Abstract
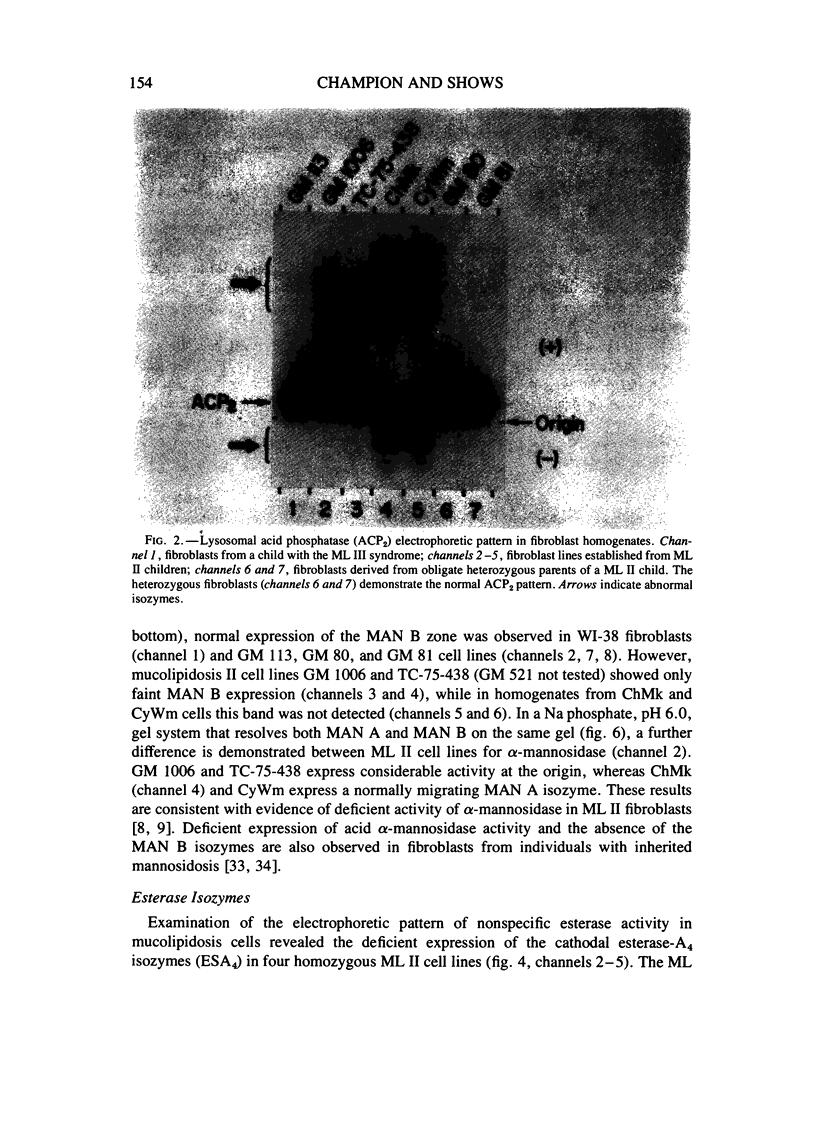
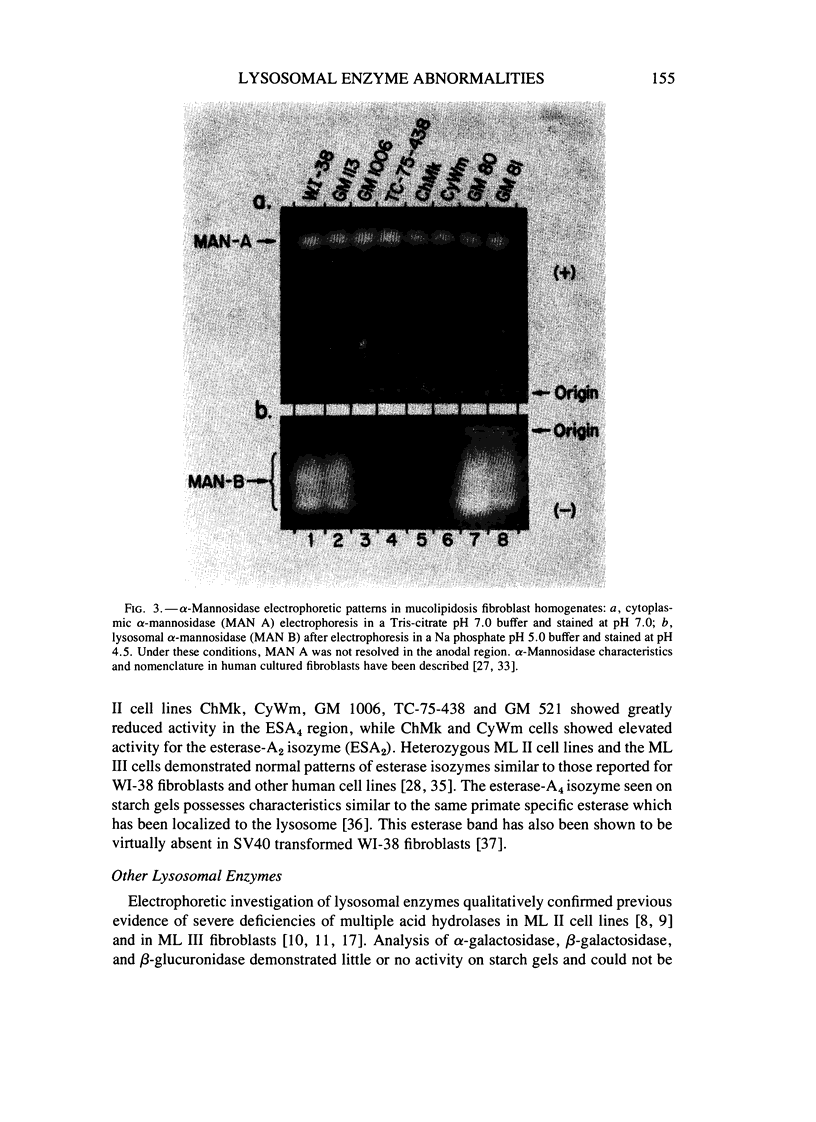
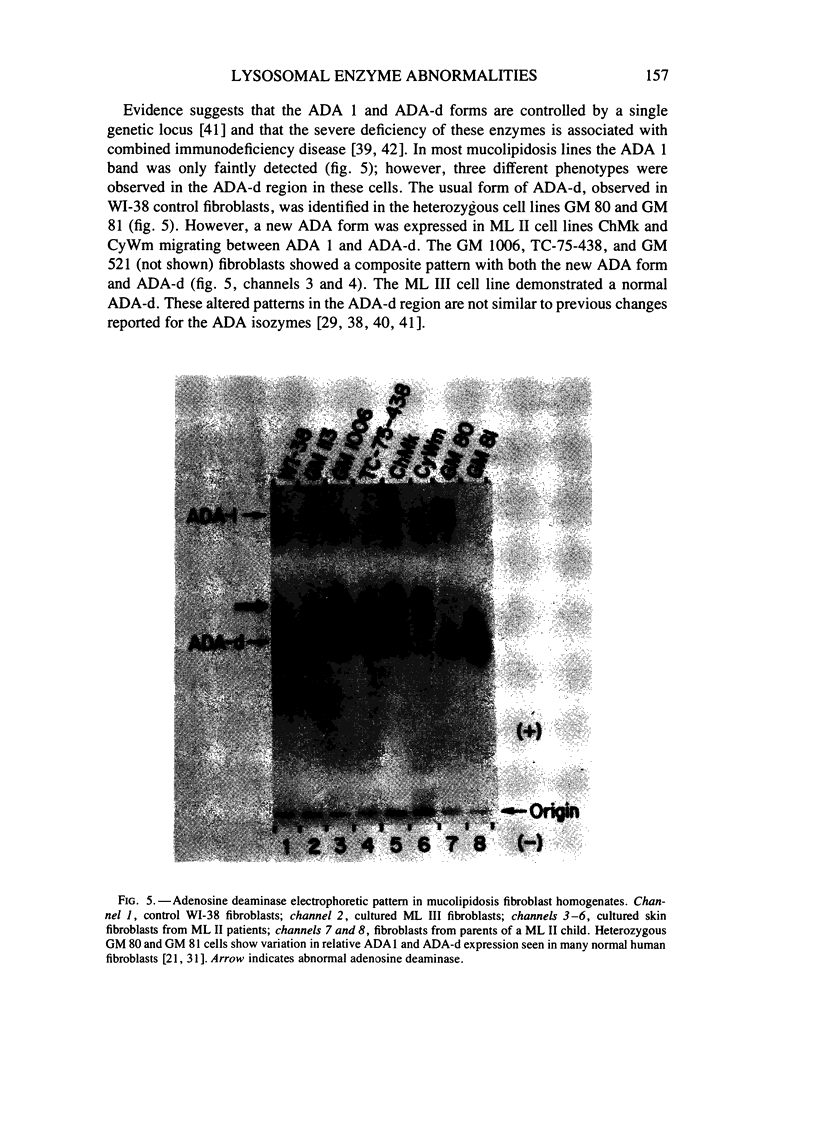
Electrophoretic properties of eight lysosomal hydrolases and 36 nonlysosomal enzymes were investigated in cultured fibroblasts from children with the inherited storage disease mucolipidosis II (ML II); fibroblasts from a child with a related disorder, mucolipidosis III (ML III); and two obligate heterozygous cell lines from parents of a ML II child. Cell homogenates of ML II fibroblast lines showed altered mobilities for lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase, acid phosphatase2, and alpha-mannosidase and deficient activity for the esterase-A4 and lysosomal alpha-mannosidase-B electrophoretic phenotypes. Altered mobility was also detected for the nonlysosomal enzyme adenosine deaminase-d. Deficient activities of other lysosomal enzymes were observed as previously reported. In a single ML III fibroblast line, only beta-hexosaminidase showed an abnormal electrophoretic pattern suggesting a difference between these cells and ML II fibroblasts. Thirty-five nonlysosomal enzymes associated with other cellular organelles and metabolic pathways were electrophoretically normal in all mucolipidosis cell lines. Heterozygous ML II cells showed normal expression for all enzymes. Two major patterns of altered lysosomal enzymes and adenosine deaminase were demonstrated in ML II cell lines, suggesting that at least two genetic forms of this disorder may exist. Neuraminidase treatment of ML II homogenates converted altered forms of acid phosphatase2 and adenosine deaminase-d and in two ML II lines, recovered the previously undetected lysosomal alpha-mannosidase band. These results are consistent with the mucolipidosis defect(s) being associated with abnormal post-translatinal processing of multiple lysosomal enzymes and adenosine deaminase-d.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew E. M., Bartholomew W. R., Rose N. R. Isoenzyme differences between a human diploid cell line, WI-38, and SV40-transformed WI-38. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):787–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman E. R., Kohn G., Yatziv S., Stein H. Acid hydrolase deficiencies and abnormal glycoproteins in mucolipidosis. 3 (pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy). Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Mar;52(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Dance N., Masson P. K., Robinson D., Winchester B. G. Human mannosidosis--the enzyme defect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Scott C. R., Swedberg D. R. Heterogeneity for adenosine deaminase deficiency: Expression of the enzyme in cultured skin fibroblasts and amniotic fluid cells. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):46–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Tandt W. R., Lassila E., Philippart M. Leroy's l-cell disease: markedly increased activity of plasma acid hydrolases. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Mar;83(3):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y. H., Hopkinson D. A., Harris H. Adenosine deaminase isozymes in human tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Oct;35(2):207–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert E. F., Dawson G., zu Rhein G. M., Opitz J. M., Spranger I-cell disease, mucolipidosis II. Pathological, histochemical, ultrastructural and biochemical observations in four cases. Z Kinderheilkd. 1973;114(4):259–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., McAlister W. H., Sly W. S. Genetic heterogeneity in multiple lysosomal hydrolase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1974 Aug;85(2):192–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstone A., Konecny P., Koenig H. Lysosomal hydrolases: Conversion of acidic to basic forms by neuraminidase. FEBS Lett. 1971 Feb 12;13(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Levytaka V., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Evidence for control of several different tissue-specific isozymes of adenosine deaminase by a single genetic locus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):200–202. doi: 10.1038/newbio246200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. E. The mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976 Jan-Feb;(114):116–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. E., Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Jr, McKusick V. A., Sly W. S., Glaser J. H., Robinow M., Luzzatti L., Espiritu C., Feingold M. Mucolipidosis III (pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy): Clinical and laboratory studies in a series of 12 patients. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1975 Oct;137(4):156–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Rattazzi M. C., Shows T. B. Human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B: expression and linkage relationships in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1569–1573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Ho M. W., MacBrinn M. C., Zielke K., Jacob J., O'Brien J. S. I-cell disease: biochemical studies. Pediatr Res. 1972 Oct;6(10):752–757. