Abstract
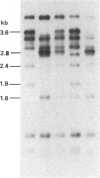
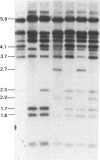
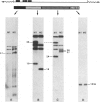
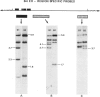
This investigation was undertaken to study genetic variation in the human immunoglobulin gamma heavy-chain (IgG) genes using Southern blot hybridization techniques to identify restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). A genomic Ig gamma-1 clone was used as a probe, and variants were identified with two restriction enzymes (R.E.), each of which defined RFLPs at two separate IgG loci. Once alleles and haplotypes were determined, molecular localization of the alleles was made through genetic analysis of recombinant haplotypes and through the use of regional specific subclones. Linkage between the newly defined RFLPs and switch region variants as well as protein allotypic markers (Gm) was complete. This analysis included markers for Ig Mu, Alpha 1, Alpha 2, Gamma 1, Gamma 2, Gamma 3, and Pseudo Gamma. The picture that emerges from the molecular study of two common haplotypes, each with many rare variants resulting from recombination or mutation, confirms and extends the earlier immunological observations. The accumulated differences between the two major Caucasian IgG haplotypes indicate that their separation may be ancient and maintained through heterozygote advantage.
Full text
PDF





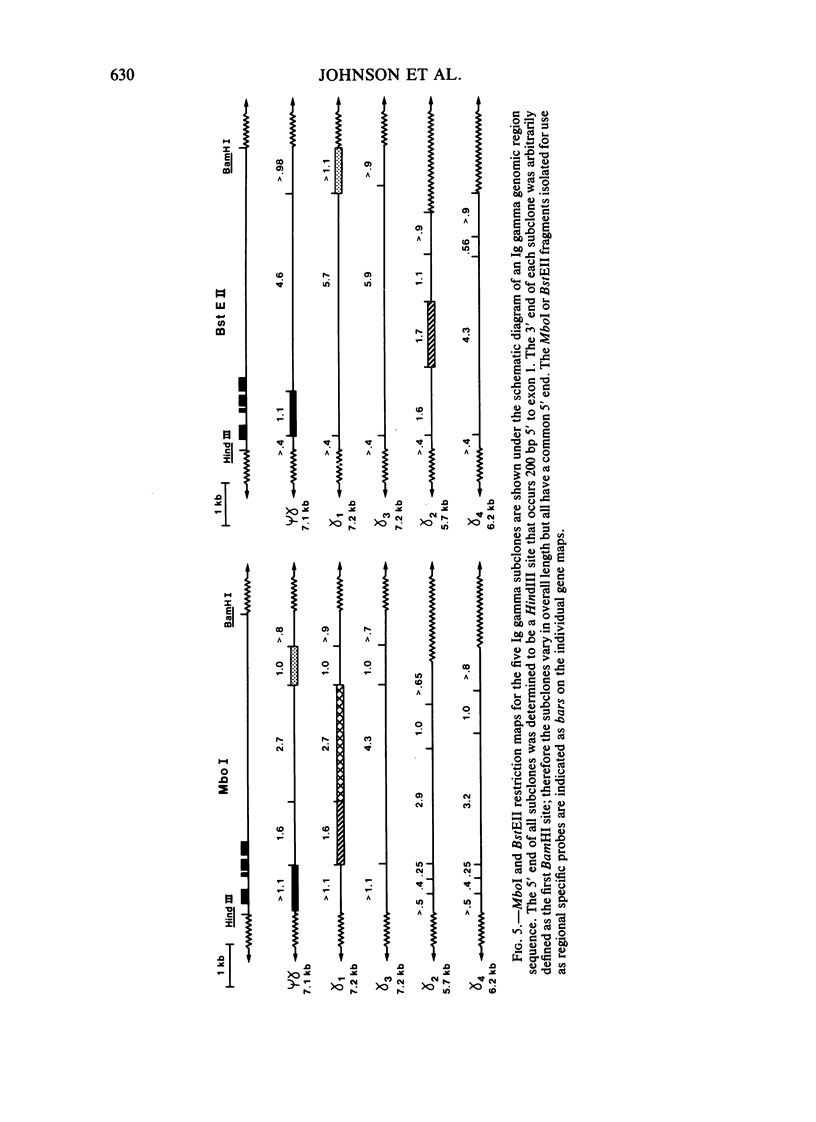
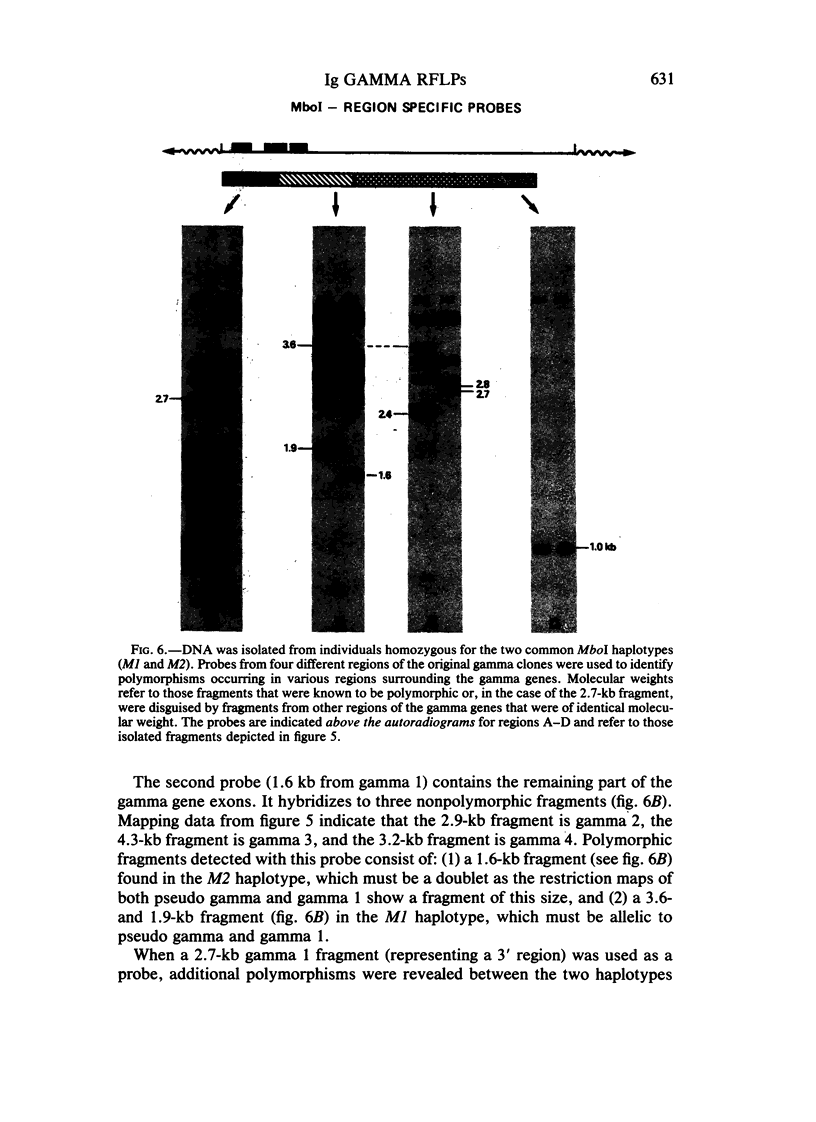

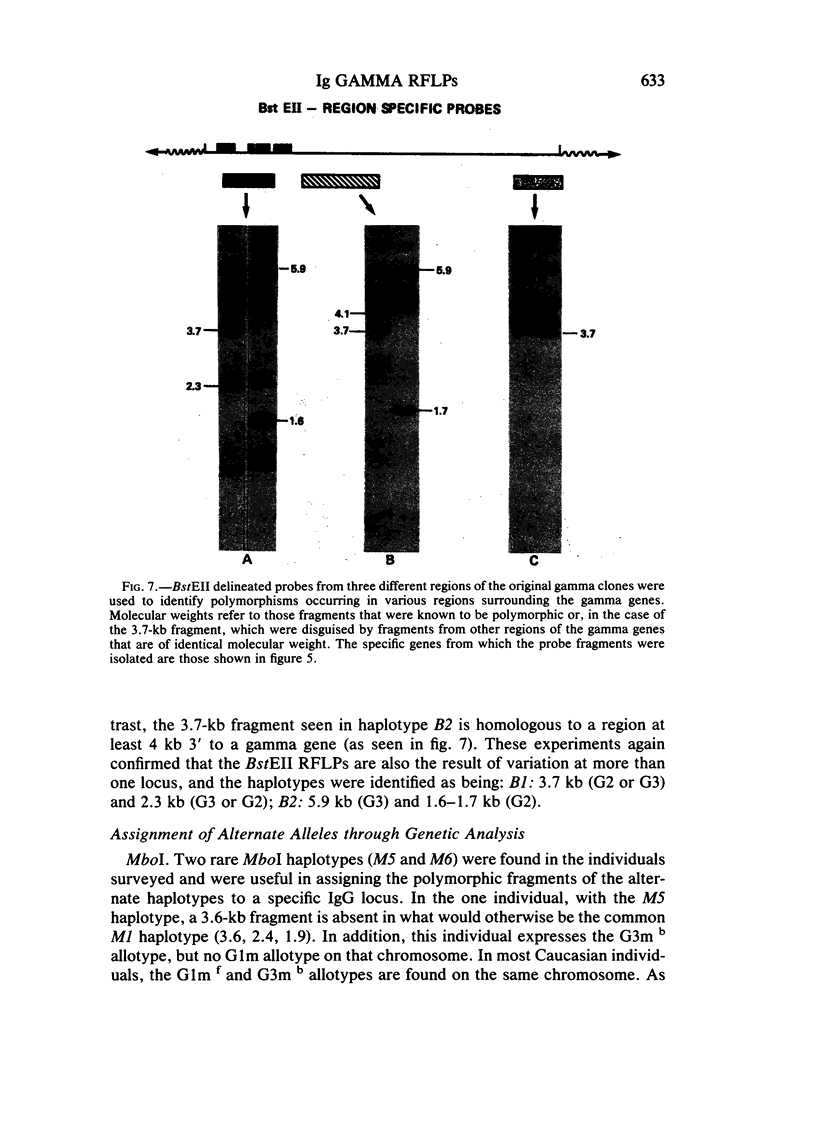

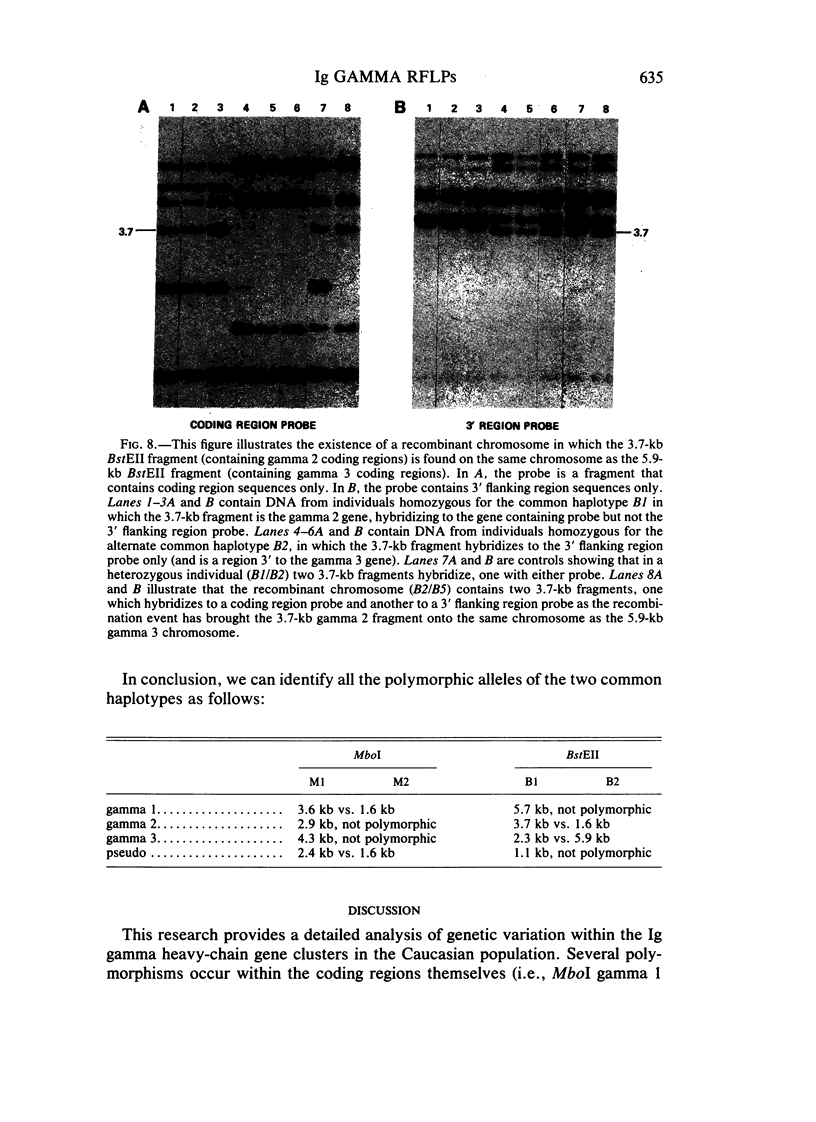





