Abstract
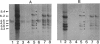
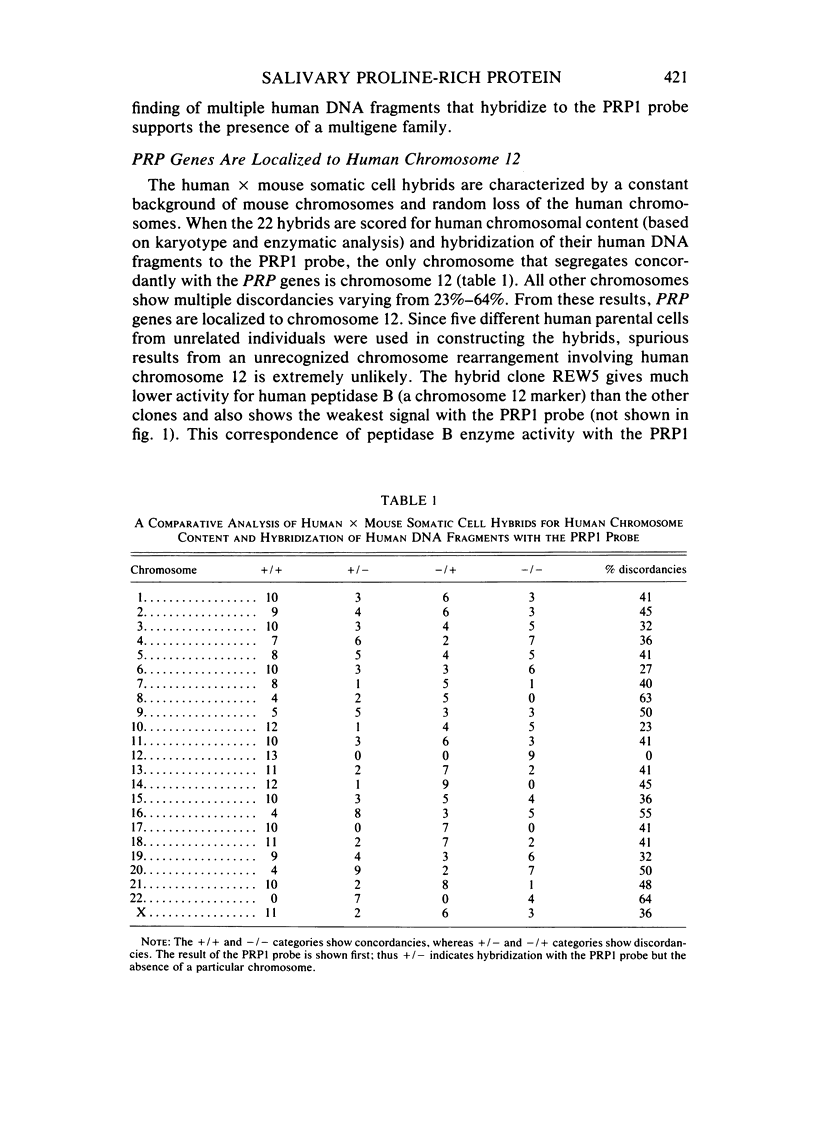
A DNA probe (PRP1) for the proline-rich protein (PRP) genes was used to analyze the segregation of human PRP genes in human X mouse somatic cell hybrids. Endonuclease restriction analysis of 22 independent hybrid clones segregating human chromosomes demonstrated that PRP genes segregate with human chromosome 12 only and were therefore assigned to that chromosome. The PRP1 probe should prove useful for further mapping studies of human chromosome 12.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azen E. A., Carlson D. M., Clements S., Lalley P. A., Vanin E. Salivary proline-rich protein genes on chromosome 8 of mouse. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):967–969. doi: 10.1126/science.6095444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E. A., Yu P. L. Genetic polymorphism of CON 1 and CON 2 salivary proteins detected by immunologic and concanavalin A reactions on nitrocellulose with linkage of CON 1 and CON 2 genes to the SPC (salivary protein gene complex). Biochem Genet. 1984 Feb;22(1-2):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00499283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E. A., Yu P. L. Genetic polymorphisms of Pe and Po salivary proteins with probable linkage of their genes to the salivary protein gene complex (SPC). Biochem Genet. 1984 Dec;22(11-12):1065–1080. doi: 10.1007/BF00499632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs I., Purrello M., Alhadeff B., Grzeschik K. H., Szabo P. Isolation and subregional mapping of a human cDNA clone detecting a common RFLP on chromosome 12. Hum Genet. 1984;68(1):57–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00293873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Lalley P. A., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: combined use of recombinant inbred strains and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1220–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Salivary proline-rich proteins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Jun 11;45(2):83–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00223503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald P. S., Grzeschik K. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 10, 11, and 12. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):103–126. doi: 10.1159/000132006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D., Wong R., Bennick A., Keller P. Basic proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva: complete covalent structure of protein IB-9 and partial structure of protein IB-6, members of a polymorphic pair. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6558–6562. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Minna J. D., Francke U. Conservation of autosomal gene synteny groups in mouse and man. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):160–163. doi: 10.1038/274160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Rattazzi M. C., Shows T. B. Human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B: expression and linkage relationships in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1569–1573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Fritsch E. F., Lauer J., Lawn R. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobins. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:145–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Lalley P. A., Francke U. Comparative mapping using somatic cell hybrids. In Vitro. 1976 Nov;12(11):726–733. doi: 10.1007/BF02835447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Taylor B. A. Lengths of chromosomal segments conserved since divergence of man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):814–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura H., Kanai Y., Sanada K. Amino acid sequences of glycopeptides obtained from basic proline-rich glycoprotein of human parotid saliva. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):857–863. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. F., Azen E. A. Proline-rich proteins are present in serous cells of submucosal glands in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jul;130(1):115–118. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Bennick A. The primary structure of a salivary calcium-binding proline-rich phosphoprotein (protein C), a possible precursor of a related salivary protein A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5943–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P. L., Karn R. C., Merritt A. D., Azen E. A., Conneally P. M. Linkage relationships and multipoint mapping of the human parotid salivary proteins (Pr, Pa, Db). Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Jul;32(4):555–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]