Abstract
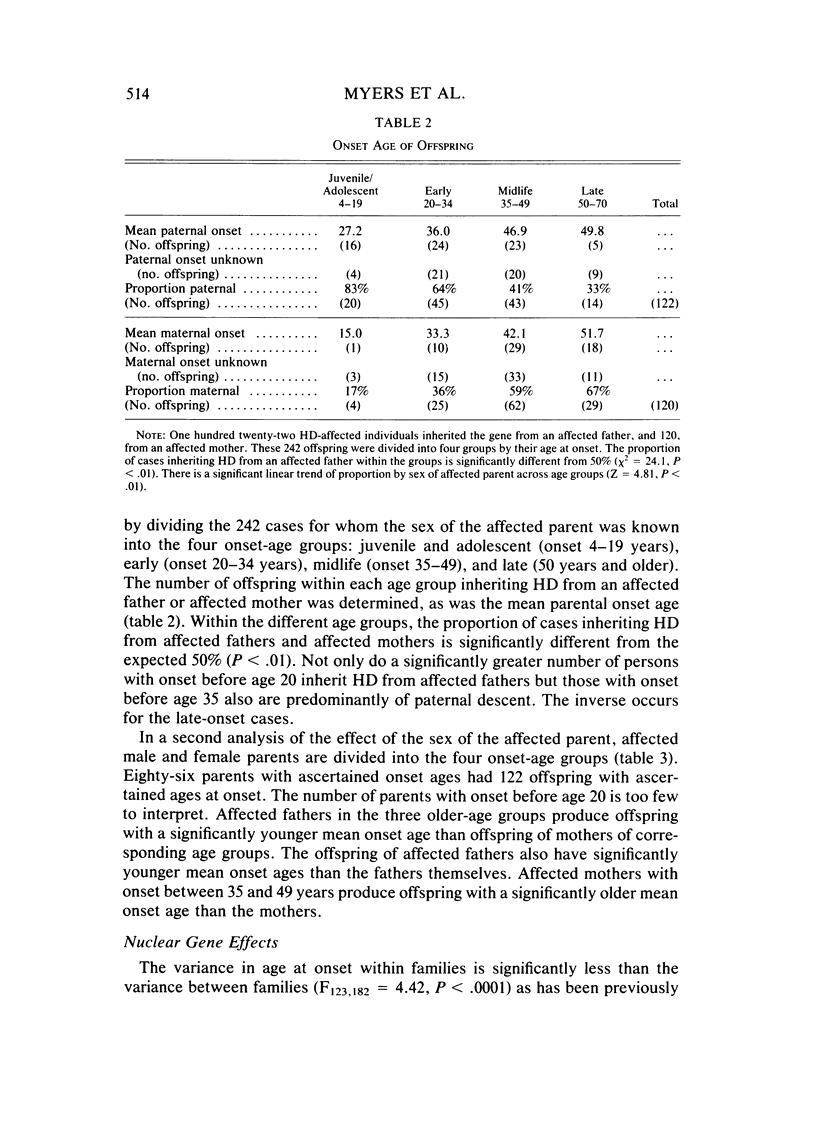
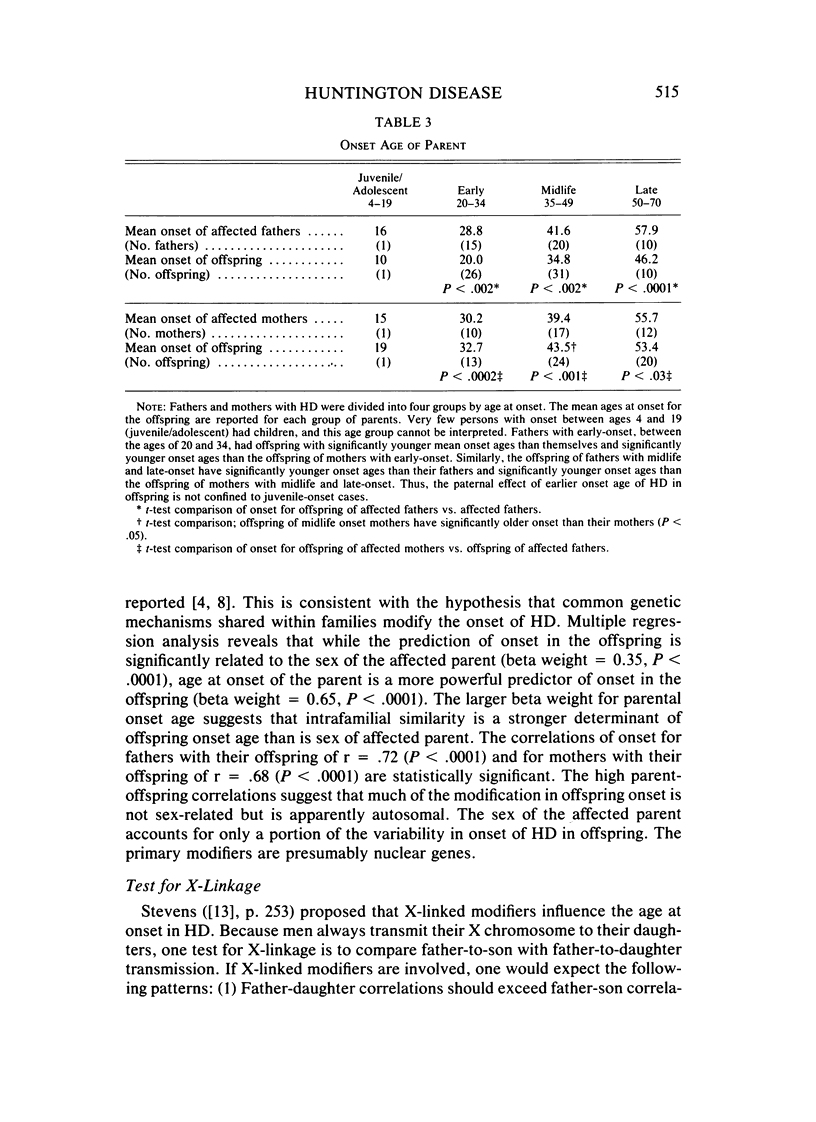
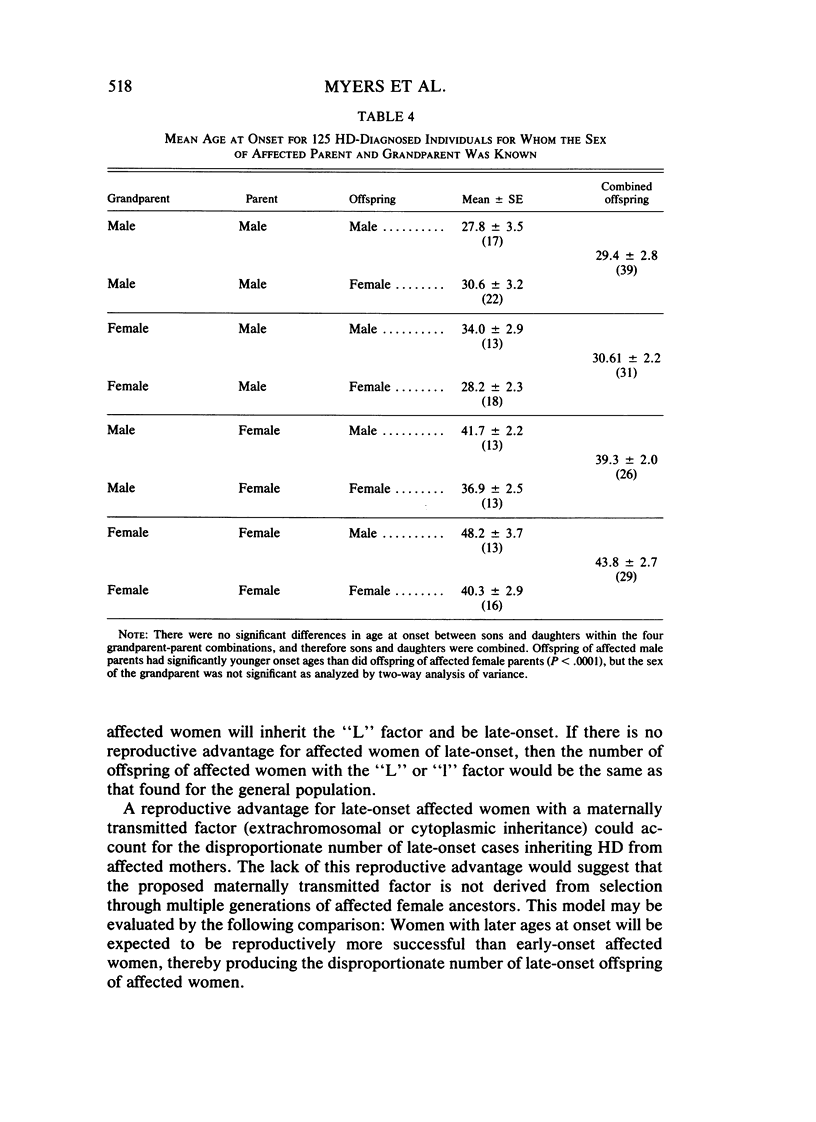
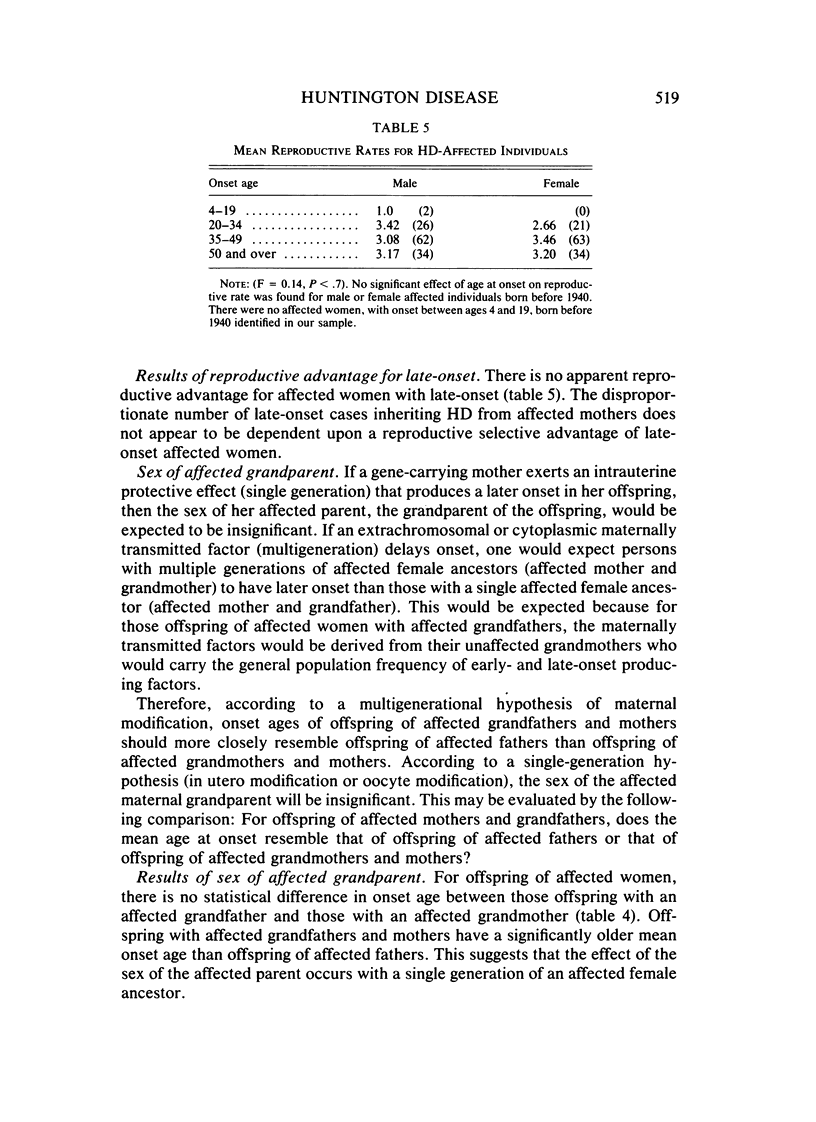
Analyses of father-offspring and mother-offspring similarity in onset age suggest that nuclear genes account for a significant portion of the modification of onset age in Huntington disease. The effects of non-nuclear modifiers are supported by the finding that the offspring of affected women have significantly older mean ages of onset than offspring of affected men irrespective of the onset age in the parent. The absence of increased father-daughter similarity indicates that modification is not X-linked. The absence of reproductive advantage for late-onset individuals and the absence of a multigenerational maternal-lineage effect suggest that the modifying effect of the sex of the affected parent occurs in a single parental generation. Offspring of affected women with onset between ages 35 and 49 had a significantly older mean onset age than their mothers. This suggests that a protective effect may be conferred upon the offspring of affected women.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird E. D., Caro A. J., Pilling J. B. A sex related factor in the inheritance of Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):255–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehnke M., Conneally P. M., Lange K. Two models for a maternal factor in the inheritance of Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):845–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenridge C. J. Familial correlations for age at onset and age at death in Huntington's disease. