Abstract
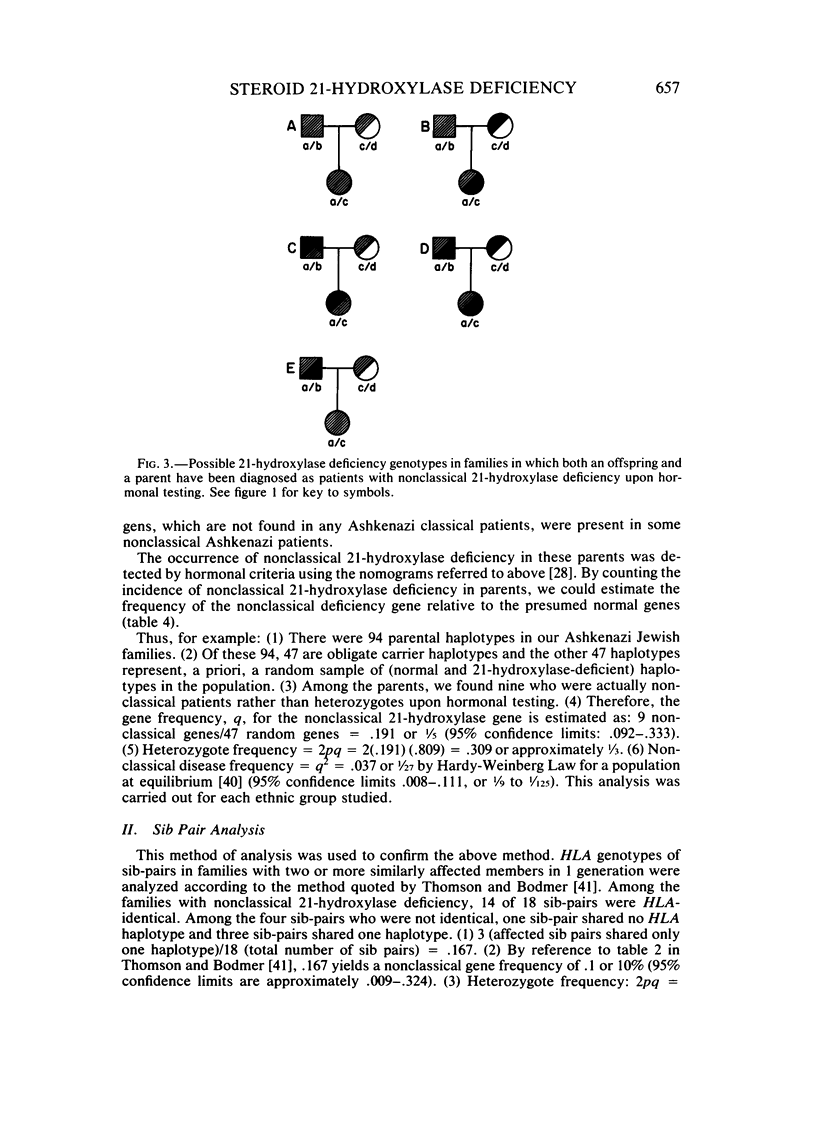
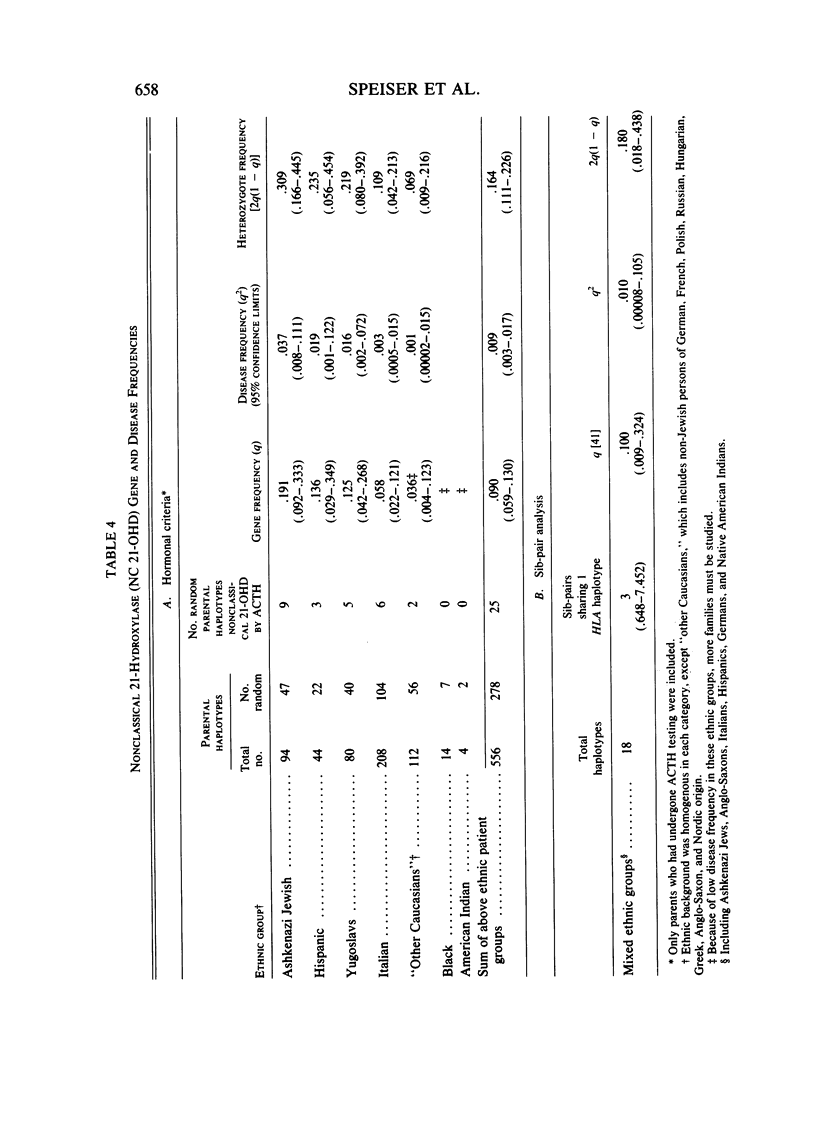
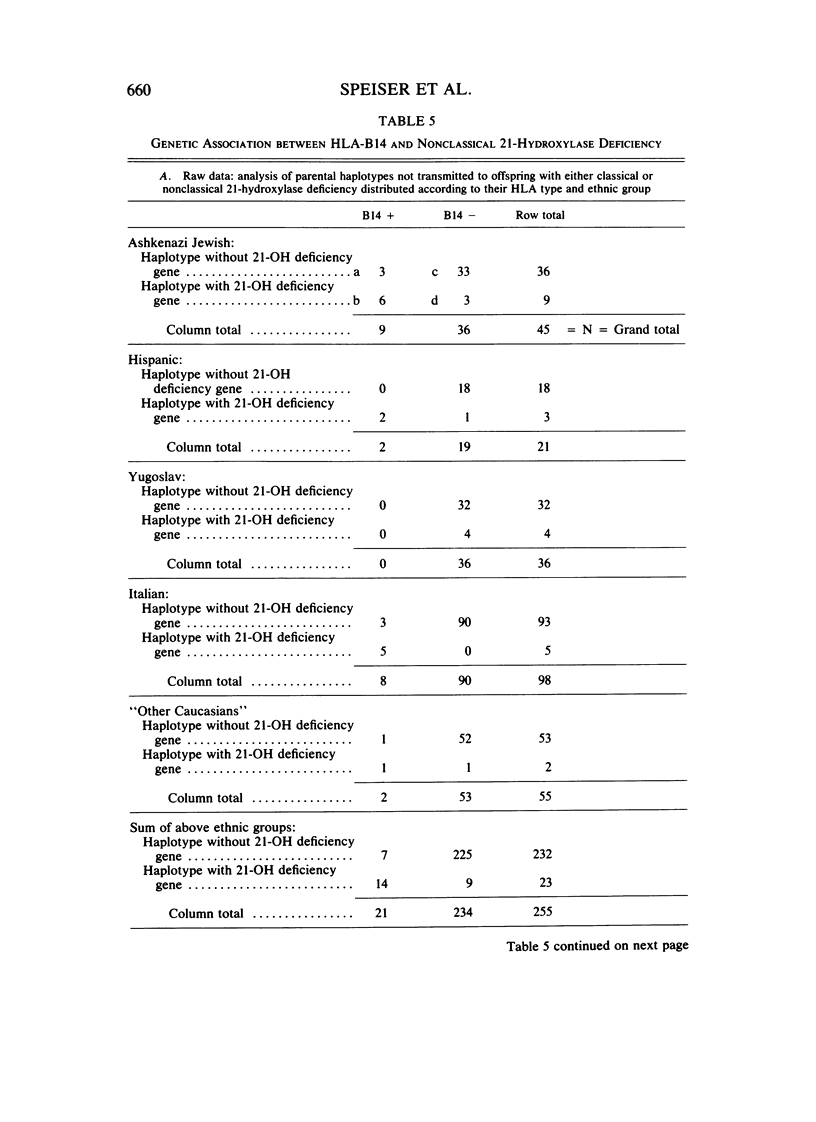
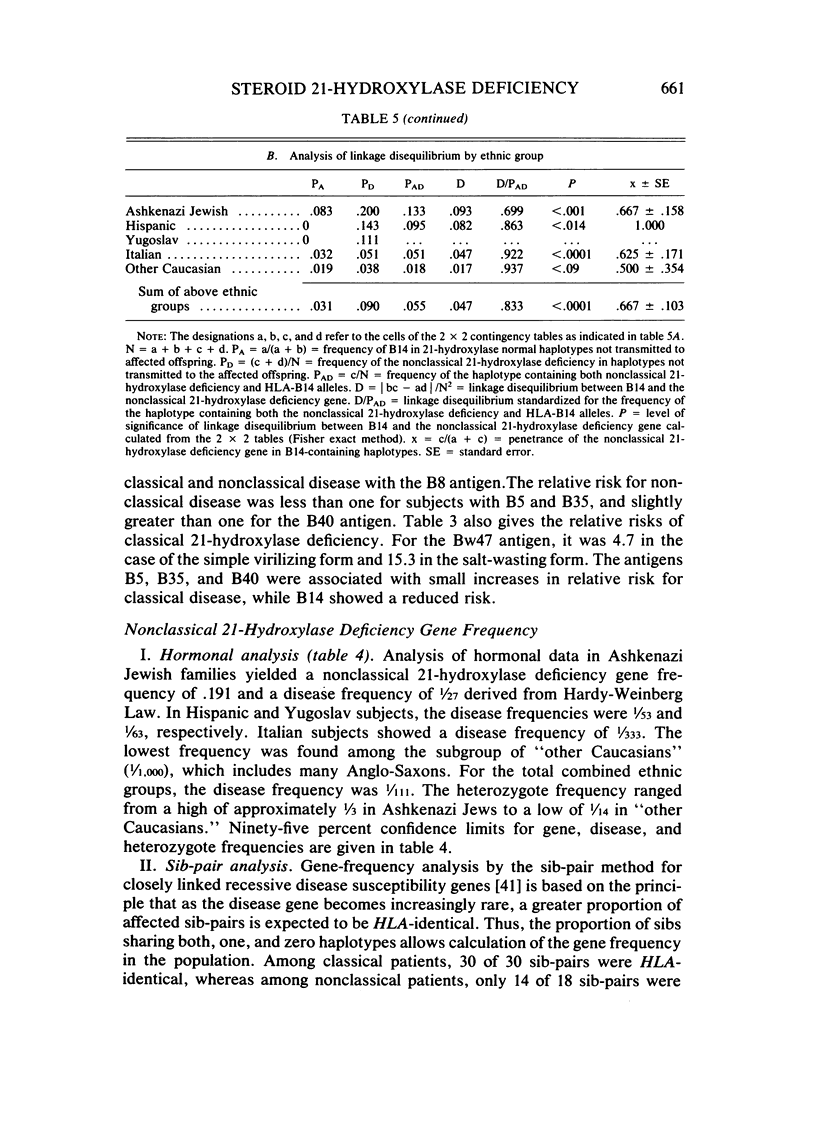
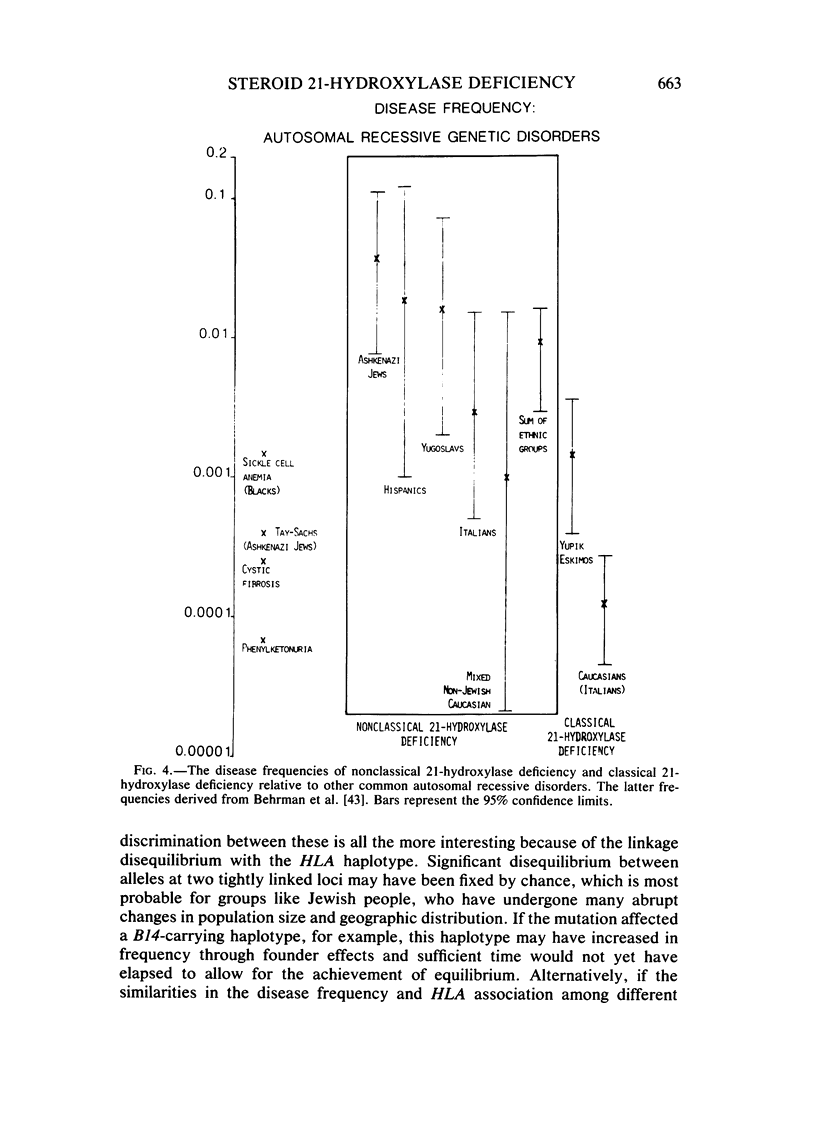
Nonclassical steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that is defined by clinical and hormonal criteria that distinguishes it from the classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. No estimates of the gene frequency of nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency, also called attenuated, late-onset, acquired, and cryptic adrenal hyperplasia, have been published thus far. Here, we have used HLA-B genotype data in families containing multiple members affected with nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency together with the results of quantitative hormonal tests to arrive at estimates of gene and disease frequencies for this disorder. We found nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency to be a far more common disorder than classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency, which occurs in 1/8,000 births. The prevalence of the disease in Ashkenazi Jews was 3.7%; in Hispanics, 1.9%; in Yugoslavs, 1.6%; in Italians, 0.3%; and in the diverse Caucasian population, 0.1%. The gene for nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency is in genetic linkage disequilibrium with HLA-B14 in Ashkenazi Jews, Hispanics, and Italians, but not in Yugoslavs or in a diverse, non-Jewish, Caucasian group. The penetrance of nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency gene in the HLA-B14 containing haplotypes was incomplete. Thus, nonclassical 21-hydroxylase deficiency is probably the most frequent autosomal recessive genetic disorder in man and is especially frequent in Ashkenazi Jews, Hispanics, Italians, and Yugoslavs.