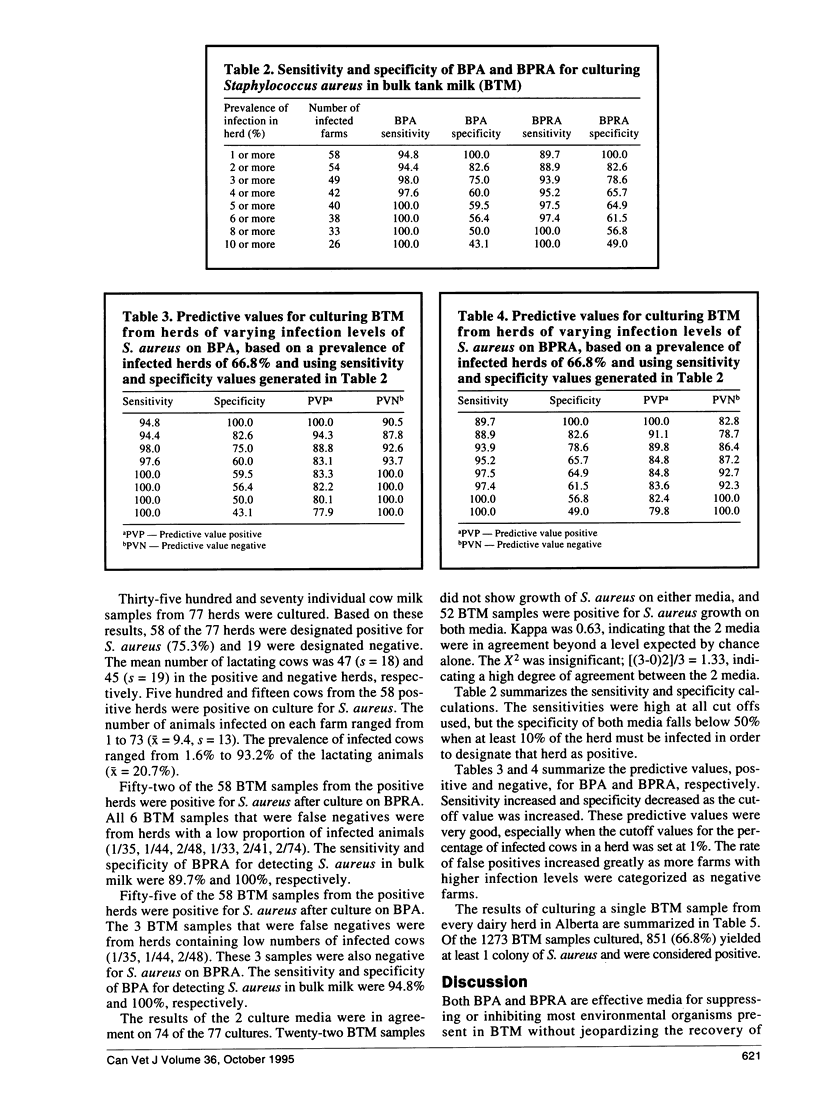
Abstract
The purpose of this project was to evaluate the use of 2 selective/differential culture media for detecting Staphylococcus aureus in bulk tank milk. One medium was Baird-Parker agar base supplemented with egg york tellurite emulsion and acriflavine. The other medium was Baird-Parker agar base supplemented with rabbit plasma/bovine fibrinogen and acriflavine. An increased inoculum of bulk tank milk (0.3 mL) was used to enhance the detection of S. aureus in samples containing low numbers of organisms. The sensitivity and specificity for detecting S. aureus in bulk tank milk were 94.8% and 100%, respectively, using Baird-Parker agar base supplemented with egg yolk tellurite emulsion and acriflavine, and 89.7% and 100%, respectively, using Baird-Parker agar base supplemented with rabbit plasma/bovine fibrinogen and acriflavine. Both media are practical for detecting S. aureus in bulk tank milk and monitoring its spread in lactating dairy herds in Alberta.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckers H. J., van Leusden F. M., Bindschedler O., Guerraz D. Evaluation of a pour-plate system with a rabbit plasma-bovine fibrinogen agar for the enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Apr;30(4):470–474. doi: 10.1139/m84-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A. Baird-Parker medium supplemented with acriflavine, polymyxins and sulphonamide for the selective isolation of Staphylococcus aureus from heavily contaminated materials. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godkin M. A., Leslie K. E. Culture of bulk tank milk as a mastitis screening test: A brief review. Can Vet J. 1993 Oct;34(10):601–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Gilmour A. Application of current methods for isolation and identification of staphylococci in raw bovine milk. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;59(3):207–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar A. H., During M. Model studies on a membrane filtration method for the enumeration of coagulase-positive staphylococci in swimming-pool water using rabbit plasma-bovine fibrinogen agar. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Apr;31(4):331–334. doi: 10.1139/m85-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isigidi B. K., Devriese L. A., Croegaert T., Van Hoof J. A highly selective two-stage isolation method for the enumeration of Staphylococcus aureus in foods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 May;66(5):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb05106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney D. The toxicity of potassium tellurite to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbit plasma fibrinogen agar. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;61(2):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonderwoerd M., McFadzen L. L., Manninen K. I., Ollis G. W. Culturing of bulk tank milk for the presence of Nocardia spp. Can Vet J. 1990 Jun;31(6):453–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