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Boehm C. D., Giardina P. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Nonrandom association of polymorphic restriction sites in the beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Irkin S. H., Cheng T. C., Scott A. F., Sexton J. P., Trusko S. P., Charache S., Kazazian H. H., Jr beta-Thalassemia in American Blacks: novel mutations in the "TATA" box and an acceptor splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm C. D., Antonarakis S. E., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Stetten G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Prenatal diagnosis using DNA polymorphisms. Report on 95 pregnancies at risk for sickle-cell disease or beta-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 5;308(18):1054–1058. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305053081803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. W., Berson B. J., Hood L. E. The nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4071–4079. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Buxbaum J., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma 4 gene. DNA. 1981;1(1):11–18. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Hood L. Linkage and sequence homology of two human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain constant region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feder J., Yen L., Wijsman E., Wang L., Wilkins L., Schroder J., Spurr N., Cann H., Blumenberg M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. A systematic approach for detecting high-frequency restriction fragment length polymorphisms using large genomic probes. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):635–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Wainscoat J. S., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Highly variable regions of DNA flank the human alpha globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4213–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., Natali A. M., Cann H. M., Honjo T., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Polymorphisms of a human variable heavy chain gene show linkage with constant heavy chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7840–7844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., Wallace D. C., Ferris S. D., Rattazzi M. C., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Radiation of human mitochondria DNA types analyzed by restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(3-4):255–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Morton C. C., Nakahara K., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6801764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Rabbitts T. H. Comparison of the hinge-coding segments in human immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain genes and the linkage of the gamma 2 and gamma 4 subclass genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):403–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G., Rabbitts T. H. Inherited deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes in normal human individuals. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):760–762. doi: 10.1038/300760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Rabbitts T. H. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain A2 gene allotype determination by restriction fragment length polymorphism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1303–1311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., Feder J., Cann H., van West B., Hwang J., Takahashi N., Honjo T., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Multiple DNA fragment polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin mu chain switch-like regions in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):467–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., de Lange G., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Genetic analysis of eight linked polymorphisms within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1146–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. Selection for heterozygotes in small populations. Genetics. 1962 Sep;47:1291–1300. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.9.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shander M., Martinis J., Croce C. M. Genetics of human immunoglobulins: assignment of the genes for mu, alpha, and gamma immunoglobulin chains to human chromosome 14. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3):417–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Ueda S., Obata M., Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Structure of human immunoglobulin gamma genes: implications for evolution of a gene family. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelaschi D., Newby C., Parsons M., van West B., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Human immunoglobulin allotypes: previously unrecognized determinants and alleles defined with monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3762–3766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange G., Wright P., van Eede P., van Leeuwen F., Hoang T. L., Nguyen T. D. Association between leprosy and immunoglobulin allotypes: Gm-A2m and Km frequencies in Vietnamese. J Immunogenet. 1984 Jun-Aug;11(3-4):173–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1984.tb01054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]