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blankstein J., Faiman C., Reyes F. I., Schroeder M. L., Winter J. S. Adult-onset familial adrenal 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Med. 1980 Mar;68(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonné-Tamir B., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F., Pickbourne P., Brautbar C., Gazit E., Nevo S., Zamir R. HLA polymorphism in Israel. 9. An overall comparative analysis. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Mar;11(3):235–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHILDS B., GRUMBACH M. M., VAN WYK J. J. Virilizing adrenal hyperplasia; a genetic and hormonal study. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):213–222. doi: 10.1172/JCI103266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacciari E., Balsamo A., Cassio A., Piazzi S., Bernardi F., Salardi S., Cicognani A., Pirazzoli P., Zappulla F., Capelli M. Neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Oct;58(10):803–806. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.10.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECOURT J., JAYLE M. F., BAULIEU E. Virilisme cliniquement tardif avec excrétion de prégnanetriol et insuffisance de la production du cortisol. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1957 May-Jun;18(3):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles C. M., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr, Robson E. B., Thorsby E., Olaisen B., Arnason A., Kissmeyer-Nielsen F., Schreuder I. Rga (Rodgers) and the HLA region: linkage and associations. Tissue Antigens. 1976 Aug;8(2):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES G. E. S., HOWARD J. E., LANGFORD H. The use of cortisone in follicular phase disturbances. Fertil Steril. 1953 Jan-Feb;4(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)31144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn B., Levine L. S., Pollack M. S., Pang S., Lorenzen F., Levy D., Lerner A. J., Rondanini G. F., Dupont B., New M. I. Late-onset steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: a variant of classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):817–827. