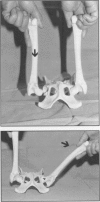
Abstract
Hip dysplasia is a common developmental problem affecting the canine population. Despite extensive research into the condition, many questions remain unanswered and numerous misconceptions are present among the general public. The purpose of this paper is to review the current knowledge on the development of hip dysplasia, factors modifying its development, and current diagnostic techniques. A computerized literature search was conducted for the period of January 1983 to April 1985 using the MEDLINE and CAB databases, and the keywords hip dysplasia, hip, dog, and canine. Other articles, wherever possible original research articles, published before 1983 were also reviewed. Animals affected by hip dysplasia are born with normal hips, but quickly develop subluxation of the femoral head. Degenerative joint disease follows. Hip dysplasia is a complex, inherited, polygenic trait. Selective breeding of only normal dogs with normal littermates, parents, and grandparents is the recommended method of reducing the incidence in the general population. Gene expression in affected individuals may be modified by a number of environmental factors. These factors do not cause hip dysplasia, but they alter manifestations of the trait and its severity. Nutrition is a major environmental factor. Excess energy consumption increases the frequency and severity of hip dysplasia in genetically predisposed dogs. Food intake should be regulated to maintain a slender figure with the ribs and dorsal vertebral spines easily palpable, but not visible. Excess dietary calcium and vitamin D contribute to hip dysplasia in genetically predisposed individuals and should be avoided. High dose vitamin C supplementation in growing puppies does not prevent hip dysplasia, and this practice should be discontinued.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



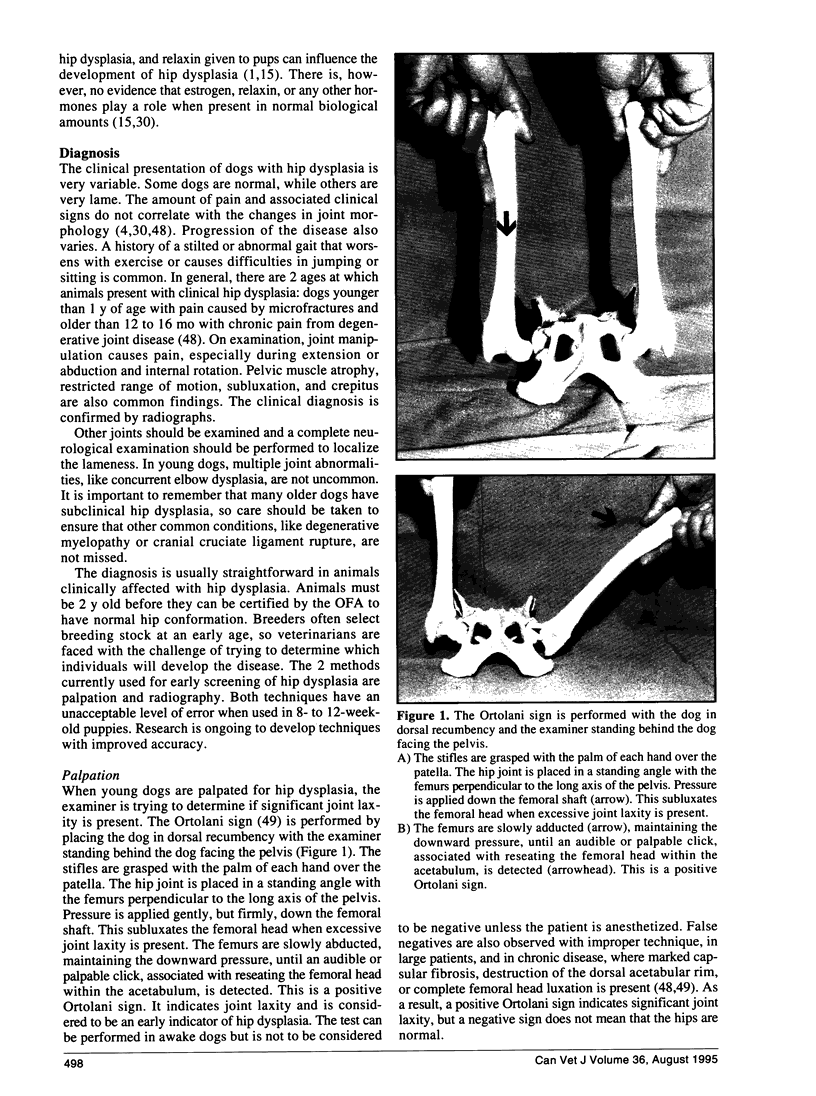
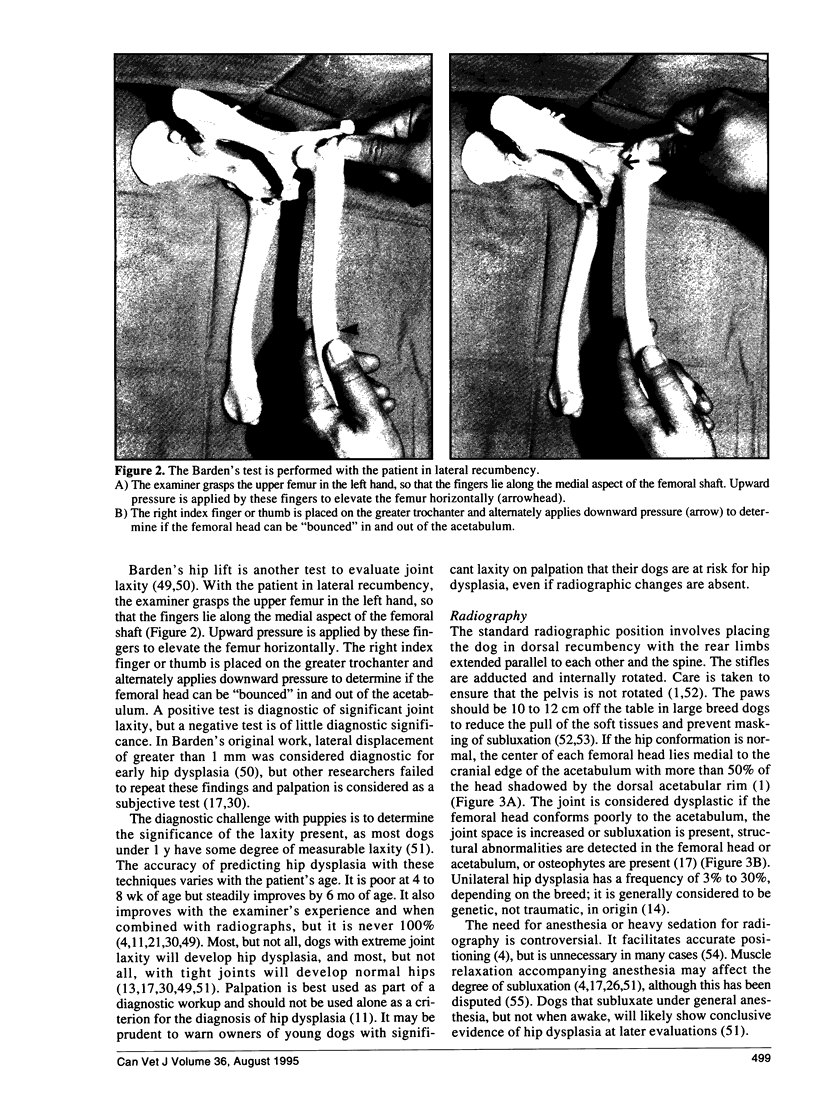
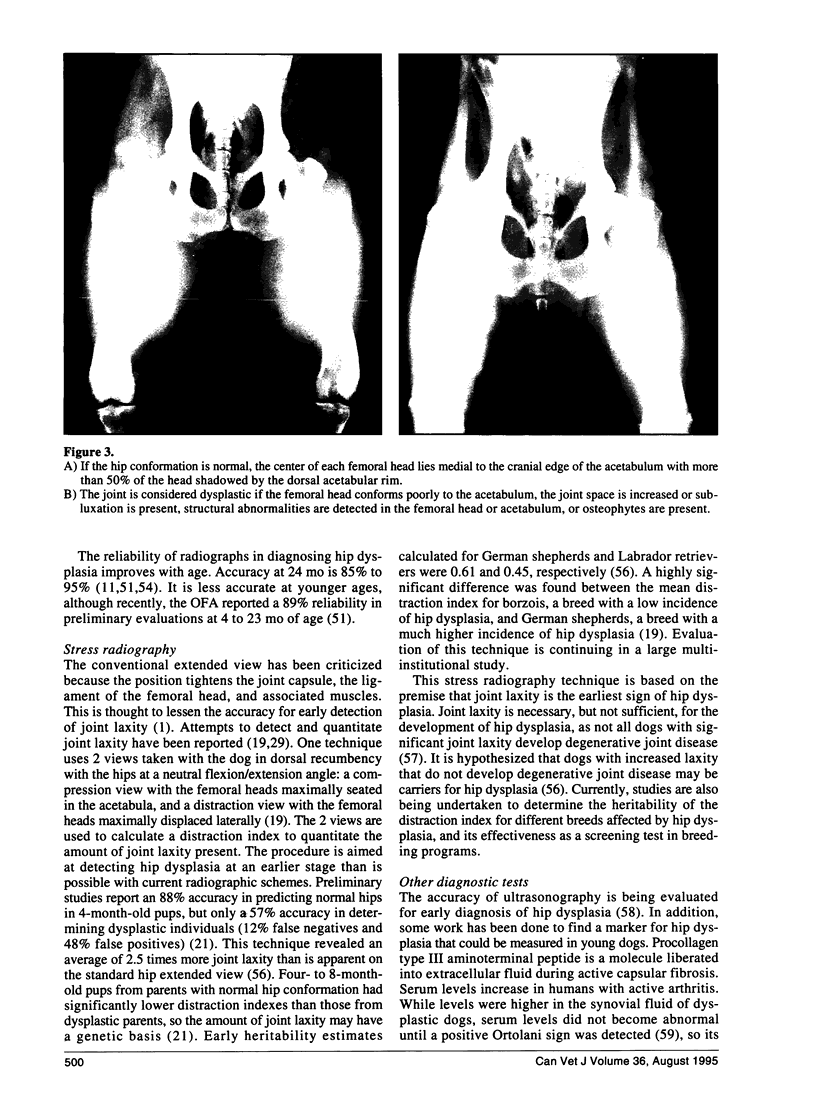


