Full text
PDF



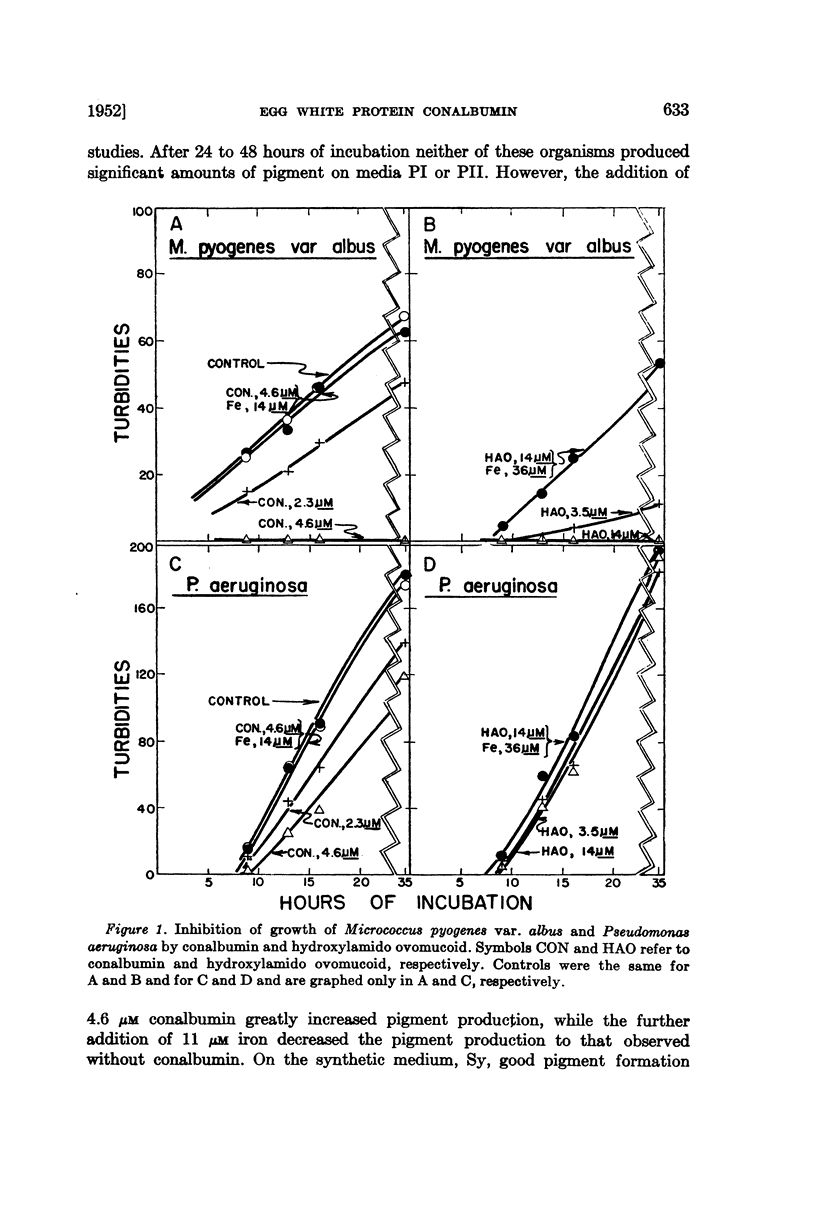
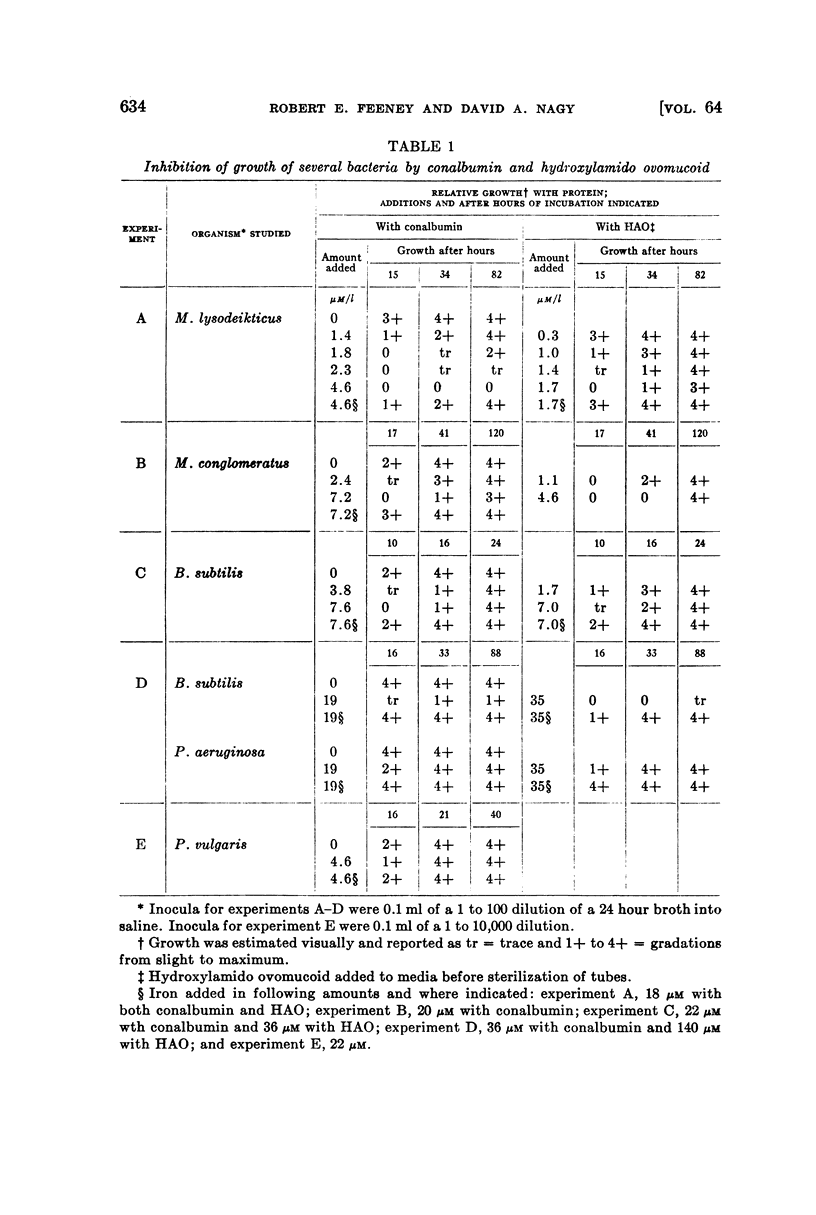
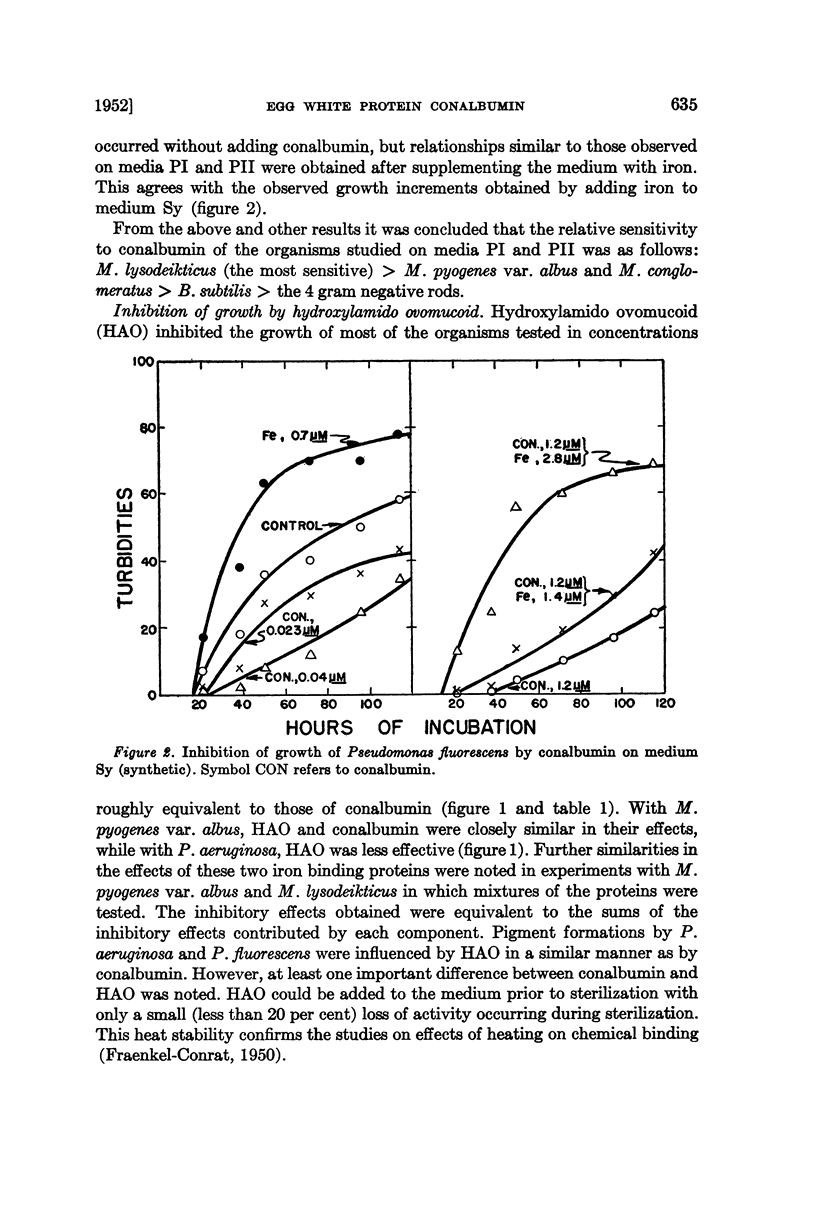
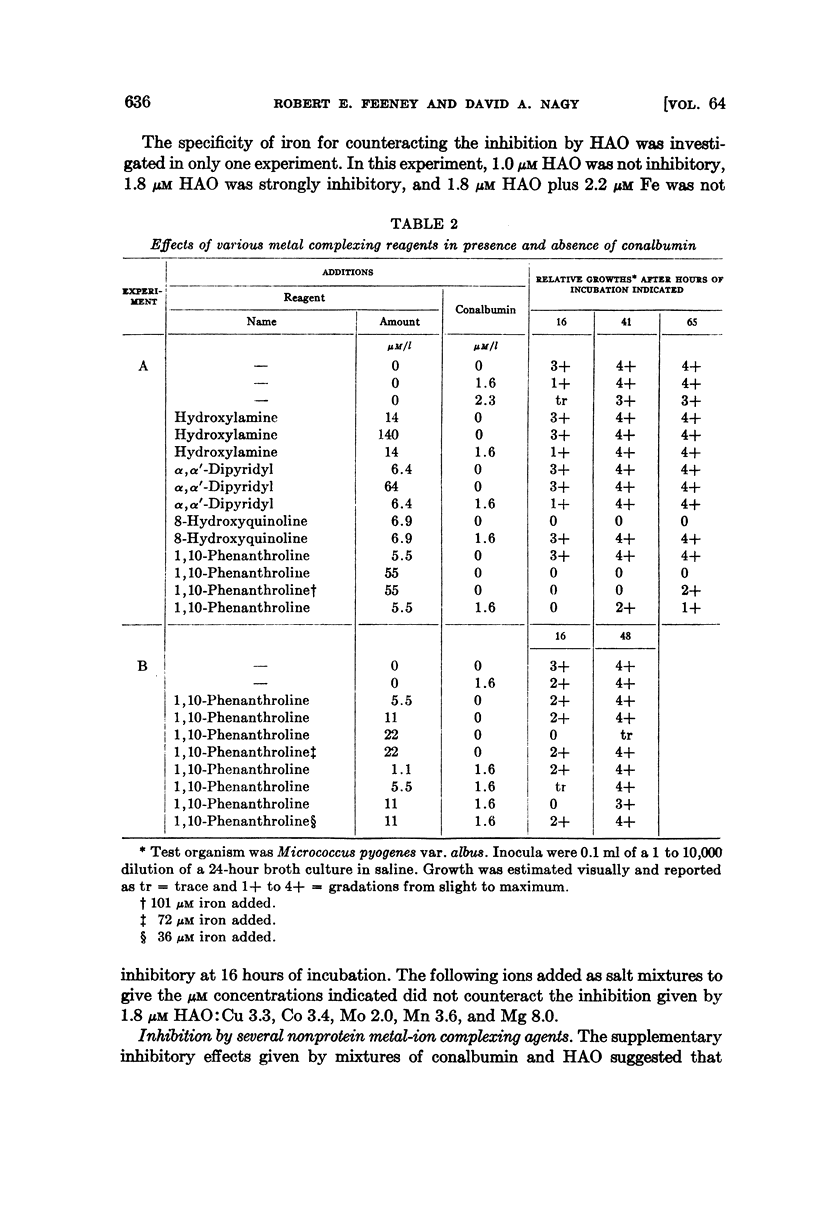





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. The metal-binding properties of riboflavin. Biochem J. 1950 Sep;47(3):xxvii–xxvii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEENEY R. E. The antagonistic activities of conalbumin and 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Nov;34(1):196–208. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(51)80025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H. Comparison of the iron-binding activities of conalbumin and of hydroxylamidoproteins. Arch Biochem. 1950 Oct;28(3):452–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., FEENEY R. E. The metal-binding activity of conalbumin. Arch Biochem. 1950 Nov;29(1):101–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson L. MAINTENANCE OF IRON SUPPLY IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS BY A SINGLE ADDITION OF FERRIC POTASSIUM ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRA-ACETATE. Plant Physiol. 1951 Apr;26(2):411–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.26.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBBO S. D., ALBERT A., GIBSON M. I. The influence of chemical constitution on antibacterial activity. V. The antibacterial action of 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine). Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Jun;31(3):425–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade A. L., Caroline L. RAW HEN EGG WHITE AND THE ROLE OF IRON IN GROWTH INHIBITION OF SHIGELLA DYSENTERIAE, STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, ESCHERICHIA COLI AND SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Science. 1944 Jul 7;100(2584):14–15. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2584.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER R. C., WEBER I. The preparation of crystalline conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


