Abstract
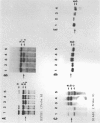
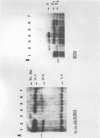
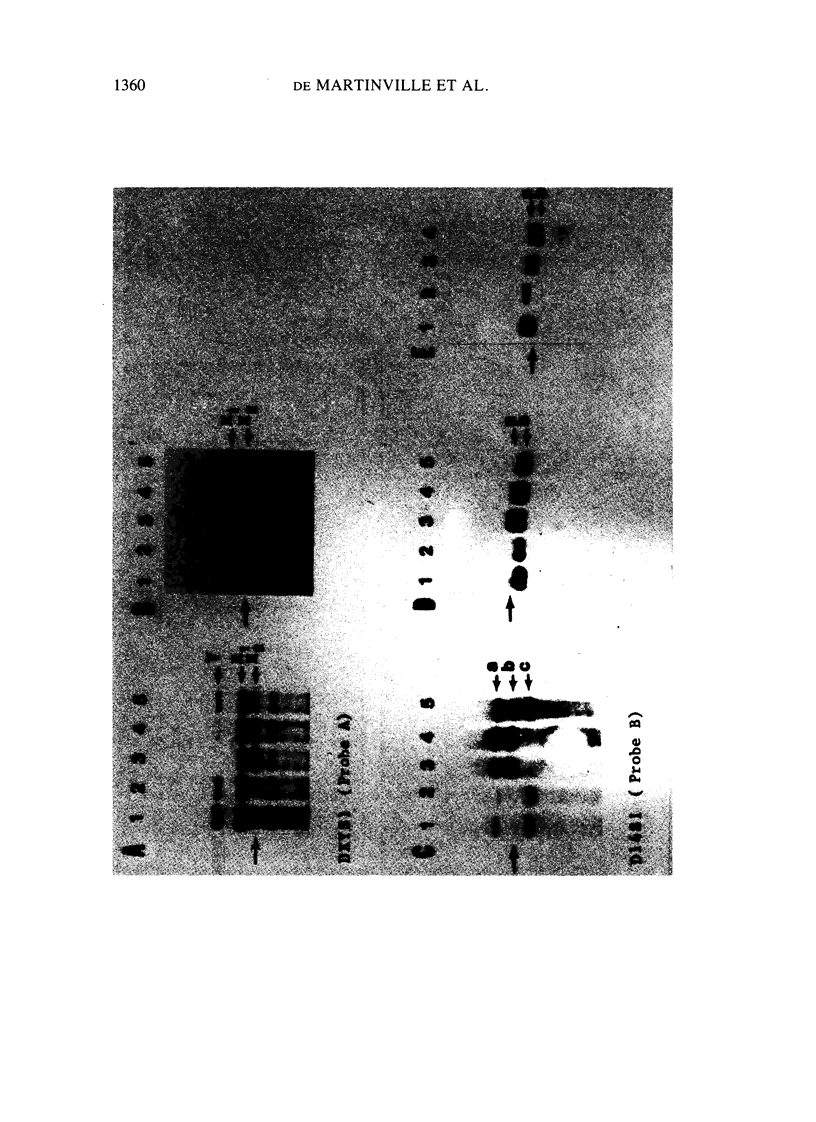
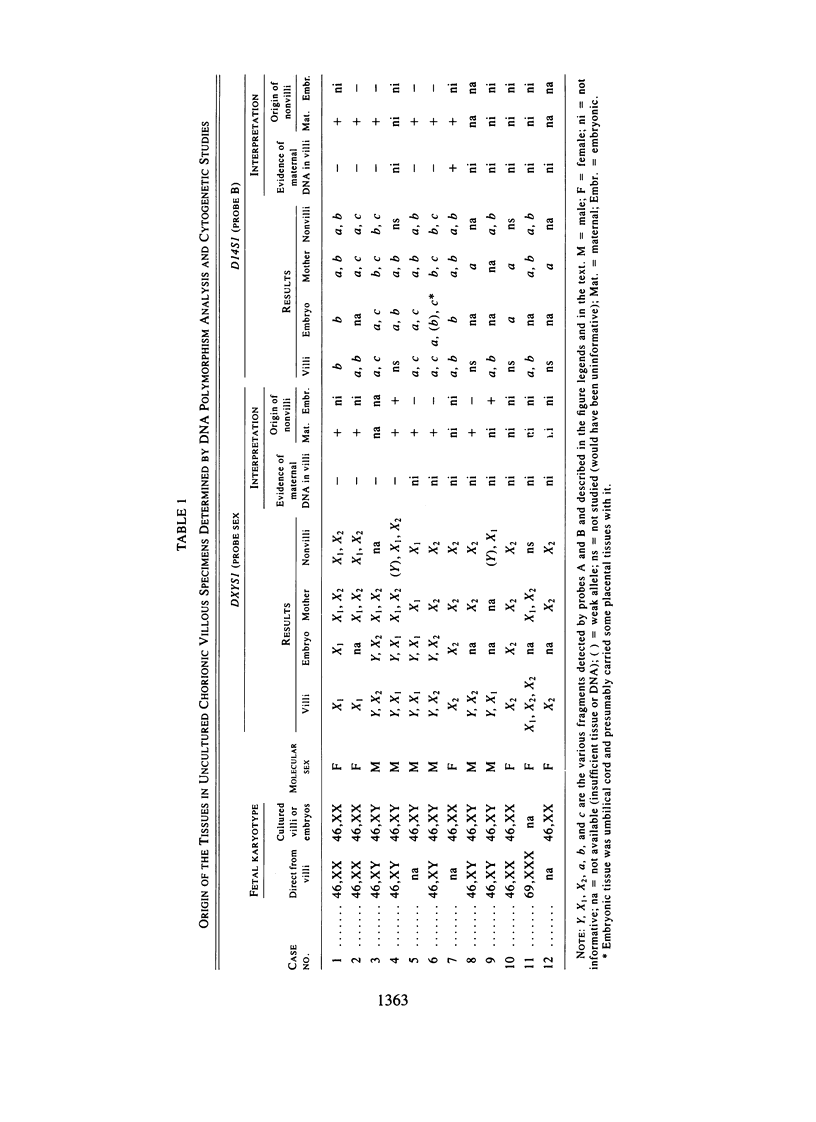
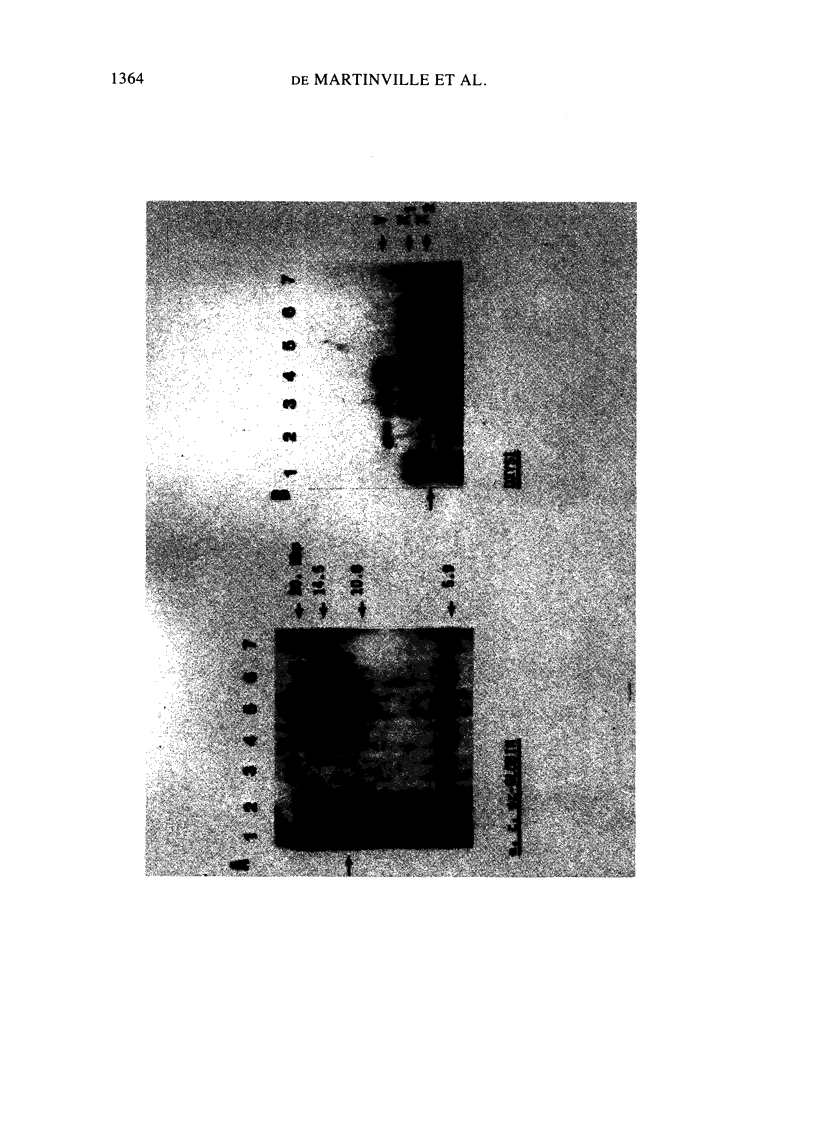
We investigated the reliability of chorionic villous biopsy as a method to obtain tissues reflecting the genetic constitution of the embryo. In 12 pregnancies before elective termination, we searched for detectable maternal tissue after careful dissection of villi from small 2-5-mg specimens that yielded 7 micrograms of DNA per mg tissue. In Southern blotting experiments (1-2 micrograms DNA per lane), restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) at an autosomal (D14S1) and a sex chromosomal (DXYS1) locus allowed recognition of maternally and embryonically derived alleles. Pure villi were obtained in six of the seven informative cases. One biopsy was not dissected satisfactorily; a mixture of embryonic and maternal DNA was found. Nonvillous tissues were mostly maternally derived in eight informative cases. Sex determination by molecular analysis (alleles at the DXYS1 locus) agreed with the karyotypes of uncultured or cultured villi. In one continuing pregnancy, distinct RFLPs indicated maternal inheritance of the alpha-thalassemia 1 trait in a female embryo without detectable maternal contamination. Reliable prenatal diagnosis depends on the specimen's purity. Maternal contamination can be evaluated by DNA analyses.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakemore K. J., Watson M. S., Samuelson J., Breg W. R., Mahoney M. J. A method of processing first-trimester chorionic villous biopsies for cytogenetic analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1386–1393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambati B., Simoni G. Diagnosis of fetal trisomy 21 in first trimester. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):586–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Solal M. M., Authier B., deRiel J. K., Murnane M. J., Forget B. G. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of human embryonic zeta-globin cDNA. DNA. 1982;1(4):355–363. doi: 10.1089/dna.1982.1.