Abstract
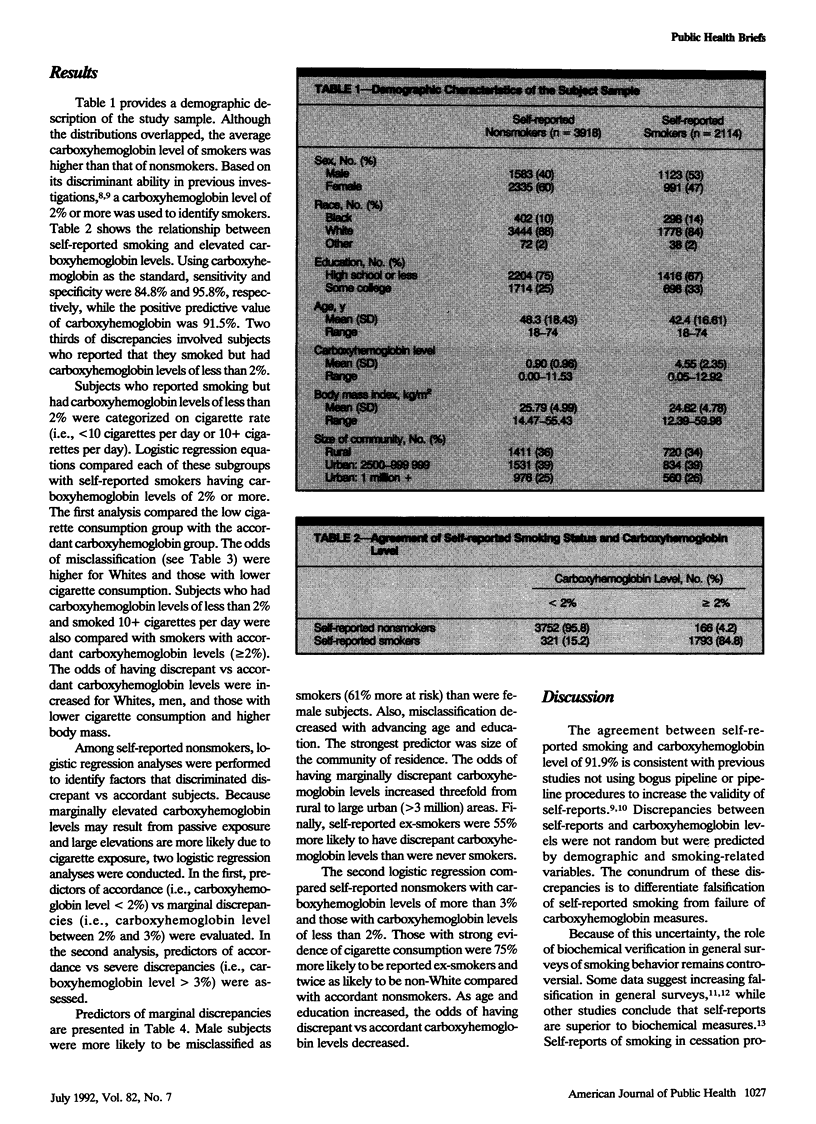
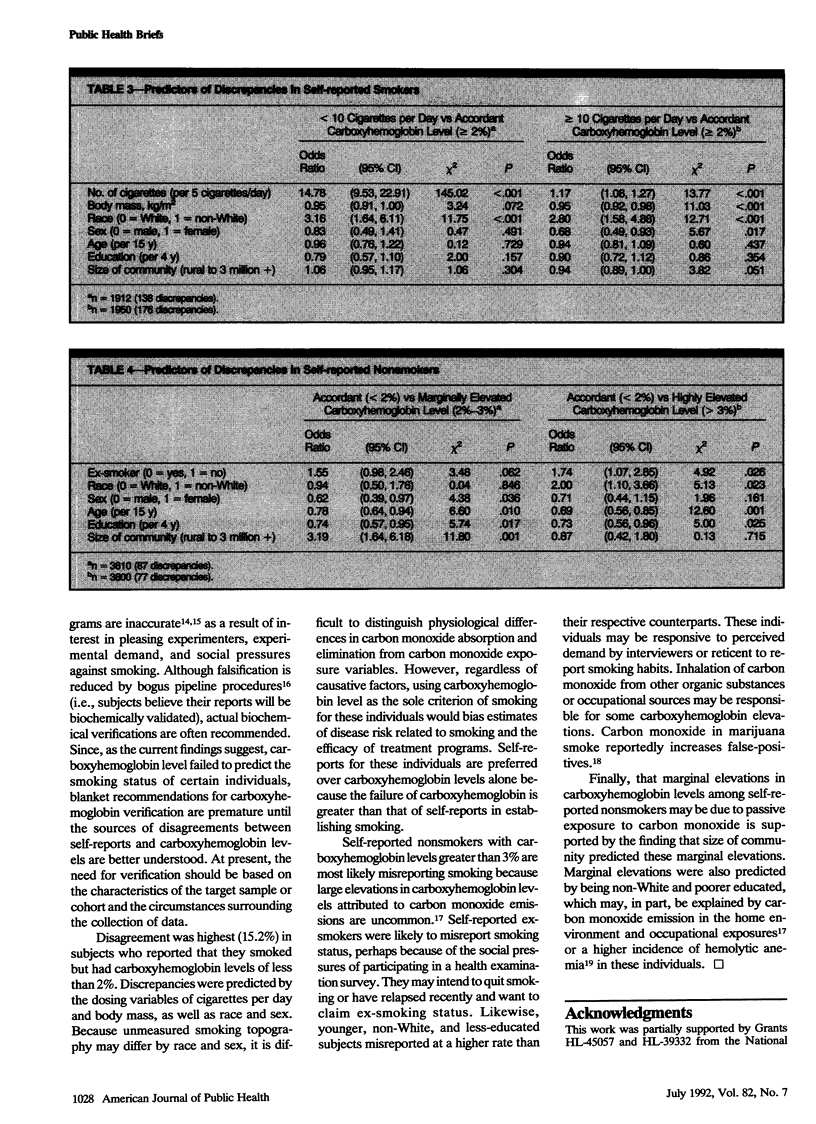
Environmental, self-report, and demographic factors mediated the relationship between self-reported cigarette smoking and carboxyhemoglobin among 2114 smokers and 3918 nonsmokers. Self-reported nonsmokers with carboxyhemoglobin levels between 2% and 3% were more likely to be self-reported ex-smokers, to live in a larger community, and to be younger, less educated, and male than were self-reported nonsmokers with carboxyhemoglobin levels of less than 2%. Self-reported nonsmokers with strong evidence of cigarette consumption (carboxyhemoglobin level greater than 3%) were more likely to be self-reported ex-smokers, younger, less educated, and non-White than were nonsmokers with carboxyhemoglobin levels of less than 2%.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen J. D., Bartsch G. E. A comparison between carboxyhemoglobin and serum thiocyanate determinations as indicators of cigarette smoking. Am J Public Health. 1980 Mar;70(3):284–286. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechacek T. F., Murray D. M., Luepker R. V., Mittelmark M. B., Johnson C. A., Shutz J. M. Measurement of adolescent smoking behavior: rationale and methods. J Behav Med. 1984 Mar;7(1):123–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00845351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitti D. B., Friedman G. D., Kahn W. Accuracy of information on smoking habits provided on self-administered research questionnaires. Am J Public Health. 1981 Mar;71(3):308–311. doi: 10.2105/ajph.71.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillett R. W., Wilson M. B., Malcolm R. E., Ball K. P. Deception among smokers. Br Med J. 1978 Oct 28;2(6146):1185–1186. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6146.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small K. A., Radford E. P., Frazier J. M., Rodkey F. L., Collison H. A. A rapid method for simultaneous measurement of carboxy- and methemoglobin in blood. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):154–160. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. D. The effect of carbon monoxide on humans. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:409–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesey C. J., Saloojee Y., Cole P. V., Russell M. A. Blood carboxyhaemoglobin, plasma thiocyanate, and cigarette consumption: implications for epidemiological studies in smokers. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 22;284(6328):1516–1518. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6328.1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt T. M., Selvin S., Widdowson G., Hulley S. B. Expired air carbon monoxide and serum thiocyanate as objective measures of cigarette exposure. Am J Public Health. 1977 Jun;67(6):545–549. doi: 10.2105/ajph.67.6.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N. J., Idle M., Boreham J., Bailey A. Carbon monoxide in breath in relation to smoking and carboxyhaemoglobin levels. Thorax. 1981 May;36(5):366–369. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.5.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N., Howard S., Smith P. G., Kjeldsen K. Association between atherosclerotic diseases and carboxyhaemoglobin levels in tobacco smokers. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 31;1(5856):761–765. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5856.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


