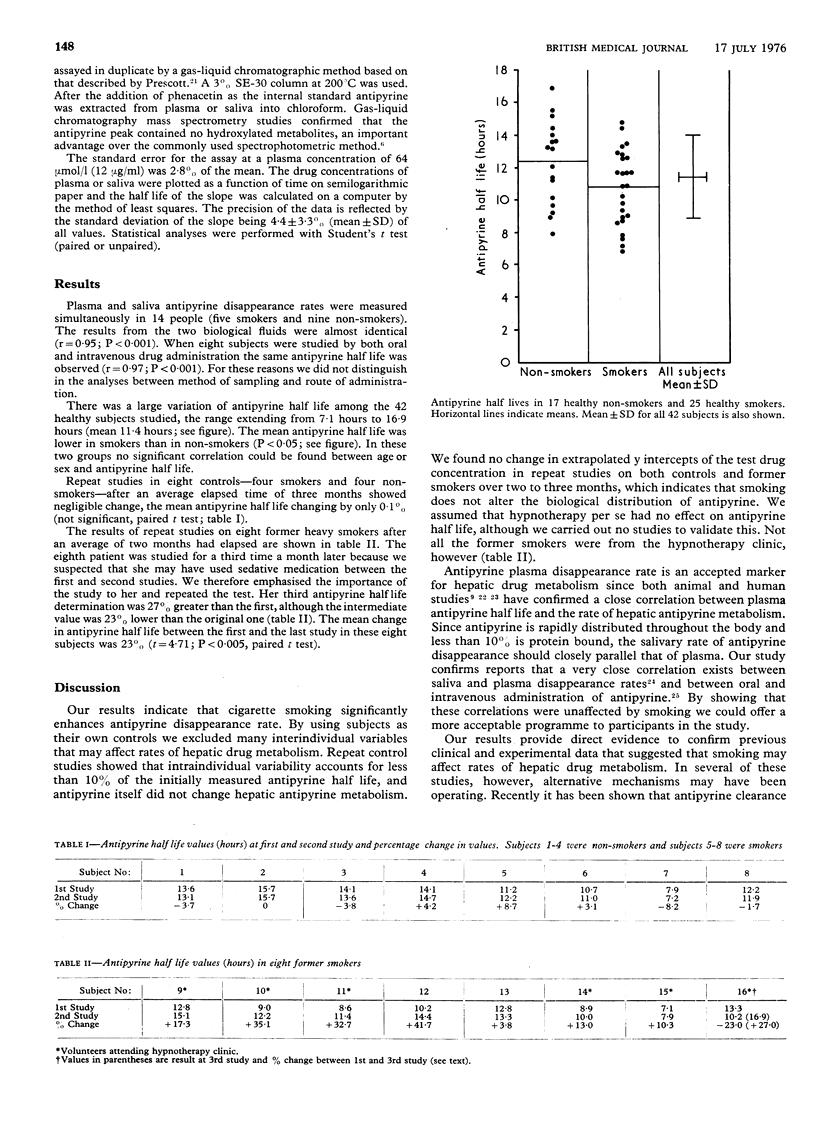
Abstract
The effect of cigarette smoking on salivary antipyrine disappearance rate, and as an index of hepatic drug metabolism, was studied in 42 healthy subjects. Antipyrine half life was significantly shorter in smokers compared with non-smokers. To determine whether this difference was due solely to tobacco consumption eight subjects were restudied two months after they stopped smoking. The mean antipyrine disappearance rate in this group increased by 23% in contrast to that of a control group, which did not alter. Cigarette smoking contributes to the considerable variation in interindividual rates of drug metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. B., Vesell E. S. Comparison of plasma levels of antipyrine, tolbutamide, and warfarin after oral and intravenous administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Dec;16(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1002/cpt19741661059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell E. T., Warr G. A., Busbee D. L., Martin R. R. Induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in human pulmonary alveolar macrophages by cigarette smoking. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1881–1884. doi: 10.1172/JCI107371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H., Burns J. J. Metabolic interactions among environmental chemicals and drugs. Science. 1972 Nov 10;178(4061):576–586. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4061.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Vesell E. S., Wolff S. M. Effects of etiocholanolone-induced fever on plasma antipyrine half-lives and metabolic clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Apr;17(4):447–457. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975174447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffman D. H., Shoeman D. W., Azarnoff D. L. Correlation of the plasma elimination of antipyrine and the appearance of 4-hydroxy antipyrine in the urine of man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jan 15;23(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jick H. Smoking and clinical drug effects. Med Clin North Am. 1974 Sep;58(5):1143–1149. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeri-Szanto M., Pomeroy J. R. Atmospheric pollution and pentazocine metabolism. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):947–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91448-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Avant G. R., Hoyumpa A., Schenker S., Wilkinson G. R. The effects of age and liver disease on the disposition and elimination of diazepam in adult man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):347–359. doi: 10.1172/JCI107938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmodin B., Azarnoff D. L., Sjöqvist F. Effect of environmental factors on drug metabolism: decreased plasma half-life of antipyrine in workers exposed to chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Sep-Oct;10(5):638–642. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969105638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter M., Black M., Arias I. M. The metabolism of antipyrine in patients with chronic renal failure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Dec;187(3):612–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V. The in vivo and in vitro induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in mammalian cells of different species, tissues, strains, and developmental and hormonal states. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Oct;134(1):76–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantuck E. J., Hsiao K. C., Maggio A., Nakamura K., Kuntzman R., Conney A. H. Effect of cigarette smoking on phenacetin metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Jan;15(1):9–17. doi: 10.1002/cpt19741519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Adjepon-Yamoah K. K., Roberts E. Rapid gas-liquid chromatographic estimation of antipyrine in plasma. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;25(3):205–207. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statland B. E., Astrup P., Black C. H., Oxholm E. Plasma antipyrine half-life and hepatic microsomal antipyrine hydroxylase activity in rabbits. Pharmacology. 1973;10(6):329–337. doi: 10.1159/000136454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G. Genetic control of drug levels in man: antipyrine. Science. 1968 Jul 5;161(3836):72–73. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3836.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G. Genetic control of the phenobarbital-induced shortening of plasma antipyrine half-lives in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2202–2209. doi: 10.1172/JCI106186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G., Passananti G. T. Genetic and environmental factors affecting ethanol metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):192–201. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Passananti G. T. Inhibition of drug metabolism in man. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Jan-Feb;1(1):402–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestal R. E., Norris A. H., Tobin J. D., Cohen B. H., Shock N. W., Andres R. Antipyrine metabolism in man: influence of age, alcohol, caffeine, and smoking. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):425–432. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. M., DeAngelis R. L., Wingfield M., Farmer T. W. Elimination of antipyrine from saliva as a measure of metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Sep;18(3):249–258. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975183249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. M., Harrison Y. E., Gommi B. W., Poppers P. J., Finster M., Conney A. H. Stimulatory effect of cigarette smoking on the hydroxylation of 3,4-benzpyrene and the N-demethylation of 3-methyl-4-monomethylaminoazobenzene by enzymes in human placenta. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Jan-Feb;10(1):100–109. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969101100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



