(8399):410–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90581-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C. DNA in heritable disease. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):787–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainscoat J. S., Hill A. V., Boyce A. L., Flint J., Hernandez M., Thein S. L., Old J. M., Lynch J. R., Falusi A. G., Weatherall D. J. Evolutionary relationships of human populations from an analysis of nuclear DNA polymorphisms. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):491–493. doi: 10.1038/319491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainscoat J. S., Kulozik A. E., Ramsay M., Falusi A. G., Weatherall D. J. A Taq 1 gamma-globin DNA polymorphism: an African-specific marker. Hum Genet. 1986 Sep;74(1):90–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00278792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson L. B., deRiel J. K., Villa-komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Insertion of synthetic copies of human globin genes into bacterial plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):563–581. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybury L. E., Shannon I. L. Is Classic Coca-Cola the real thing? Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):21–21. doi: 10.1038/322021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