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth-Schutz S., Virdis R., Saenger P., Chow D. M., Levine L. S., New M. I. Serum androgens as a continuing index of adequacy of treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Mar;46(3):452–458. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-3-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Pollack M. S., Zamir R., Roitman A., Dickerman Z., Levine L. S., Lorenzen F., O'Neill G. J., Pang S., New M. I. Late onset 21-hydroxylase deficiency and HLA in the Ashkenazi population: a new allele at the 21-hydroxylase locus. Hum Immunol. 1980 Jul;1(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(80)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. S., Dupont B., Lorenzen F., Pang S., Pollack M., Oberfield S. E., Kohn B., Lerner A., Cacciari E., Mantero F. Genetic and hormonal characterization of cryptic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Dec;53(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-6-1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. S., Dupont B., Lorenzen F., Pang S., Pollack M., Oberfield S., Kohn B., Lerner A., Cacciari E., Mantero F. Cryptic 21-hydroxylase deficiency in families of patients with classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Dec;51(6):1316–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-6-1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. S., Zachmann M., New M. I., Prader A., Pollack M. S., O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Oberfield S. E., Dupont B. Genetic mapping of the 21-hydroxylase-deficiency gene within the HLA linkage group. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):911–915. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen F., Pang S., New M. I., Dupont B., Pollack M., Chow D. M., Levine L. S. Hormonal phenotype and HLA-genotype in families of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Pediatr Res. 1979 Dec;13(12):1356–1360. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197912000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen F., Pang S., New M., Pollack M., Oberfield S., Dupont B., Chow D., Schneider B., Levine L. Studies of the C-21 and C-19 steroids and HLA genotyping in siblings and parents of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Mar;50(3):572–577. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton J., Crookston M. C., Falk J. A., Robson E. B., Cook P. J., Batchelor J. R., Bodmer J., Ferrara G. B., Festenstein H., Harris R. Linkage of Chido and HL-A. Tissue Antigens. 1974;4(4):366–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1974.tb00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon C. J., Rosenwaks Z., Lee P. A., Urban M. D., Bias W. B. The attenuated form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia as an allelic form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):647–649. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Levine L. S. Recent advances in 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:649–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Lorenzen F., Lerner A. J., Kohn B., Oberfield S. E., Pollack M. S., Dupont B., Stoner E., Levy D. J., Pang S. Genotyping steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency: hormonal reference data. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Aug;57(2):320–326. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-2-320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Pollack M. S., Yang S. Y., Levine L. S., New M. I., Dupont B. Gene frequencies and genetic linkage disequilibrium for the HLA-linked genes Bf, C2, C4S, C4F, 21-hydroxylase deficiency, and glyoxalase I. Transplant Proc. 1979 Dec;11(4):1713–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Chido and Rodgers blood groups: relationship to C4 and HLA. Transplant Proc. 1978 Dec;10(4):749–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S., Hotchkiss J., Drash A. L., Levine L. S., New M. I. Microfilter paper method for 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone radioimmunoassay: its application for rapid screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., O'Neill