Abstract
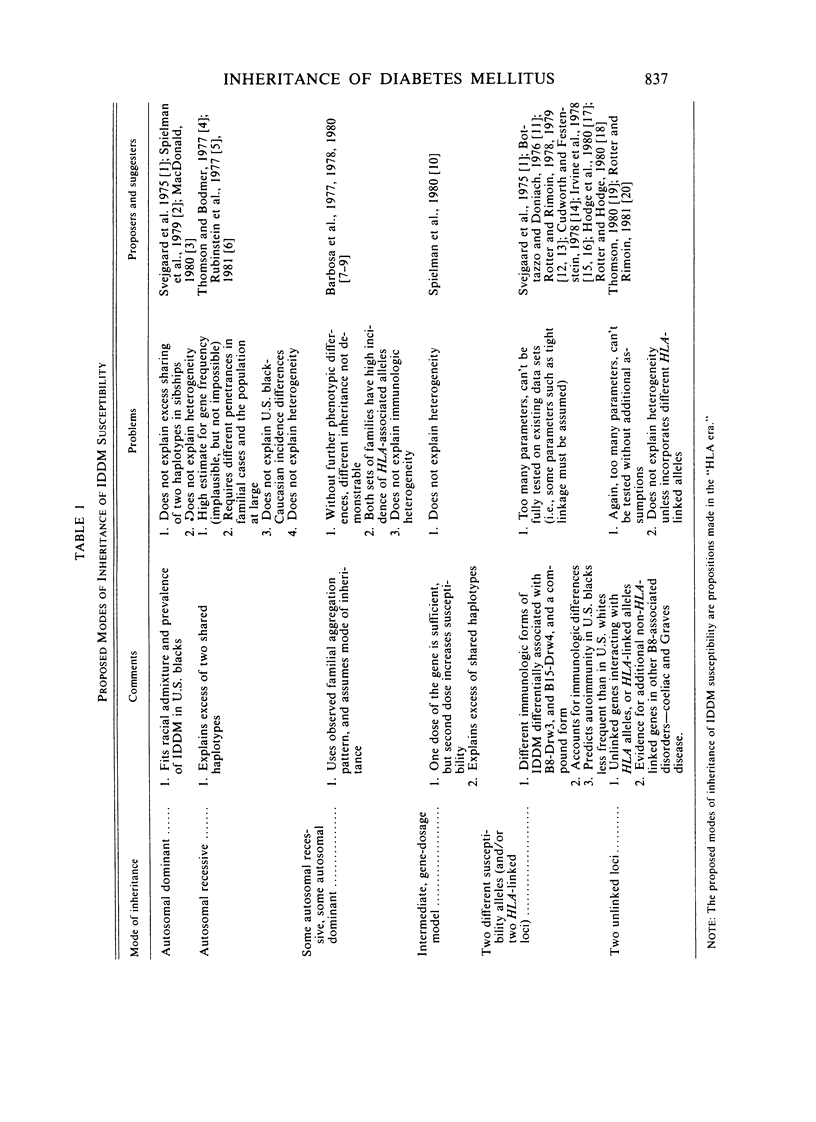
The discovery of HLA antigen associations with juvenile-type insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) provided strong evidence separating this disorder, or group of disorders, from maturity-type noninsulin-dependent diabetes, as well as adding to the evidence for an immunologic pathogenesis. In addition, it was hoped that the use of these disease-marker associations in appropriate studies might clarify the genetics of IDDM. While these associations have provided a useful tool to further investigate the genetics and pathogenesis of IDDM, the mode or modes of inheritance of this group of disorders remain an area of great controversy. Susceptibility to IDDM is currently being proposed as being inherited as a single autosomal dominant, as a single autosomal recessive, as recessive and some dominant forms, in an intermediate gene dosage model, in a heterogeneous three-allele or two HLA loci model, and as a two-locus disorder. The arguments for each of these proposals is presented, as well as the problems of each. We surmise that the weight of evidence supports the heterogeneity hypothesis but that the modes of inheritance of IDDM will be fully resolved only when we can more reliably identify the diabetogenic genotype, rather than being limited in our investigations to the study of only full-blown clinical disease.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa J., Chern M. M., Anderson V. E., Noreen H., Johnson S., Reinsmoen N., McCarty R., King R., Greenberg L. Linkage analysis between the major histocompatibility system and insulin-dependent diabetes in families with patients in two consecutive generations. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):592–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI109704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Chern M. M., Noreen H., Anderson V. E. Analysis of linkage between the major histocompatibility system and juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetes in multiplex families. Reanalysis of data. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):492–495. doi: 10.1172/JCI109151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Cohen R. A., Chavers B., Michael A. F., Steffes M., Hoogwerf B., Szalapski E., Mauer M. Muscle extracellular membrane immunofluorescence and HLA as possible markers of prediabetes. Lancet. 1980 Aug 16;2(8190):330–333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., King R., Noreen H., Yunis E. J. The histocompatibility system in juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetic multiplex kindreds. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):989–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI108879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta L., Simon S. Role of HLA-B8 and Bw15 antigens in diabetic children. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 17;296(7):397–397. doi: 10.1056/nejm197702172960715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrams J., Baur M. P., Grüneklee D., Gries F. A. Association of BfF1, HLA-B18 and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1979 Jul 14;2(8133):98–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrams J., Jansen F. K., Grüneklee D., Reis H. E., Drost H., Beyer J., Gries F. A., Kuwert E. HLA antigens and immunoresponsiveness to insulin in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Tissue Antigens. 1976 Jul;8(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1976.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G., Moul D. J., Doniach D., Festenstein H. Evidence for a primary autoimmune type of diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 4;2(6147):1253–1255. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6147.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Doniach D. [Pancreatic autoimmunity and HLA antigens]. Lancet. 1976 Oct 9;2(7989):800–800. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Mann J. I., Thorogood M., Baum J. D., Doniach D. Autoimmunity in juvenile diabetics and their families. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 15;2(6131):165–168. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6131.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr Current concepts of diabetic complications with emphasis on hereditary factors: a brief review. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;32:113–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathelineau G., Cathelineau L., Hors J., Schmid M., Dausset J. Les groupes HLA dans le diabète à début précoce. Nouv Presse Med. 1976 Feb 28;5(9):586–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy M., Green A., Christau B., Kromann H., Nerup J., Platz P., Thomsen M., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A. Studies of the HLA system and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):209–214. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Bonaïti-Pellié C. Epistasis effect: an alternative to the hypothesis of linkage disequilibrium in HLA associated diseases. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Oct;44(Pt 2):195–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Festenstein H. HLA genetic heterogeneity in diabetes mellitus. Br Med Bull. 1978 Sep;34(3):285–289. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G. Type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1978 May;14(5):281–291. doi: 10.1007/BF01223018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Evidence for HL-A-linked genes in "juvenile" diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 19;3(5976):133–135. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5976.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Genetic susceptibility in diabetes mellitus: analysis of the HLA association. Br Med J. 1976 Oct 9;2(6040):846–848. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6040.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnbol B., Green A. Diabetes mellitus among first- and second-degree relatives of early onset diabetics. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Jul;42(1):25–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps I., Lestradet H., Bonaïti C., Schmid M., Busson M., Benajam A., Marcelli-Barge A., Hors J. HLA genotype studies in juvenile insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetologia. 1980 Sep;19(3):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00275267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornan J., Allan P., Noel E. P., Larsen B., Farid N. R. Properdin factor B(Bf) allele BfF1 specifies an HLA-B18 diabetogenic haplotype. Diabetes. 1980 Jun;29(6):423–427. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.6.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Barnard J. M., Pepper B., Noel E. P., Kelly F., Davis A. J., Hobeika C., Marshall W. H. The association of HLA with juvenile diabetes mellitus in Newfoundland. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Sep;12(3):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Newton R. M., Noel E. P., Barnard J. M., Marshall W. H. The operation of immunological networks in Graves' disease. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Sep;12(3):205–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Sampson L., Noel P., Barnard J. M., Davis A. J., Hillman D. A. HLA-D--related (DRw) antigens in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1979 Jun;28(6):552–557. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.6.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Zavala C., Nielsen R. Thyroid autoimmunity: increased frequency in relatives of insulin-dependent diabetes patients. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Aug;83(2):170–176. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-2-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein S., Zeller E., Walford R. L. No relation between HL-A and juvenile diabetes. Tissue Antigens. 1972;2(1):74–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1972.tb00120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorwitz K., Howen G. G., Thompson T. Prevalence of diabetes in Michigan school-age children. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):122–127. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Root H. F. Diabetes mellitus in twins. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):693–704. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Rotter J. I. Two locus models for gluten sensitive enteropathy: population genetic considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1981;8(2):205–214. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Rotter J. I., Lange K. L. A three-allele model for heterogeneity of juvenile onset insulin-dependent diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 May;43(4):399–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Spence M. A. Some epistatic two-locus models of disease. II. The confounding of linkage and association. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 May;33(3):396–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilonen J., Herva E., Tiilikainen A., Akerblom H. K., Koivukangas T., Kouvalainen K. HLA-Dw2 as a marker of resistance against juvenile diabetes mellitus. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Feb;11(2):144–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J. Classification of idiopathic diabetes. Lancet. 1977 Mar 19;1(8012):638–642. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., McCallum C. J., Gray R. S., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Farquhar J. W., Vaughan H., Morris P. J. Pancreatic islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus correlated with the duration and type of diabetes, coexistent autoimmune disease, and HLA type. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):138–147. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Sawers J. S., Feek C. M., Prescott R. J., Duncan L. J. The value of islet cell antibody in predicting secondary failure of oral hypoglycaemic agent therapy in Diabetes mellitus. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Apr;2(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyllo C. J., Nuttall F. Q. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in school-age children in Minnesota. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):57–60. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendrum R., Walker G., Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C., Gamble D. R. HLA-linked genes and islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1976 Jun 26;1(6025):1565–1567. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6025.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsson J., Säfwenberg J., Heding L. G. HLA-types, C-peptide and insulin antibodies in juvenile diabetes. Diabetologia. 1977 Jan;13(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00996321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R. Ia-Type alloantigens and humoral autoimmune responsiveness in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1979 Aug;28(8):797–800. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R. Inselzellantikörper beim juvenilen Diabetes mellitus. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1977 Aug 26;102(34):1221–1224. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1105483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. The frequencies of juvenile diabetes in American Blacks and Caucasians are consistent with dominant inheritance. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):110–114. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A., McDevitt H. The association between the HLA system and disease. Prog Med Genet. 1977;2:39–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. J., Irvine W. J., Gray R. S., Duncan L. J., Vaughan H., McCallum F. J., Campbell C. J., Farquhar J. W. HLA and pancreatic islet cell antibodies in diabetes. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):652–653. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Mizuno N., Arima N., Wakisaka A., Okimoto K., Akazawa Y., Tsuji K., Fujita T. IgG heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and immune response to insulin in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):407–409. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Nishitani H., Takatsuki K., Kasukawa R., Nakayama S., Izumi S., Fujita T., Tsuji K. IgG heavy chain allotypes (Gm) in autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Oct;42(1):20–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A. HLA, islet cell antibodies, and types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):247–250. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld M. R., Maclaren N. K., Riley W. J. HLA in American blacks with juvenile diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):111–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld M., Maclaren N. K., Riley W. J., Lezotte D., McLaughlin J. V., Silverstein J., Rosenbloom A. L. Islet cell and other organ-specific antibodies in U.S. Caucasians and Blacks with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1980 Aug;29(8):589–592. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.8.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Drash A. L., Blizzard R. M., Sperling M., Childs B. Comparison of juvenile diabetics with positive and negative organ specific antibody titers. Evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Diabetes. 1973 Jan;22(1):63–65. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Mann D. L., Hague N. E., Heck J. A., van Leeuwen H. A., van Rood J. J., Strober W. Genetic basis of gluten-sentitive enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke D. A. Diabetes: the genetic connections. Diabetologia. 1979 Dec;17(6):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01236266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Alper C. A., Stein R., Gabbay K. H. Genetic marker for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1208–1210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91895-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richens E. R., Quilley J., Hartog M. Immunological features of juvenile onset diabetic patients correlated to HLA type. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 May;36(2):198–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Neufeld M. Adrenal autoantibodies and Addison disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L. Genetics of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1967 May;16(5):346–351. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.5.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Hodge S. E. Racial differences in juvenile-type diabetes are consistent with more than one mode of inheritance. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):115–118. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Rimoin D. L. Diabetes mellitus: the search for genetic markers. Diabetes Care. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):215–226. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Rimoin D. L. Heterogeneity in diabetes mellitus--update, 1978. Evidence for further genetic heterogeneity within juvenile-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):599–605. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Ginsberg-Fellner F., Falk C. Genetics of Type I diabetes mellitus: a single, recessive predisposition gene mapping between HLA-B and GLO. With an appendix on the estimation of selection bias. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Nov;33(6):865–882. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Suciu-Foca N., Nicholson J. F. Genetics of juvenile diabetes mellitus. A recessive gene closely linked to HLA D and with 50 per cent penetrance. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 10;297(19):1036–1040. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711102971905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schernthaner G., Ludwig H., Mayr W. R. Immunoglobulin G-insulin antibodies and immune region-associated alloantigens in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):403–407. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schernthaner G., Ludwig H., Mayr W. R., Willvonseder R. Letter: Genetic factors on insulin antibodies in juvenile-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 9;295(11):622–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609092951115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. I., Jr, Rabin B. S., Huellmantel A., Van Thiel D. H., Drash A. Immunopathology of juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. I. IgA deficiency and juvenile diabetes. Diabetes. 1978 Nov;27(11):1092–1097. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.11.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solow H., Hidalgo R., Singal D. P. Juvenile-onset diabetes HLA-A, -B, -C, and -DR alloantigens. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman R. S., Baker L., Zmijewski C. M. Gene dosage and suceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Oct;44(Pt 2):135–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B. K., Hodge S. E. A simple method to detect linkage for rare recessive diseases: an application to juvenile diabetes. Clin Genet. 1979 Feb;15(2):126–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb01751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B., Hodge S. E., Reich T. Is juvenile diabetes determined by a single gene closely linked to HLA? Diabetes. 1979 Jun;28(6):527–532. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.6.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M. HL-A and disease associations--a survey. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:3–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. A two locus model for juvenile diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 May;43(4):383–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