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W. The pathogenesis of canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):503–511. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardens J. W., Hardwick H. New observations on the diagnosis and cause of hip dysplasia. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1968 Mar;63(3):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfield W. O. Chronic subclinical scurvy and canine hip dysplasia. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1976 Oct;71(10):1399–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. Hip dysplasia and ascorbate therapy: fact or fancy? Semin Vet Med Surg (Small Anim) 1987 May;2(2):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corley E. A. Role of the Orthopedic Foundation for Animals in the control of canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dämmrich K. Relationship between nutrition and bone growth in large and giant dogs. J Nutr. 1991 Nov;121(11 Suppl):S114–S121. doi: 10.1093/jn/121.suppl_11.S114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow C. S., Back R. T. Radiographic evaluation of nonanesthetized and nonsedated dogs for hip dysplasia. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1989 Feb 15;194(4):524–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanssen I., Lunde H., Gjessing L. R. Plasma amino acids in dogs with osteochondrosis or hip dysplasia. Acta Vet Scand. 1989;30(1):111–112. doi: 10.1186/BF03548076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazewinkel H. A., Van den Brom W. E., Van 'T Klooster A. T., Voorhout G., Van Wees A. Calcium metabolism in Great Dane dogs fed diets with various calcium and phosphorus levels. J Nutr. 1991 Nov;121(11 Suppl):S99–106. doi: 10.1093/jn/121.suppl_11.S99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedhammar A., Olsson S. E., Andersson S. A., Persson L., Pettersson L., Olausson A., Sundgren P. E. Canine hip dysplasia: study of heritability in 401 litters of German Shepherd dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979 May 1;174(9):1012–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. A. Radiographic development of canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):559–578. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kealy R. D., Lawler D. F., Monti K. L., Biery D., Helms R. W., Lust G., Olsson S. E., Smith G. K. Effects of dietary electrolyte balance on subluxation of the femoral head in growing dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1993 Apr;54(4):555–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kealy R. D., Olsson S. E., Monti K. L., Lawler D. F., Biery D. N., Helms R. W., Lust G., Smith G. K. Effects of limited food consumption on the incidence of hip dysplasia in growing dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1992 Sep 15;201(6):857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanting F. Canine hip dysplasia and the breeder. A layman's point of view. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):739–743. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Craig P. H., Ross G. E., Jr, Geary J. C. Studies on pectineus muscles in canine hip dysplasia. Cornell Vet. 1972 Oct;62(4):628–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Geary J. C., Sheffy B. E. Development of hip dysplasia in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Jan;34(1):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Rendano V. T., Summers B. A. Canine hip dysplasia: concepts and diagnosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Sep 15;187(6):638–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Summers B. A. Early, asymptomatic stage of degenerative joint disease in canine hip joints. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1849–1855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Williams A. J., Burton-Wurster N., Pijanowski G. J., Beck K. A., Rubin G., Smith G. K. Joint laxity and its association with hip dysplasia in Labrador retrievers. Am J Vet Res. 1993 Dec;54(12):1990–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie S. A., Oltenacu E. A., Leighton E. Heritability estimate for temperament scores in German shepherd dogs and its genetic correlation with hip dysplasia. Behav Genet. 1985 Sep;15(5):475–482. doi: 10.1007/BF01066240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen J. S., Jensen L. T., Strøm H., Hørslev-Petersen K., Svalastoga E. Procollagen type-III aminoterminal peptide in serum and synovial fluid of dogs with hip dysplasia and coxarthrosis. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Oct;51(10):1544–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan S. J. The pathology of canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nap R. C., Hazewinkel H. A., Voorhout G., Van den Brom W. E., Goedegebuure S. A., Van 'T Klooster A. T. Growth and skeletal development in Great Dane pups fed different levels of protein intake. J Nutr. 1991 Nov;121(11 Suppl):S107–S113. doi: 10.1093/jn/121.suppl_11.S107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. C. The role of nutrition in canine hip dysplasia. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):529–540. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser W. H. A half century of canine hip dysplasia. Semin Vet Med Surg (Small Anim) 1987 May;2(2):87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riser W. H., Shirer J. F. Correlation between canine hip dysplasia and pelvic muscle mass: a study of 95 dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1967 May;28(124):769–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. K., Biery D. N., Gregor T. P. New concepts of coxofemoral joint stability and the development of a clinical stress-radiographic method for quantitating hip joint laxity in the dog. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990 Jan 1;196(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. K., Gregor T. P., Rhodes W. H., Biery D. N. Coxofemoral joint laxity from distraction radiography and its contemporaneous and prospective correlation with laxity, subjective score, and evidence of degenerative joint disease from conventional hip-extended radiography in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1993 Jul;54(7):1021–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teare J. A., Krook L., Kallfelz F. A., Hintz H. F. Ascorbic acid deficiency and hypertrophic osteodystrophy in the dog: a rebuttal. Cornell Vet. 1979 Oct;69(4):384–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J. Canine hip dysplasia: past and present. Semin Vet Med Surg (Small Anim) 1987 May;2(2):92–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel J. P., Wasserman J. F. Biomechanics of the normal and abnormal hip joint. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 May;22(3):513–528. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]