G. J., Pang S., Lorenzen F., Kohn B., Rondanini G. F., Chiumello G., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA linkage and B14, DR1, BfS haplotype association with the genes for late onset and cryptic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):540–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Levine L., Zachmann M., Prader A., New M., Oberfield S., Dupont B. Possible genetic linkage disequilibrium between HLA and the 21-hydroxylase deficiency gene (congenital adrenal hyperplasia). Transplant Proc. 1979 Jun;11(2):1315–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Maurer D., Levine L. S., New M. I., Pang S., Duchon M., Owens R. P., Merkatz I. R., Nitowsky B. M., Sachs G. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency) by HLA typing. Lancet. 1979 May 26;1(8126):1107–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91789-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., New M. I., O'Neill G. J., Levine L. S., Callaway C., Pang S., Cacciari E., Mantero F., Cassio A., Scaroni C. HLA genotypes and HLA-linked genetic markers in Italian patients with classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Genet. 1981;58(3):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00294933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh W., Levine L. S., Gottesdiener K., New M. I. Mineralocorticoids, salt balance and blood pressure after prolonged ACTH administration in juvenile hypertension. Klin Wochenschr. 1978;56 (Suppl 1):161–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01477468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P. HLA and disease 1982--a survey. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:193–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Levine L. S., Zachmann M., New M. I., Prader A., Oberfield S. E., O'Neill G. J., Pollack M. S., Dupont B. Mapping of the 21-hydroxylase deficiency gene within the HLA linkage group. Transplant Proc. 1978 Dec;10(4):753–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