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):23–32. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield D. A., Oeswein J. Q., Markesbery W. R. Electron spin resonance study of membrane protein alterations in erythrocytes in Huntington's disease. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):453–455. doi: 10.1038/267453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers R. K., Gilles F. H., Fung C. Huntington's disease in children. Neuropathologic study of four cases. Neurology. 1973 Jun;23(6):561–569. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.6.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M. Huntington disease: genetics and epidemiology. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):506–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Nicholson J. F., Hays A. P., Eastwood A. B., Papadimitriou A., Koenigsberger R., DeVivo D. C. Benign infantile mitochondrial myopathy due to reversible cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Ann Neurol. 1983 Aug;14(2):226–234. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger J., Wilson J. Mitochondrial inheritance in a mitochondrially mediated disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 21;309(3):142–146. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307213090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Conneally P. M., Yu P. L. The natural history of Huntington disease: possible role of "aging genes". Am J Med Genet. 1984 May;18(1):115–123. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein S. E., Franz M. L., Jensen B. A., Chase G. A., Folstein M. F. Conduct disorder and affective disorder among the offspring of patients with Huntington's disease. Psychol Med. 1983 Feb;13(1):45–52. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700050054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles R. E., Blanc H., Cann H. M., Wallace D. C. Maternal inheritance of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Te-Juatco L. Association between age of onset and parental inheritance in Huntington chorea. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):289–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Goldman D., Bird E. D., Sax D. S., Merril C. R., Schoenfeld M., Wolf P. A. Maternal transmission in Huntington's disease. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):208–210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Madden J. J., Teague J. L., Falek A. Factors related to onset age of Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):481–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe R. G. A life table for onset of Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Oct;45(Pt 4):375–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe R. G., Walker D. A., Harper P. S. Factors influencing age at onset and duration of survival in Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Oct;45(Pt 4):387–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Van de Walle M. J., Laipis P. J., Hauswirth W. W. Nucleotide sequence evidence for rapid genotypic shifts in the bovine mitochondrial DNA D-loop. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):400–402. doi: 10.1038/306400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettegrew J. W., Nichols J. S., Stewart R. M. Fluorescence spectroscopy on Huntington's fibroblasts. J Neurochem. 1979 Oct;33(4):905–911. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb09920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED T. E., CHANDLER J. H. Huntington's chorea in Michigan. I. Demography and genetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1958 Jun;10(2):201–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld M., Myers R. H., Cupples L. A., Berkman B., Sax D. S., Clark E. Increased rate of suicide among patients with Huntington's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Dec;47(12):1283–1287. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.12.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsky L., Myers R. H., Walshe T. M. Huntington's disease in monozygotic twins reared apart. J Med Genet. 1983 Dec;20(6):408–411. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.6.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. A., Harper P. S., Newcombe R. G., Davies K. Huntington's chorea in South Wales: mutation, fertility, and genetic fitness. J Med Genet. 1983 Feb;20(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Went L. N., Vegter-van der Vlis M., Bruyn G. W. Parental transmission in Huntington's disease. Lancet. 1984 May 19;1(8386):1100–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92510-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