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elles R. G., Williamson R., Niazi M., Coleman D. V., Horwell D. Absence of maternal contamination of chorionic villi used for fetal-gene analysis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1433–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens M., Dumez Y., Kaplan L., Lupker M., Chabret C., Henrion R., Rosa J. Prenatal diagnosis of sickle-cell anemia in the first trimester of pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):831–833. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Mitchell A. R., Gosden C. M., Rodeck C. H., Morsman J. M. Direct vision chorion biopsy and chromosome-specific DNA probes for determination of fetal sex in first-trimester prenatal diagnosis. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1416–1419. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Wainscoat J. S., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Highly variable regions of DNA flank the human alpha globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4213–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilford R., Maxwell D., Coleman D., Czepulkowski B., Heaton D. Diagnosis, four hours after chorion biopsy, of female fetus in pregnancy at risk of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lancet. 1983 Dec 24;2(8365-66):1491–1491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90830-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie I. Z., Lindenbaum R. H., Patel C., Clarke G., Crocker M., Jonasson J. A. Prenatal diagnosis of an unbalanced chromosome translocation identified by direct karyotyping of chorionic biopsy. Lancet. 1983 Dec 17;2(8364):1426–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90962-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man-made mineral fibres--a safe alternative to asbestos? Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1125–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niazi M., Coleman D. V., Loeffler F. E. Trophoblast sampling in early pregnancy. Culture of rapidly dividing cells from immature placental villi. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Nov;88(11):1081–1085. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old J. M., Ward R. H., Petrou M., Karagözlu F., Modell B., Weatherall D. J. First-trimester fetal diagnosis for haemoglobinopathies: three cases. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1413–1416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D., de Martinville B., Barker D., Wyman A., White R., Francke U., Botstein D. Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressley L., Higgs D. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Gene deletions in alpha thalassemia prove that the 5' zeta locus is functional. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3586–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Morsman J. M. First-trimester chorion biopsy. Br Med Bull. 1983 Oct;39(4):338–342. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Morsman J. M., Nicolaides K. H., McKenzie C., Gosden C. M., Gosden J. R. A single-operator technique for first-trimester chorion biopsy. Lancet. 1983 Dec 10;2(8363):1340–1341. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs E. S., Van Hemel J. O., Galjaard H., Niermeijer M. F., Jahoda M. G. First trimester chromosomal analysis of complex structural rearrangements with RHA banding on chorionic villi. Lancet. 1983 Dec 17;2(8364):1426–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90961-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni G., Brambati B., Danesino C., Rossella F., Terzoli G. L., Ferrari M., Fraccaro M. Efficient direct chromosome analyses and enzyme determinations from chorionic villi samples in the first trimester of pregnancy. Hum Genet. 1983;63(4):349–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00274761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. H., Modell B., Petrou M., Karagözlu F., Douratsos E. Method of sampling chorionic villi in first trimester of pregnancy under guidance of real time ultrasound. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 14;286(6377):1542–1544. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6377.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]