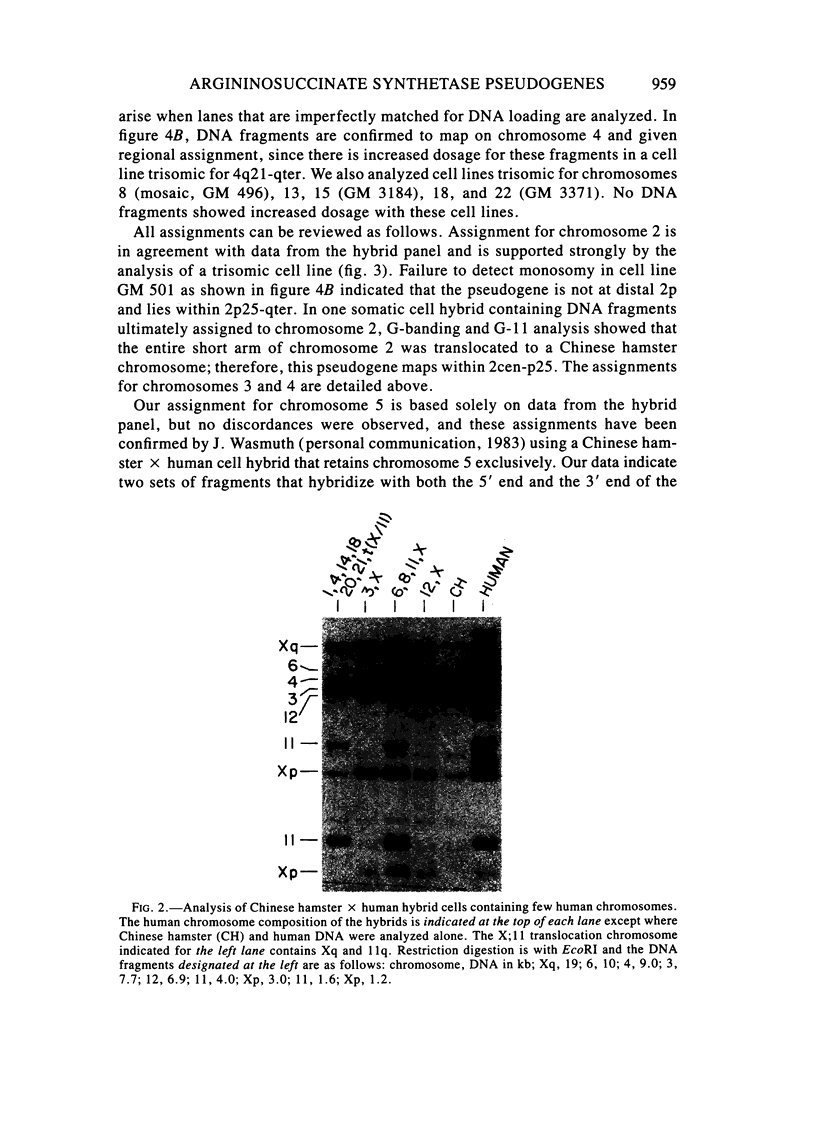
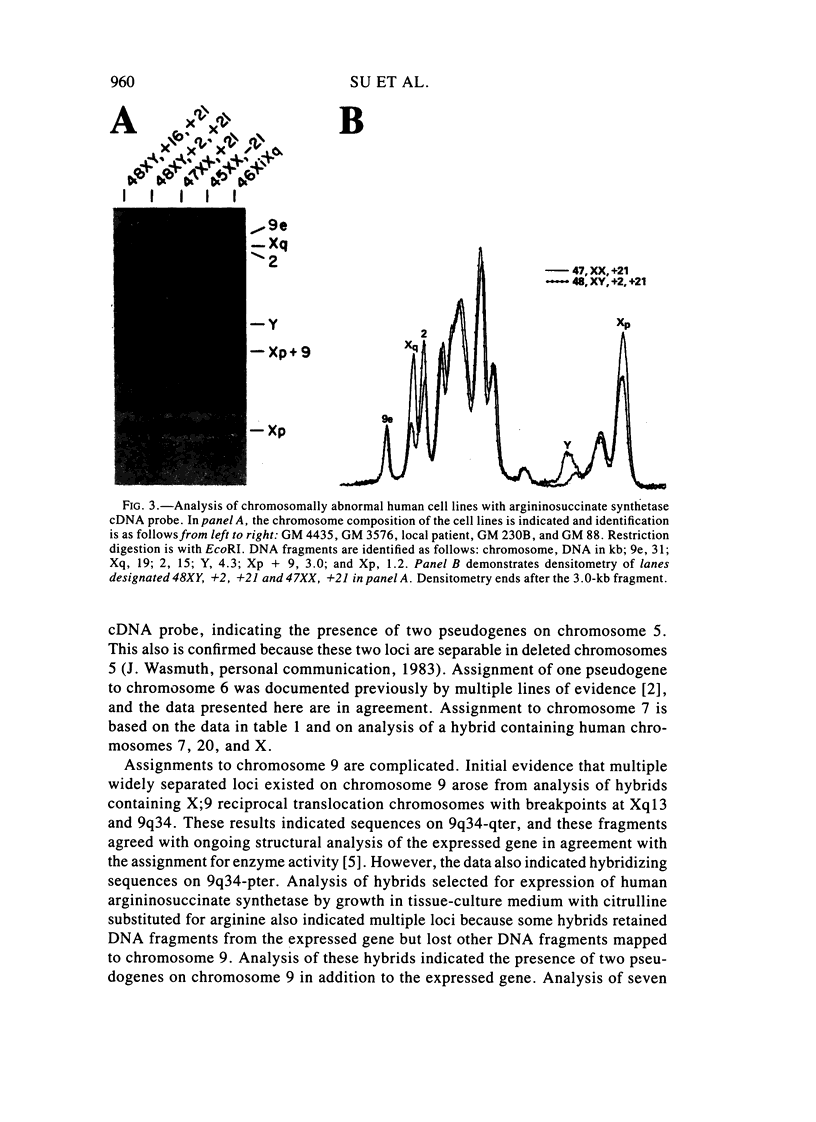
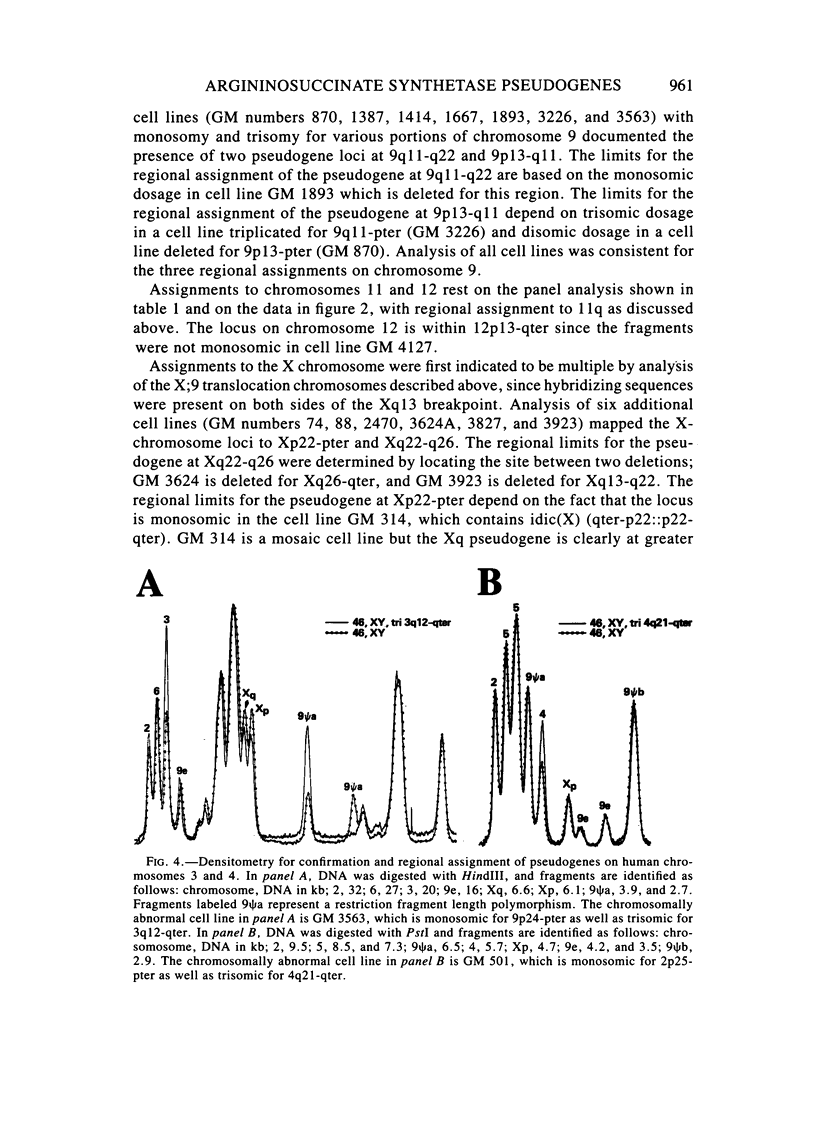
Abstract
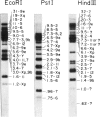
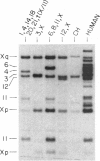
There are multiple, processed, dispersed pseudogenes for human argininosuccinate synthetase. Chinese hamster X human somatic cell hybrids were used to map DNA fragment groups corresponding to the single expressed gene and 14 pseudogene loci. Each chromosomal assignment was confirmed using hybrids containing very few human chromosomes and/or by demonstrating monosomic or trisomic dosage in human cell lines with chromosomal abnormalities. Pseudogenes were mapped to chromosomes 2cen-p25, 3q12-qter, 4q21-qter, 5 (two loci), 6, 7, 9p13-q11, 9q11-q22, 11q, 12, Xp22-pter, Xq22-q26, and Ycen-q11. DNA fragments from the expressed gene were mapped to 9q34-qter in agreement with the previous assignment for enzyme activity. A high-frequency restriction fragment length polymorphism mapped to 9q11-q22. The analyses emphasized the feasibility of using chromosomally abnormal human cell lines for confirmation and regionalization of gene-mapping assignments made using somatic-cell hybrids. Conversely, cloned DNA probes, once mapped and characterized, can be very valuable for determining the chromosomal composition of interspecies hybrids and the dosage of loci in human cells. The argininosuccinate synthetase cDNA is