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197210000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Spranger J. W., Feingold M., Opitz J. M., Crocker A. C. I-cell disease: a clinical picture. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):360–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie K. K., Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Sensenbrenner J. A. Analysis of N-acetyl- -D-glucosaminidase in mucolipidosis II (I-cell disease). Clin Chim Acta. 1973 May 18;45(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melhem R., Dorst J. P., Scott C. I., Jr, McKusick V. A. Roentgen findings in mucolipidosis III (Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy). Radiology. 1973 Jan;106(1):153–160. doi: 10.1148/106.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Lim T. W., Shapiro L. J. Inherited disorders of lysosomal metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:357–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F. The biochemical basis for mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses. Prog Med Genet. 1974;10:81–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara H., Ishikawa S., Shinkai K., Akedo H. Multiple forms of human adenosine deaminase. II. Isolation and properties of a conversion factor from human lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):429–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenaru L., Dreyfus J. C. Electrophoretic heterogeneity of human -mannosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 23;303(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattazzi M. C., Brown J. A., Davidson R. G., Shows T. B. Studies on complementation of beta hexosaminidase deficiency in human GM2 gangliosidosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Mar;28(2):143–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaws T. B., Lalley P. A. Control of lysosomal acid phosphatase expression in man-mouse cell hybrids. Biochem Genet. 1974 Feb;11(2):121–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00485769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A. Human X-Linked genes regionally mapped utilizing X-autosome translocations and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2125–2129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A. Mapping chromosomes 1 and 2 employing a 1/2 translocation in somatic cell hybrids. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(3):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B. Genetics of human-mouse somatic cell hybrids: linkage of human genes for lactate dehydrogenase-A and esterase-A 4 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Lagwinska E., Schlesinger S. Enveloped virus acquires membrane defect when passaged in fibroblasts from I-cell disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Harris H. A new variant of the placental acid phosphatases: its implications regarding their subunit structures and genetical determination. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Nov;36(2):141–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1972.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. A., Thomas G. H., Aylsworth A., Stevenson R. E., Reynolds L. W. Mannosidosis: deficiency of a specific alpha-mannosidase component in cultured fibroblasts. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Feb 22;59(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Reynolds L. W., Miller C. S. Mucolipidosis 3 (Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy): multiple lysosomal enzyme abnormalities in serum and cultured fibroblast cells. Pediatr Res. 1973 Sep;7(9):751–756. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197309000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Tiller G. E., Jr, Reynolds L. W., Miller C. S., Bace J. W. Increased levels of sialic acid associated with a sialidase deficiency in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II) fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):188–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Beratis N. G., Turner V. S., Hirschhorn K. Isozymes of human alpha-L-fucosidase detectable by starch gel electrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Nov 20;57(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rattazzi M. C. Abnormal lysosomal hydrolases excreted by cultured fibroblasts in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):956–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90768-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rose N. R. Intracellular distribution of a primate-specific esterase in cultured cells and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):560–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann U. N., Herschkowitz N. N. Studies on the pathogenetic mechanism of I-cell disease in cultured fibroblasts. Pediatr Res. 1974 Nov;8(11):865–869. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197411000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









