Abstract
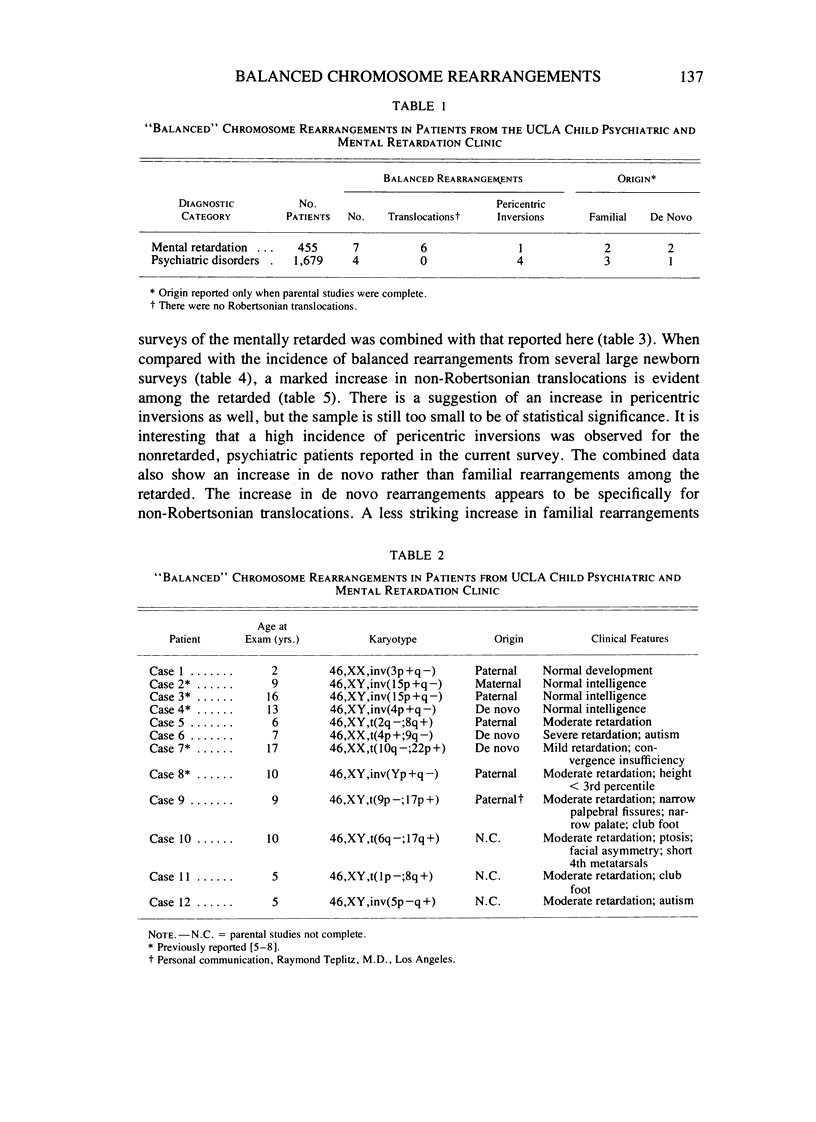
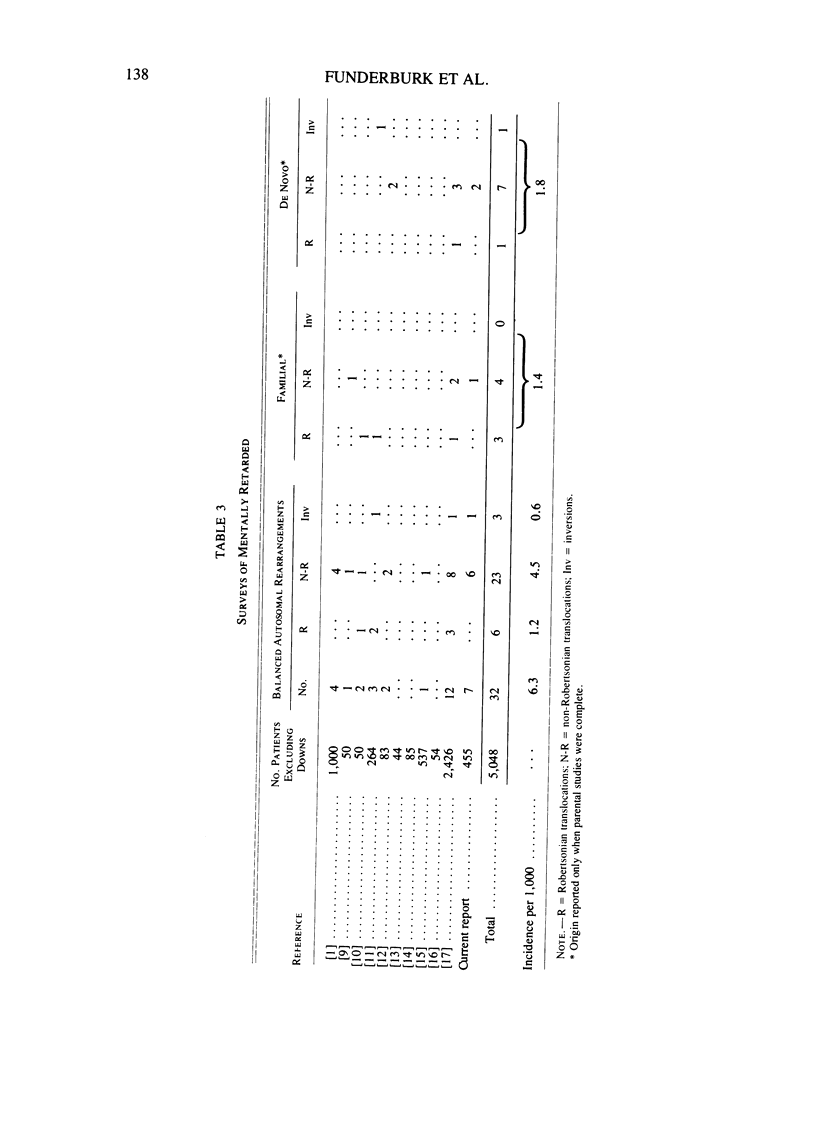
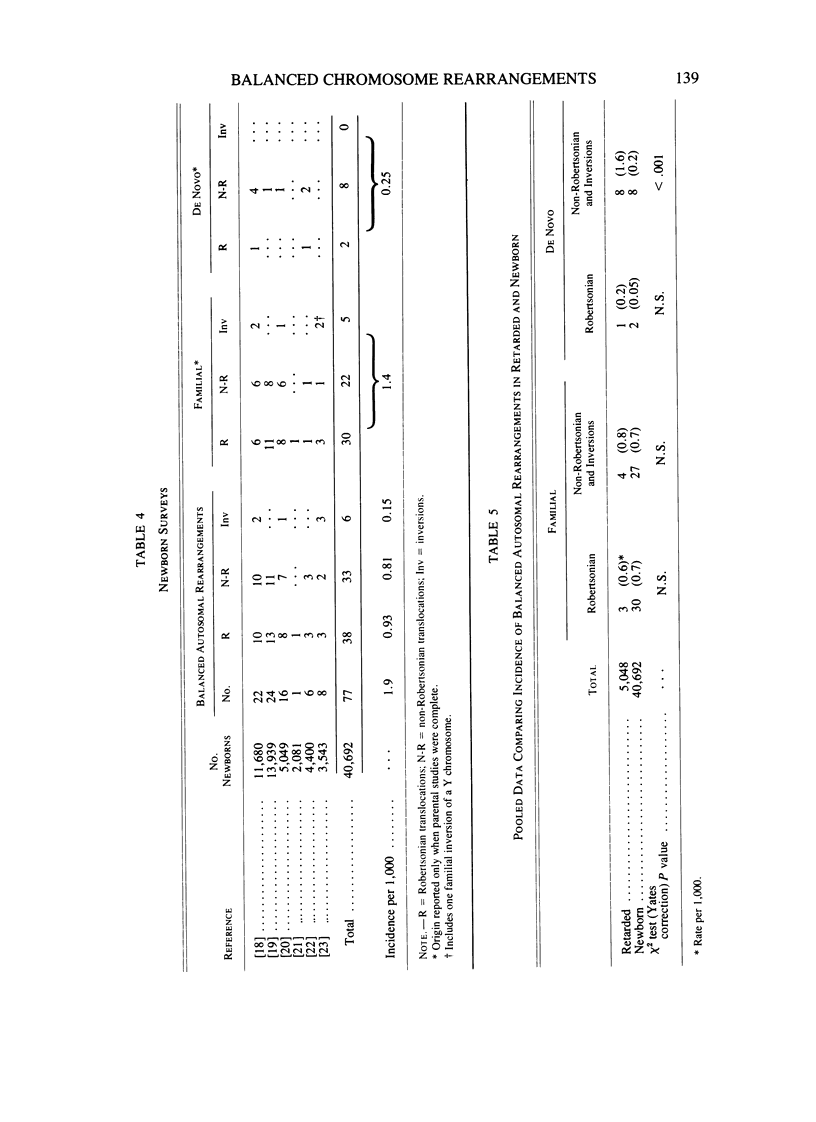
Balanced chromosome rearrangements were found in seven of 455 retarded children vs. four of 1,679 nonretarded, psychiatric children (P less than .05). The combined incidence of non-Robertsonian balanced rearrangements from this and reported surveys of the mentally retarded was five times greater than that from newborn surveys, whereas Robertsonian translocations were not increased among the retarded. The combined data show an increase in de novo rather than familial rearrangements among the retarded; the increase in de novo rearrangements is specifically for non-Robertsonian translocation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askrog V., Harvald B. Teratogen effekt af inhalationsanaestetika. Nord Med. 1970 Apr 16;83(16):498–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg W. R., Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W., Miller O. J. Identification of translocation chromosomes by quinacrine fluorescence. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jun;123(6):561–564. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110120085007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Modest E. J. Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00282002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. T., Sergovich F. R., McKim J. S., Barr M. L., Gruber D. Chromosome studies in full-term, low-birth-weight, mentally retarded patients. J Pediatr. 