Abstract
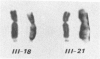
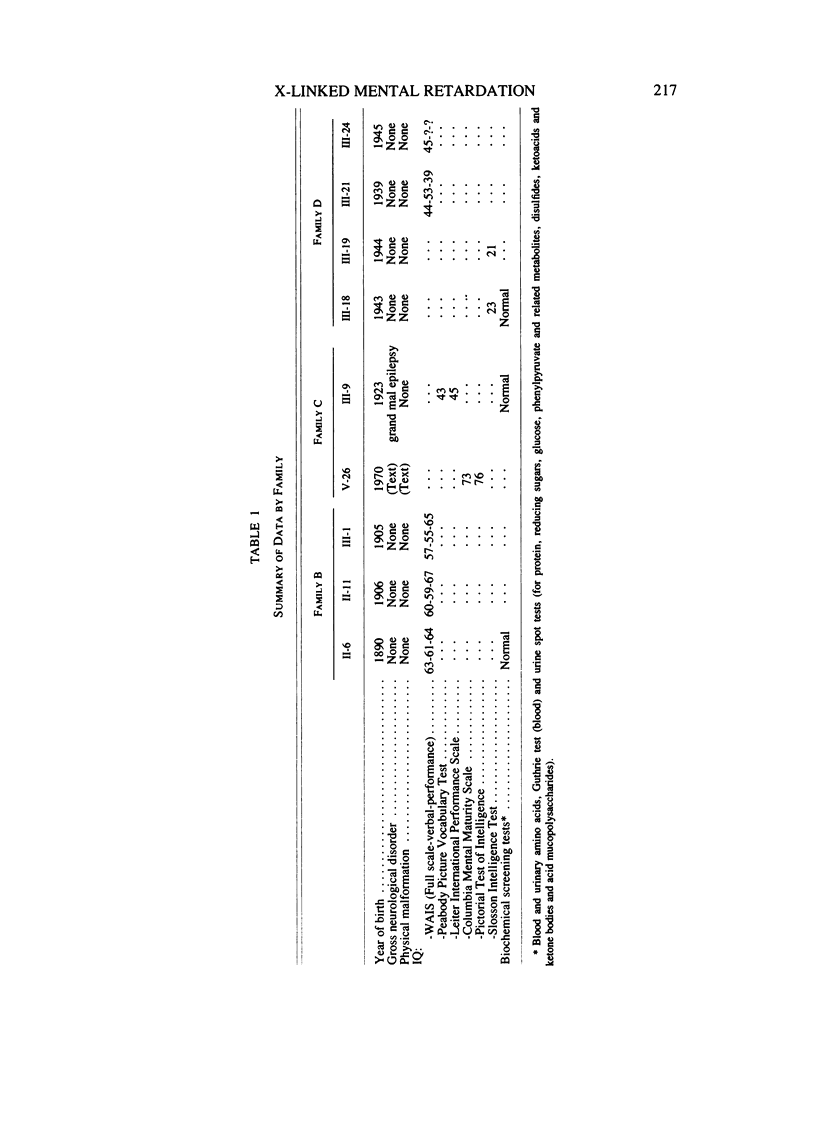
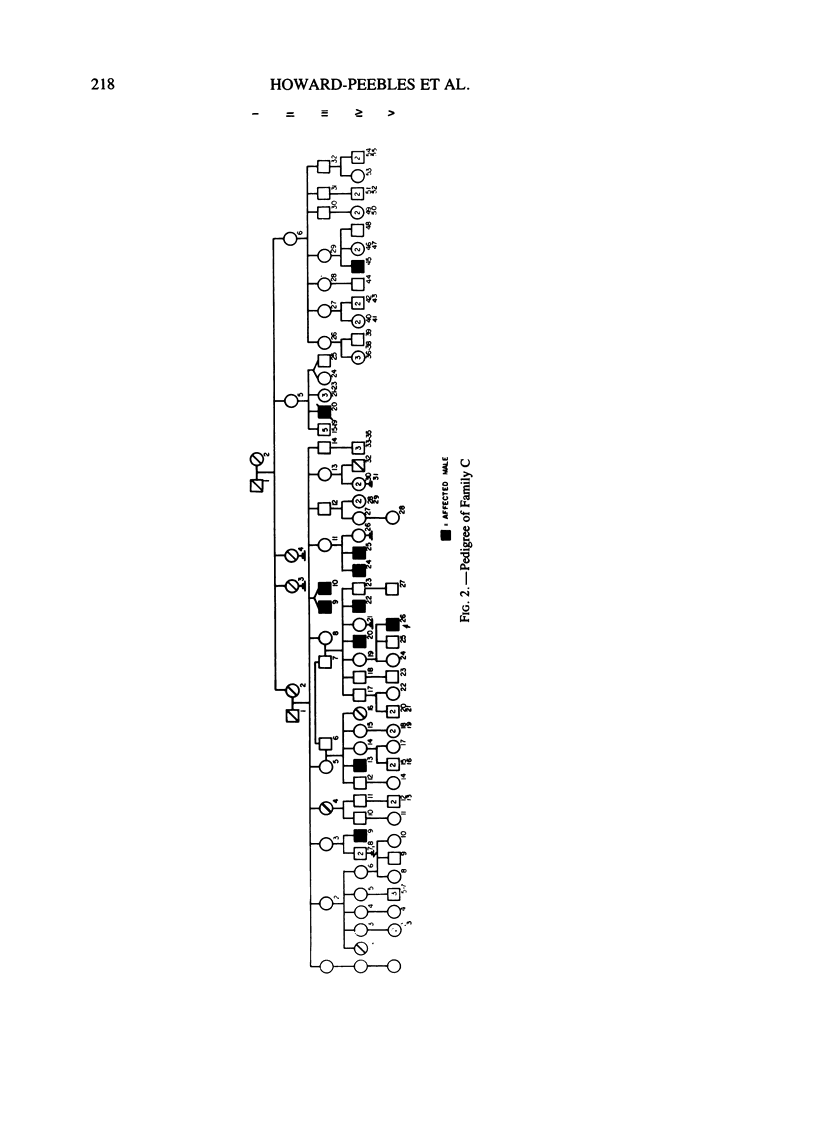
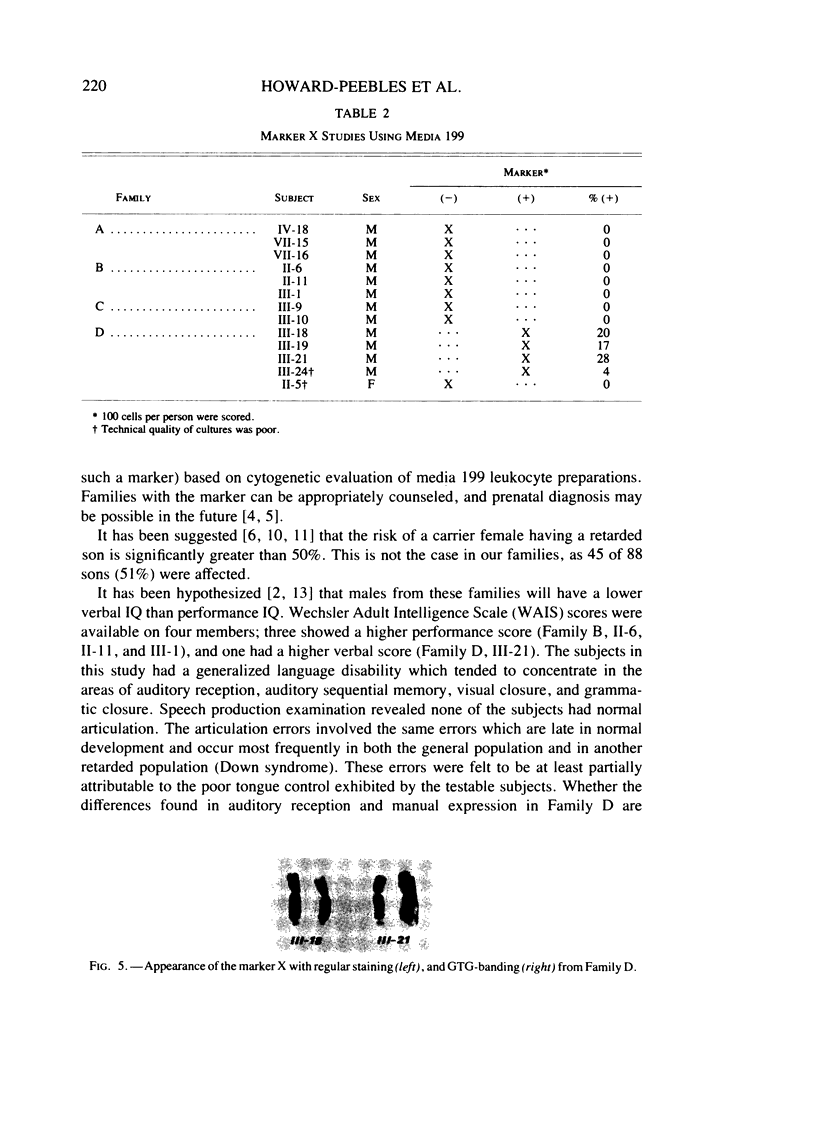
Cytogenetic and verbal studies were done on members of four families with non-specific X-linked mental retardation. Cytogenetic analysis was done using media 199 and GTG-banding; one family had a marker X with a fragile site in band Xq27 or 28. Preliminary results indicate variation of culture conditions can effect the frequency of the marker X. A generalized language disability was found which tended to concentrate in the areas of auditory reception, auditory sequential memory, visual closure and grammatic closure. Articulation errors involved the same sounds which are late in normal development and occur most frequently in both the general population and a Down syndrome population.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deroover J., Fryns J. P., Parloir C., Van den Berghe H. X-linked recessively inherited non-specific mental retardation. Report of a large family. Ann Genet. 1977 Dec;20(4):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraud F., Ayme S., Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G. Constitutional chromosomal breakage. Hum Genet. 1976 Oct 28;34(2):125–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00278880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Judge C., Wiener S. Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENPENNING H., GERRARD J. W., ZALESKI W. A., TABATA T. Familial sex-linked mental retardation. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Nov 3;87:954–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. D., Robinson A. Recessive sex-linked mental retardation in the absence of other recognizable abnormalities. Report of a family. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1969 Nov;8(11):669–674. doi: 10.1177/000992286900801114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Fragile sites on human chromosomes: demonstration of their dependence on the type of tissue culture medium. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):265–266. doi: 10.1126/science.877551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Marker X chromosomes and mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 16;296(24):1415–1415. doi: 10.1056/nejm197706162962423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Till R., Daniel A. Marker X chromosomes, mental retardation and macro-orchidism. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1472–1472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough K. M., Howard-Peebles P. N. X-linked nonspecific mental retardation. Report of a large kindred. Clin Genet. 1976 Feb;9(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]