Abstract
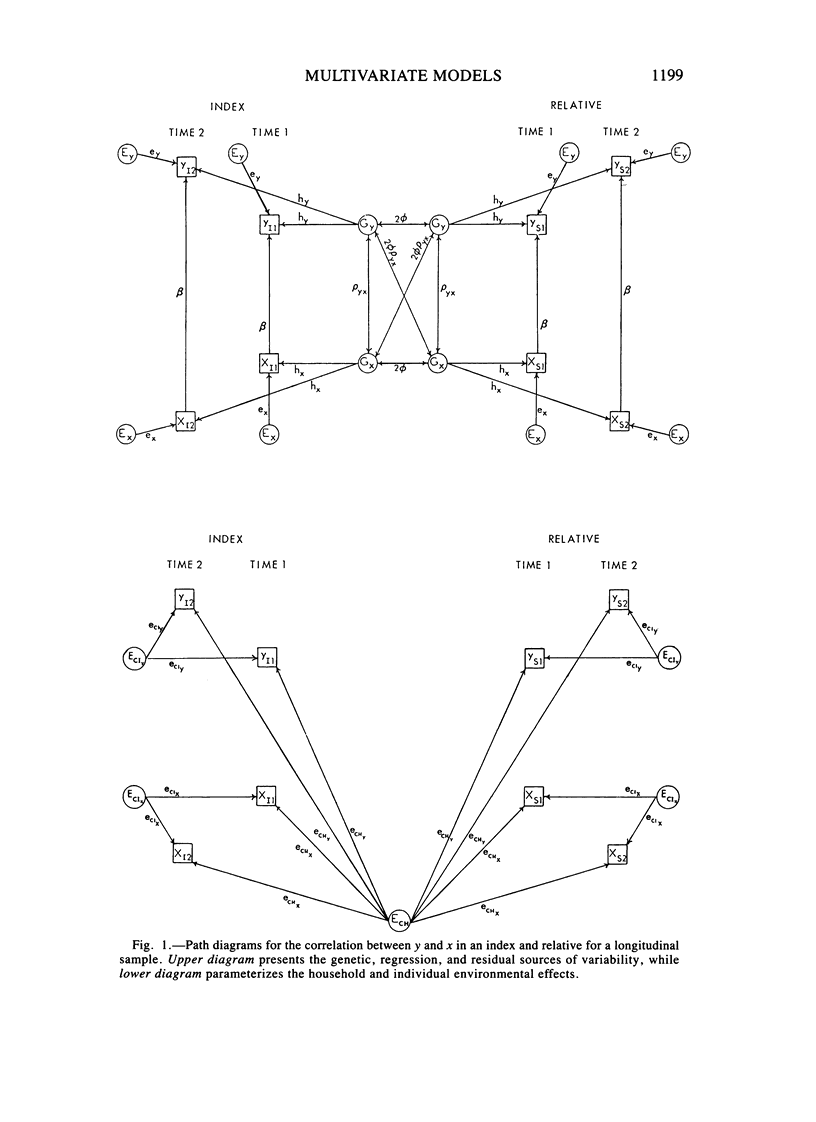
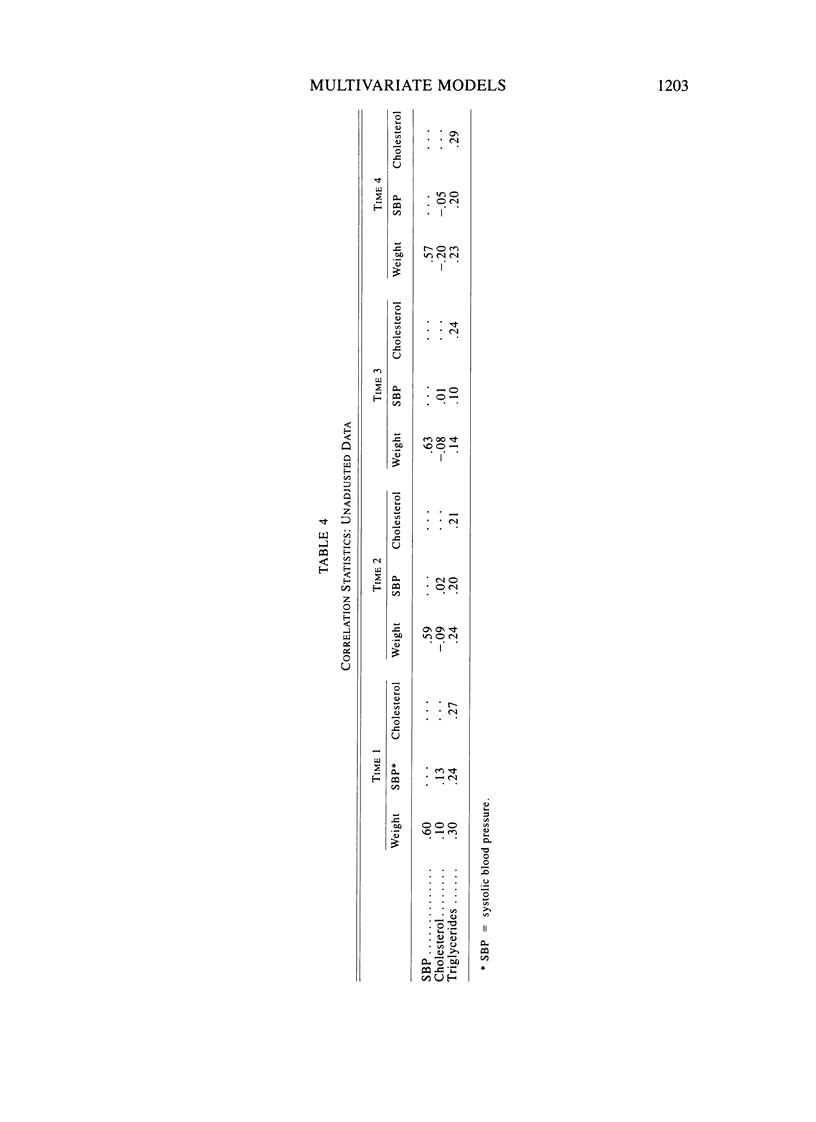
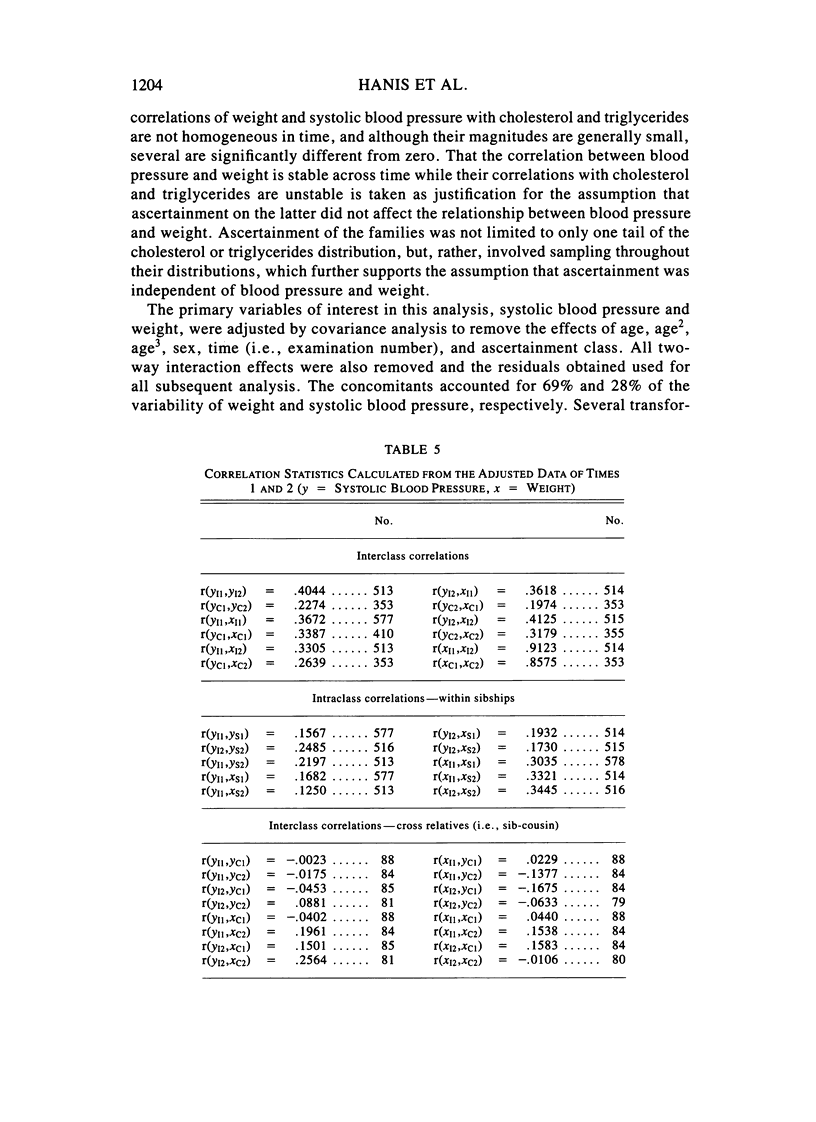
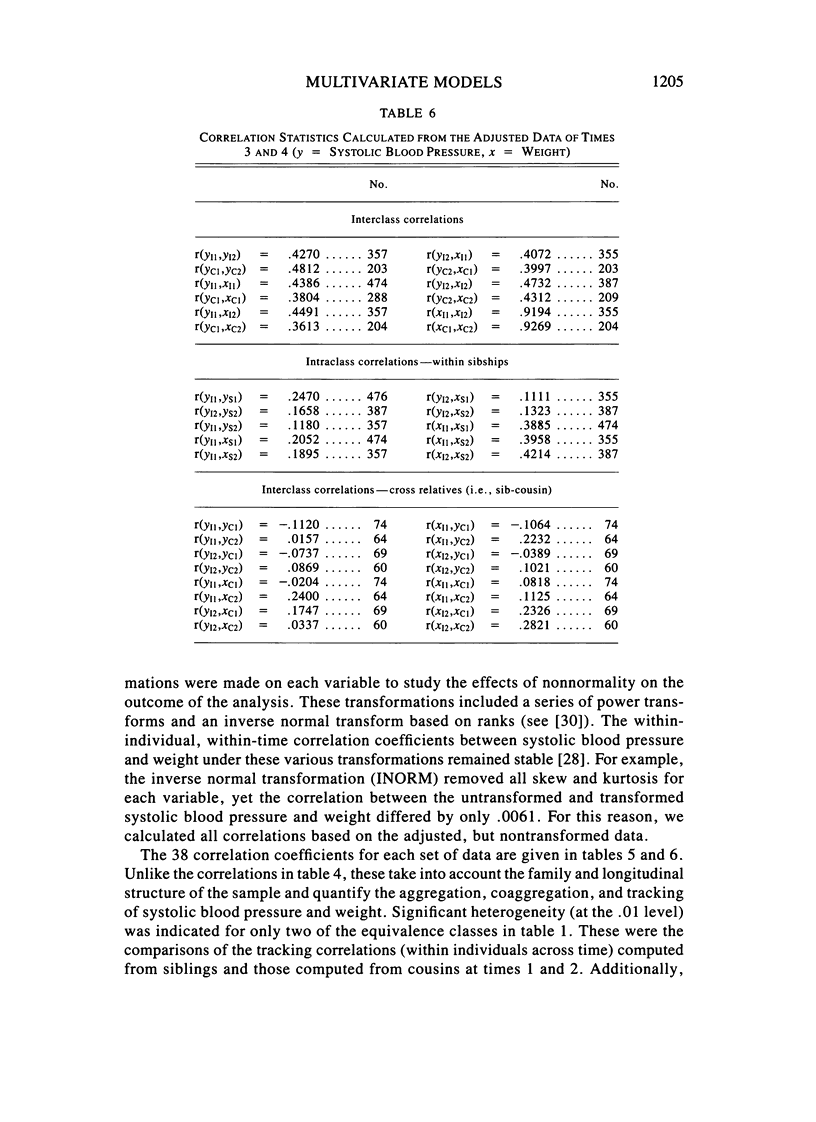
A multivariate path model parameterizing the sources of familial aggregation and coaggregation of systolic blood pressure and weight, as well as their tracking across time, is applied to longitudinal data collected in Muscatine, Iowa. Genetic, common household, and individual environmental effects, pleiotropy, and a direct regression effect of blood pressure on weight are parameterized. The sample consisted of 998 individuals distributed in 261 families of whom 601 were measured on four successive occasions. The data were divided with times 1 and 2 forming group 1, and times 3 and 4, group 2. Model fitting and estimation was performed using group 1, followed by testing the model and estimates using the data in group 2. Heritability estimates for systolic blood pressure and weight were .15 and .54, respectively. The genetic correlation between these traits was nonsignificant, but there was a significant direct regression effect. The results indicate that 30% of the full-sib correlation for systolic blood pressure is attributable to the aggregation of weight. In terms of tracking, 59% and 60% of the predicted systolic blood pressure and weight correlations, respectively, were attributable to genetic effects. Testing the model from group 1 in group 2 indicates that the qualitative relationships between blood pressure and weight are stable with time.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annest J. L., Sing C. F., Biron P., Mongeau J. G. Familial aggregation of blood pressure and weight in adoptive families. I. Comparisons of blood pressure and weight statistics among families with adopted, natural, or both natural and adopted children. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Oct;110(4):479–491. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annest J. L., Sing C. F., Biron P., Mongeau J. G. Familial aggregation of blood pressure and weight in adoptive families. II. Estimation of the relative contributions of genetic and common environmental factors to blood pressure correlations between family members. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Oct;110(4):492–503. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annest J. L., Sing C. F., Biron P., Mongeau J. G. Familial aggregation of blood pressure and weight in adoptive families. III. Analysis of the role of shared genes and shared household environment in explaining family resemblance for height, weight and selected weight/height indices. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Apr;117(4):492–506. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron P., Mongeau J. G., Bertrand D. Familial resemblance of body weight and weight/height in 374 homes with adopted children. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang B. N., Perlman L. V., Epstein F. H. Overweight and hypertension. A review. Circulation. 1969 Mar;39(3):403–421. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.39.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke W. R., Schrott H. G., Leaverton P. E., Connor W. E., Lauer R. M. Tracking of blood lipids and blood pressures in school age children: the Muscatine study. Circulation. 1978 Oct;58(4):626–634. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M., Keller J., Moore F., Ostrander L., Metzner H., Stock L. Studies of blood pressure in Tecumseh, Michigan. I. Blood pressure in young people and its relationship to personal and familial characteristics and complications of pregnancy in mothers. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Feb;111(2):142–155. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON B. C., EPSTEIN F. H., KJELSBERG M. O. DISTRIBUTIONS AND FAMILIAL STUDIES OF BLOOD PRESSURE AND SERUM CHOLESTEROL LEVELS IN A TOTAL COMMUNITY--TECUMSEH, MICHIGAN. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Feb;18:147–160. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotchen J. M. Effect of relative weight on familial blood pressure aggregations. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Mar;105(3):214–222. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger H., Morton N. E., Rao D. C., Azevêdo E. Familial determinants of blood pressure in northeastern Brazil. Hum Genet. 1980;53(3):415–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00287065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Boehnke M. Extensions to pedigree analysis. IV. Covariance components models for multivariate traits. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Mar;14(3):513–524. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer R. M., Connor W. E., Leaverton P. E., Reiter M. A., Clarke W. R. Coronary heart disease risk factors in school children: the Muscatine study. J Pediatr. 1975 May;86(5):697–706. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll P. P., Sing C. F., Brewer G. J., Gilroy T. E. Multivariate analysis of the genetic effects on red blood cell glycolysis. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1978;21:385–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Gulbrandsen C. L., Rao D. C., Rhoads G. G., Kagan A. Determinants of blood pressure in Japanese-American Families. Hum Genet. 1980 Feb;53(2):261–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00273508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plomin R., DeFries J. C. Multivariate behavioral genetic analysis of twin data on scholastic abilities. Behav Genet. 1979 Nov;9(6):505–517. doi: 10.1007/BF01067347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. C., MacLean C. J., Morton N. E., Yee S. Analysis of family resemblance. V. Height and weight in northeastern Brazil. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;27(4):509–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. J., Miller J. Z., Grim C. E., Christian J. C. Aggregation of blood pressure in the families of identical twins. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 May;109(5):503–511. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrott H. G., Bucher K. A., Clarke W. R., Lauer R. M. The Muscatine hyperlipidemia family study program. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;32:619–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voors A. W., Webber L. S., Frerichs R. R., Berenson G. S. Body height and body mass as determinants of basal blood pressure in children--The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Aug;106(2):101–108. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Levy P. S., Kass E. H. Familial aggregation of blood pressure in childhood. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 25;284(8):401–404. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102252840801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