a convenient reagent for dosage analysis of 15 human loci on 11 different chromosomes. Improved reagents could be designed that would simplify Southern blot patterns by eliminating overlapping DNA fragments and providing a single DNA fragment for each locus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhadeff B., Velivasakis M., Siniscalco M. Simultaneous identification of chromatid replication and of human chromosomes in metaphases of man-mouse somatic cell hybrids. (With 1 color plate). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(4):236–239. doi: 10.1159/000130814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A. L., Su T. S., O'Brien W. E., D'Eustachio P., Barker P. E., Ruddle F. H. Dispersion of argininosuccinate-synthetase-like human genes to multiple autosomes and the X chromosome. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carritt B., Povey S. Regional asssignments of the loci AK3, ACONS, and ASS on human chromosome 9. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;23(3):171–181. doi: 10.1159/000131323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Hoffman N. S., Wildin R. S., Su T. S. Multiple, independent restriction site polymorphisms in human DNA detected with a cDNA probe to argininosuccinate synthetase (AS). Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):736–749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Wildin R. S., Su T. S. Sequences on the human Y chromosome homologous to the autosomal gene for argininosuccinate synthetase. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):682–684. doi: 10.1038/298682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Bock H. G., Beaudet A. L., O'Brien W. E. Molecular structures of human argininosuccinate synthetase pseudogenes. Evolutionary and mechanistic implications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3160–3166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Riccardi V. M., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J., Keenan B. S., Crawford J. D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Shulkin J. D., Toomey K. E., Funderburk S. J. Regional localization of human gene loci on chromosome 9: studies of somatic cell hybrids containing human translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;31(5):586–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Crowder W. E., Nyhan W. L., Caskey C. T. A three-allele restriction-fragment-length polymorphism at the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4035–4039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Bock H. G., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Cloning of cDNA for argininosuccinate synthetase mRNA and study of enzyme overproduction in a human cell line. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11826–11831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]