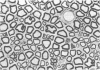
Abstract
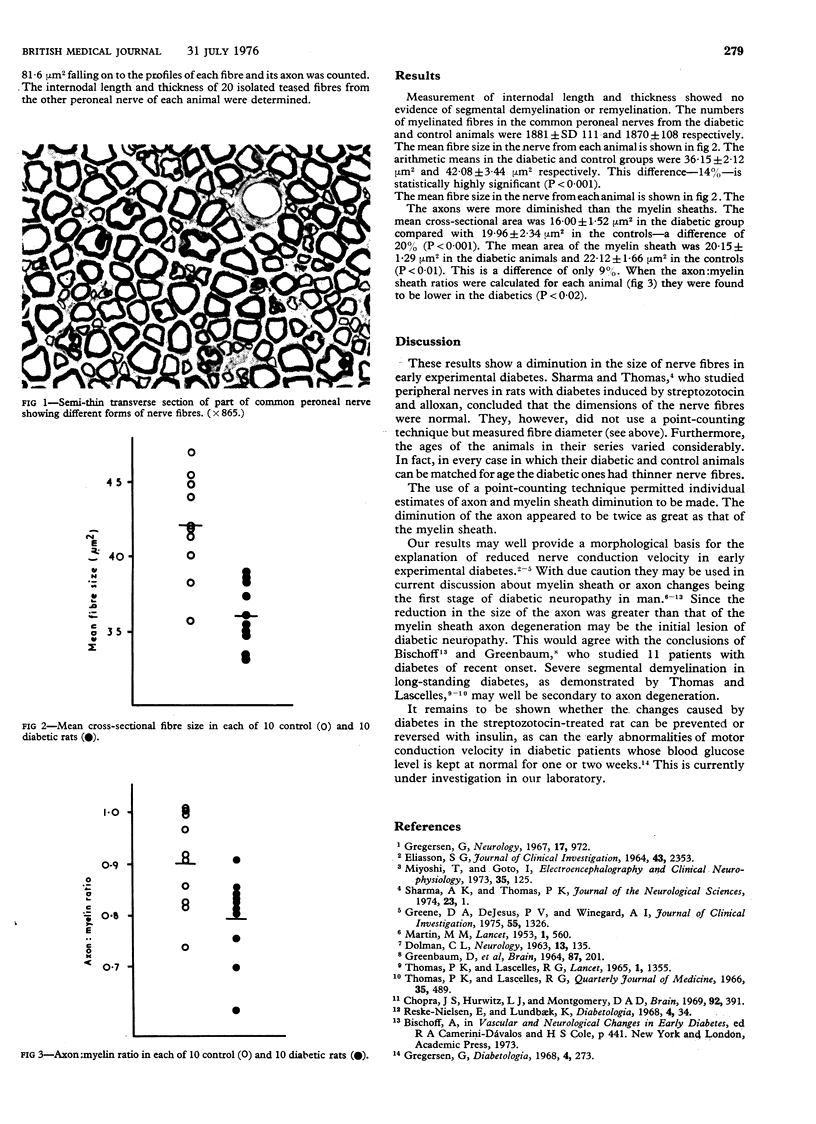
A morphometric study of the common peroneal nerve in early experimental diabetes in rats showed that fibre size was diminished. The reduction in the size of the axon was twice that of the myelin sheath. This may contribute to the understanding of the impaired motor conduction velocity found in diabetics shortly after the onset of their disease.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chopra J. S., Hurwitz L. J., Montgomery D. A. The pathogenesis of sural nerve changes in diabetes mellitus. Brain. 1969;92(2):391–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLMAN C. L. The morbid anatomy of diabetic neuropathy. Neurology. 1963 Feb;13:135–142. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIASSON S. G. NERVE CONDUCTION CHANGES IN EXPERIMENTAL DIABETES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2353–2358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBAUM D., RICHARDSON P. C., SALMON M. V., URICH H. PATHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON SIX CASES OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:201–214. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., De Jesus P. V., Jr, Winegrad A. I. Effects of insulin and dietary myoinositol on impaired peripheral motor nerve conduction velocity in acute streptozotocin diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1326–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI108052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen G. Diabetic neuropathy: influence of age, sex, metabolic control, and duration of diabetes on motor conduction velocity. Neurology. 1967 Oct;17(10):972–980. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.10.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen G. Variations in motor conduction velocity produced by acute changes of the metabolic state in diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1968 Nov;4(5):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01309900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN M. M. Involvement of autonomic nerve-fibres in diabetic neuropathy. Lancet. 1953 Mar 21;1(6760):560–565. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91693-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi T., Goto I. Serial in vivo determinations of nerve conduction velocity in rat tails. Physiological and pathological changes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1973 Aug;35(2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(73)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reske-Nielsen E., Lundbaek K. Pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system of young long-term diabetics. II. The spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Diabetologia. 1968 Jan;4(1):34–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01241031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., LASCELLES R. G. SCHWANN-CELL ABNORMALITIES IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Lancet. 1965 Jun 26;1(7400):1355–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]