Abstract
Huntington disease is a classic example of an autosomal dominant trait. Over the years, however, a number of investigators have reported anomalies regarding the age of onset of the disease that are inconsistent with this paradigm. We propose two models in which a maternal factor--cytoplasmic in one case, autosomal or X-linked in the other--acts to delay onset in a manner consistent with the previously reported anomalies. Relevant data from the Huntington's Disease Research Roster are presented that reinforce and extend the previous observations.
Full text
PDF






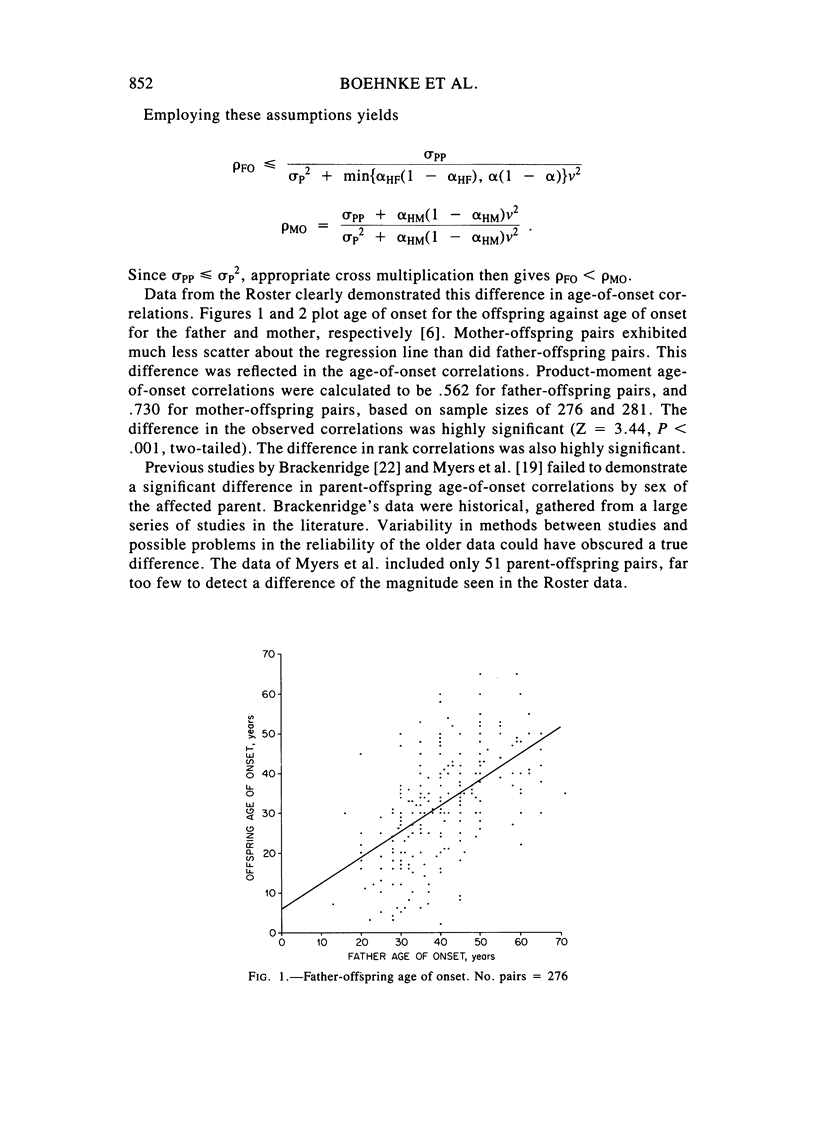
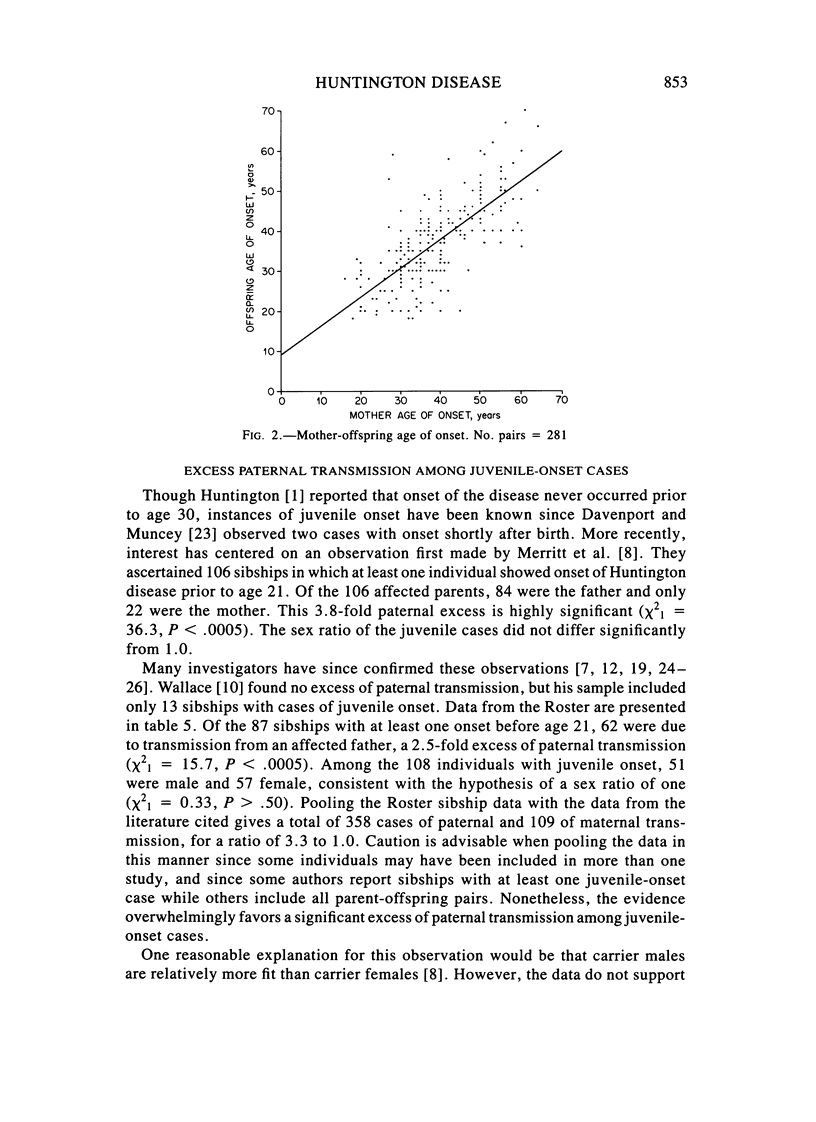







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbeau A. Parental ascent in the juvenile form of Huntington's chorea. Lancet. 1970 Oct 31;2(7679):937–937. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird E. D., Caro A. J., Pilling J. B. A sex related factor in the inheritance of Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):255–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenridge C. J. A genetic and statistical study of some sex-related factors in Huntington's disease. Clin Genet. 1971;2(5):267–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1971.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenridge C. J. A statistical study of half-sibships born to parents affected with Huntington's disease. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):17–22. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenridge C. J. Familial correlations for age at onset and age at death in Huntington's disease. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):23–32. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden M. R., Beighton P. Genetic aspects of Huntington's chorea: results of a national survey. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Feb;11(2):135–141. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst A. L., Ulfelder H., Poskanzer D. C. Adenocarcinoma of the vagina. Association of maternal stilbestrol therapy with tumor appearance in young women. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104222841604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. B., Phillips C. R. Affected parent and age of onset in Huntington's chorea. J Med Genet. 1970 Mar;7(1):20–21. doi: 10.1136/jmg.7.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Gladstien K. Further characterization of the long-run population distribution of a deleterious gene. Theor Popul Biol. 1980 Aug;18(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(80)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. H., Madden J. J., Teague J. L., Falek A. Factors related to onset age of Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):481–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe R. G., Walker D. A., Harper P. S. Factors influencing age at onset and duration of survival in Huntington's chorea. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Oct;45(Pt 4):387–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED T. E., NEEL J. V. Huntington's chorea in Michigan. 2. Selection and mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 1):107–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN C., WALLS G. L. The Cunier pedigree of color blindness. Am J Hum Genet. 1957 Dec;9(4):249–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Hall A. C. Evidence of genetic heterogeneity in Huntington's chorea. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Dec;35(6):789–800. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.6.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. The social effect of Huntington's chorea on reproductive effectiveness. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 Jan;39(3):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