1970 Mar;76(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80478-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Carrel R. E., Adams G. L., Sparkes R. S. Cytogenetic studies in a patient with a de novo t(Cq-;Gp+). J Med Genet. 1970 Dec;7(4):413–416. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Carrel R. E., Sparkes R. S. Chromosome findings in 700 children referred to a psychiatric clinic. J Pediatr. 1972 Jan;80(1):62–68. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80454-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Sparkes R. S. Pericentric inversion of a number 15 chromosome in nine members of one family. Cytogenetics. 1970;9(4):307–316. doi: 10.1159/000130100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly R. F. Chromosome aberrations in 50 patients with idiopathic mental retardation and in 50 control subjects. Madison blind study 3. J Pediatr. 1970 Sep;77(3):444–453. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Quinacrine mustard fluorescence of human chromosomes: characterization of unusual translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;24(2):189–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Nielsen J. Chromosome studies in 5,049 consecutive newborn children. Clin Genet. 1973;4(4):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerton J. L., Canning N., Ray M., Smith S. A cytogenetic survey of 14,069 newborn infants. I. Incidence of chromosome abnormalities. Clin Genet. 1975 Oct;8(4):223–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iivanainen M., Gripenberg U. Clinico-neurological findings in connection of three chromosomal aberrations: an extra chromosome in group E, a D-C translocation and an unusually long B group chromosome. Acta Neurol Scand. 1967;43(Suppl):53–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1967.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Buckton K. E., Cunningham C., Newton M. An analysis of the break points of structural rearrangements in man. J Med Genet. 1974 Mar;11(1):50–64. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A. Correlation between euploid structural chromosome rearrangements and mental subnormality in humans. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):164–165. doi: 10.1038/249164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Melville M., Ratcliffe S., Keay A. J., Syme J. A cytogenetic survey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 May;37(4):359–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergovich F., Valentine G. H., Chen A. T., Kinch R. A., Smout M. S. Chromosome aberrations in 2159 consecutive newborn babies. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 17;280(16):851–855. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904172801602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summitt R. L. Cytogenetics in mentally defective children with anomalies: a controlled study. J Pediatr. 1969 Jan;74(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn M. J., Martin P. A. Chromosome studies in 101 mentally handicapped Jamaican children. J Med Genet. 1971 Mar;8(1):59–64. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



