Abstract
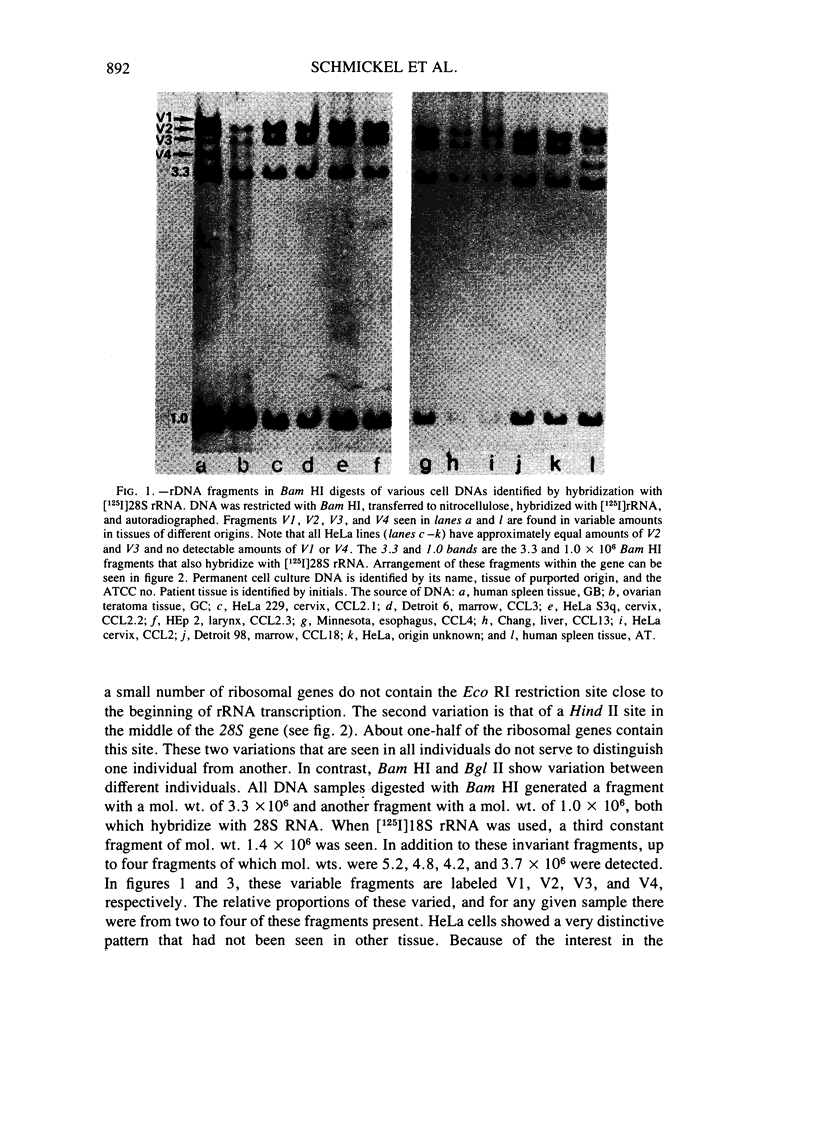
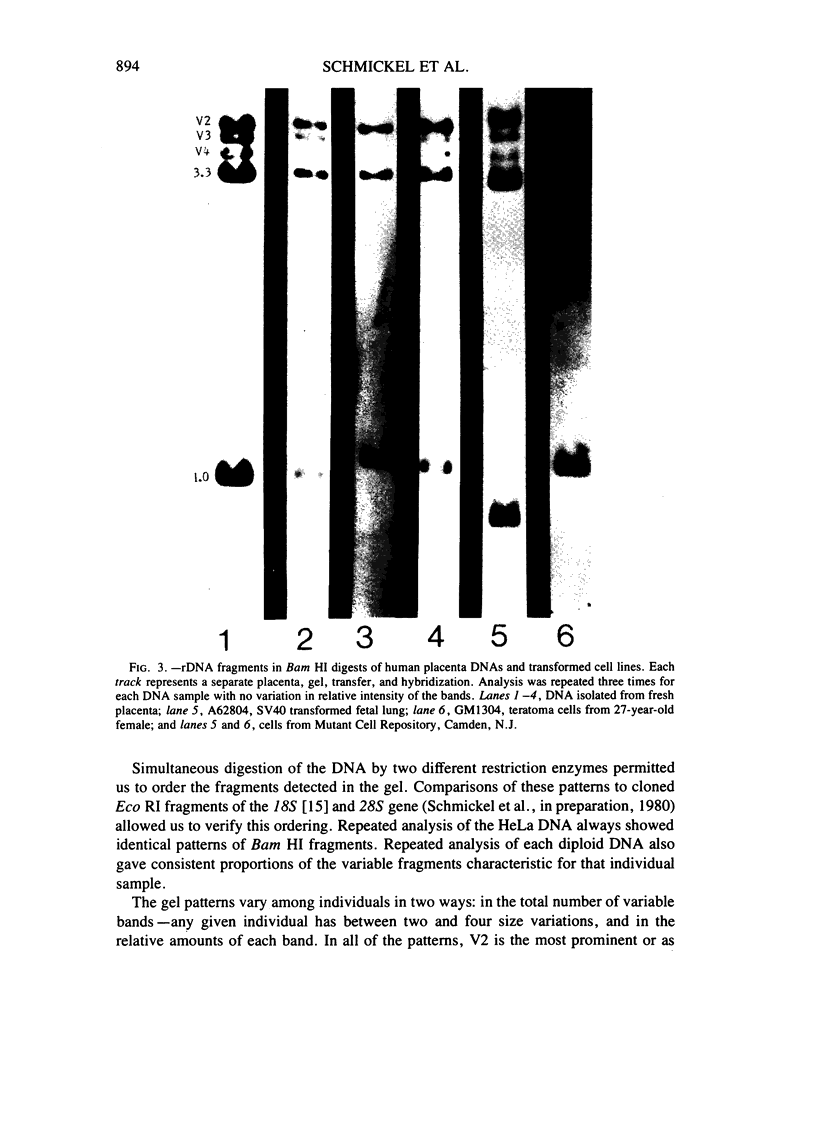
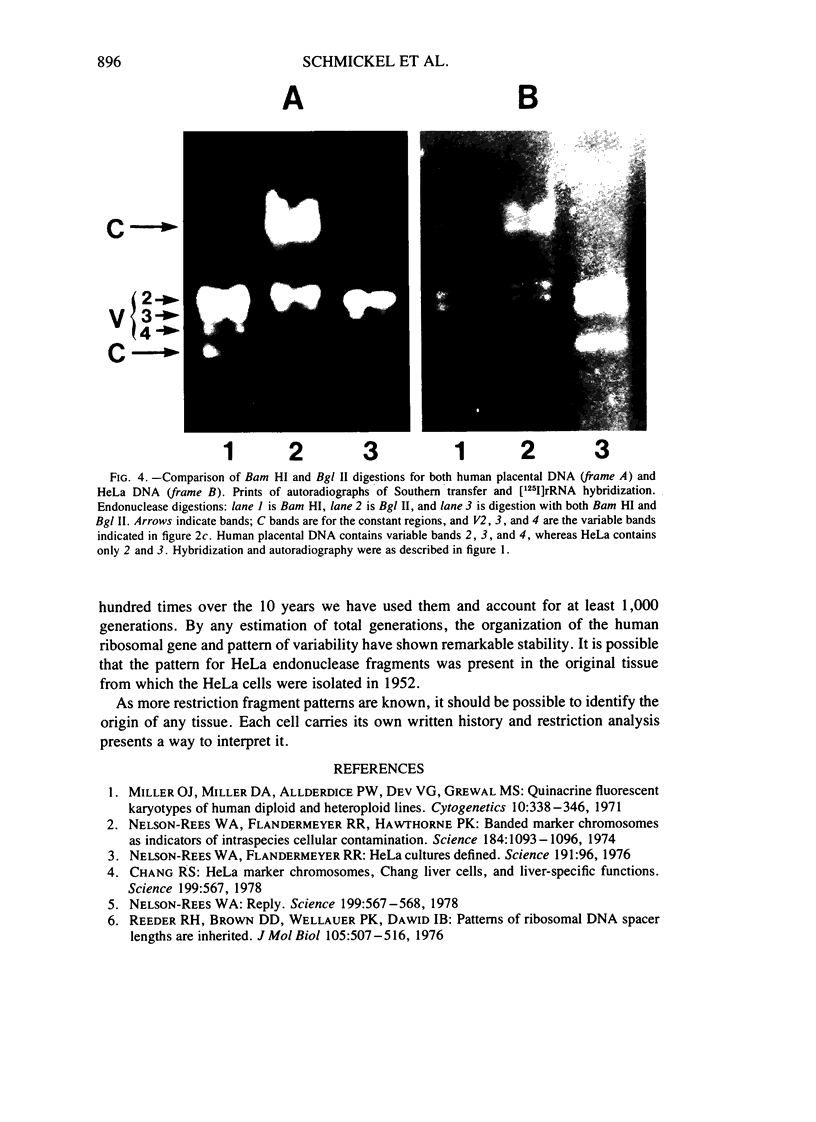
Restriction endonuclease analysis of HeLa cells and cells in which origins have been questioned provides evidence in favor of a HeLa cell origin for the questioned cells. Digestion of cellular human DNA reveals a variable ribosomal DNA (rDNA) fragment that is present in up to four discrete sizes. Cell lines of known and suspected HeLa origin contain only two size variants. This pattern of variability serves to distinguish HeLa-derived cells from others. Despite repeated passage and divergence of the HeLa phenotype and karyotype, the restriction pattern is remarkably constant.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang R. S. HeLa marker chromosomes, Chang liver cells, and liver-specific functions. Science. 1978 Feb 3;199(4328):567–568. doi: 10.1126/science.622561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S. HeLa marker chromosomes, Chang liver cells, and liver-specific functions. Science. 1978 Feb 3;199(4328):567–568. doi: 10.1126/science.622561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L. I., Parker R. C., Watson R. M., Chandler S. E., Teplitz M. Detection of a contaminant cell culture line by restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns of mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1267–1271. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Antenatal diagnosis of sickle-cell anaemia by D.N.A. analysis of amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet. 1978 Oct 28;2(8096):910–912. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91629-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Arnheim N. Length heterogeneity in a region of the human ribosomal gene spacer is not accompanied by extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S. Quinacrine fluorescent karyotypes of human diploid and heteroploid cell lines. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(5):338–346. doi: 10.1159/000130152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson-Rees W. A., Flandermeyer R. R., Hawthorne P. K. Banded marker chromosomes as indicators of intraspecies cellular contamination. Science. 1974 Jun 7;184(4141):1093–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4141.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Brown D. D., Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Patterns of ribosomal DNA spacer lengths are inherited. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Quantitation of human ribosomal DNA: hybridization of human DNA with ribosomal RNA for quantitation and fractionation. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jan;7(1):5–12. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Isolation and sequence organization of human ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Hollar B. A., Waterson J. R., Schmickel R. D. Molecular analysis of cloned human 18S ribosomal DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5367–5371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]