Abstract
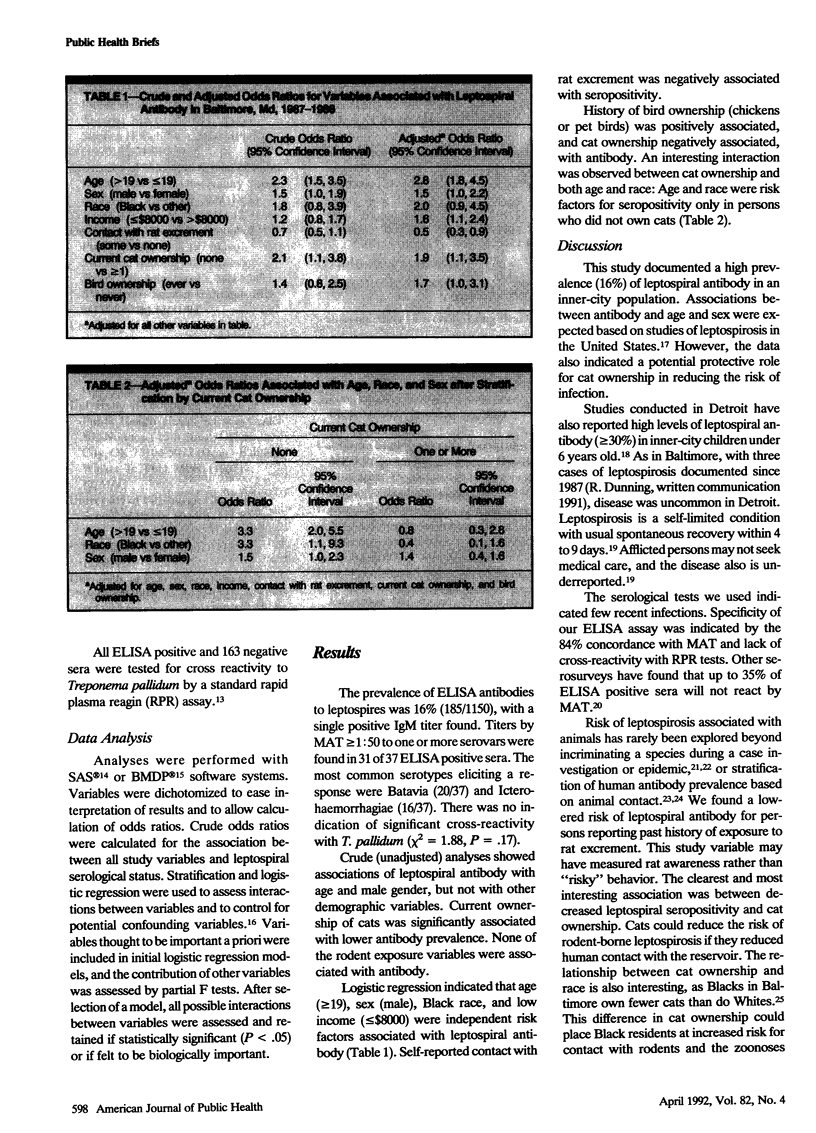
Leptospiral antibody prevalence was 16% in residents of Baltimore. Seropositivity was associated with age, gender, race, and bird ownership, reduced the antibody risk associated with age and race from odds ratios (95% confidence interval) of 3.3 (2.0, 5.5) and 3.3 (1.1, 9.3), respectively, to the baseline level. These data establish the high prevalence of leptospiral antibody in Baltimore and suggest a protective role for cats in reducing the risk of human infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cacciapuoti B., Ciceroni L., Maffei C., Di Stanislao F., Strusi P., Calegari L., Lupidi R., Scalise G., Cagnoni G., Renga G. A waterborne outbreak of leptospirosis. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Sep;126(3):535–545. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacciapuoti B., Vellucci A., Ciceroni L., Pinto A., Taggi F. Prevalence of leptospirosis in man. Pilot survey. Eur J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;3(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00239749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs J. E., Glass G. E., Ksiazek T. G., Rossi C. A., Oro J. G., Leduc J. W. Human-rodent contact and infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis and Seoul viruses in an inner-city population. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Feb;44(2):117–121. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.44.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Jr, Sulzer C. R., Pursell A. R. Improved microtechnique for the leptospiral microscopic agglutination test. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):976–980. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.976-980.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers R. Y., Frank R., Demers P., Clay M. Leptospiral exposure in Detroit rodent control workers. Am J Public Health. 1985 Sep;75(9):1090–1091. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.9.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers R. Y., Thiermann A., Demers P., Frank R. Exposure to Leptospira icterohaemorrhagiae in inner-city and suburban children: a serologic comparison. J Fam Pract. 1983 Dec;17(6):1007–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale D. A., Everard C. O., Carrington D. G., Everard J. D. Leptospiral antibodies in patients from a Barbadian general practice. Eur J Epidemiol. 1990 Jun;6(2):150–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00145787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann A. F., Mann J. M., Gardiner T. M., Heaton F., Poland J. D., Barnes A. M., Maupin G. O. Public health implications of plague in domestic cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Nov 1;179(9):875–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI H. Y., DAVIS D. E. The prevalence of carriers of Leptospira and Salmonella in Norway rats of Baltimore. Am J Hyg. 1952 Jul;56(1):90–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martone W. J., Kaufmann A. F. Leptospirosis in humans in the United States, 1974-1978. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):1020–1022. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter G. Leptospirosis: a zoonosis of protean manifestations. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Jul-Aug;1(4):282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. R., Winn R. E., Keefe T. J. Leptospirosis. Epidemiological features of a sporadic case. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Aug;149(8):1878–1880. doi: 10.1001/archinte.149.8.1878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutsch S. M., Juranek D. D., Sulzer A., Dubey J. P., Sikes R. K. Epidemic toxoplasmosis associated with infected cats. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 29;300(13):695–699. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903293001302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Canine leptospirosis in Detroit. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1659–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Incidence of leptospirosis in the detroit rat population. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Sep;26(5 Pt 1):970–974. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


