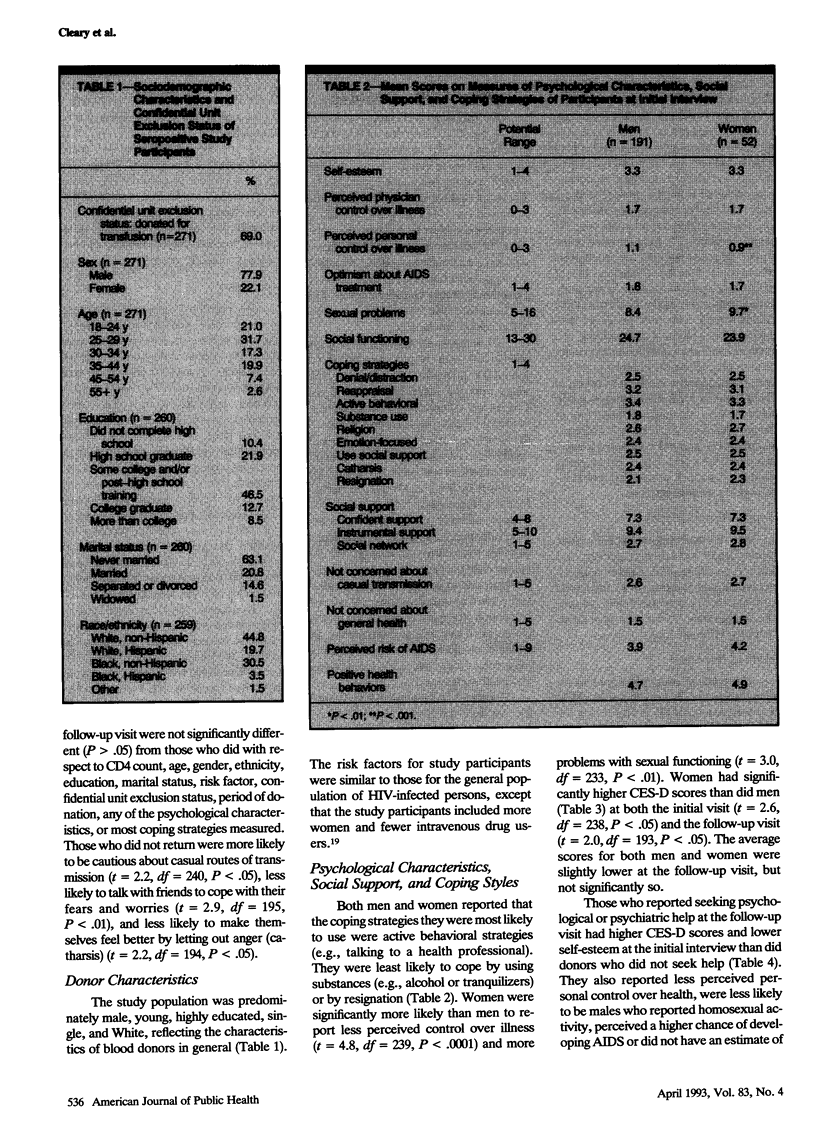
Abstract
OBJECTIVES. Understanding more about the psychological state of persons notified of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is critical for designing notification and counseling programs that will have the most positive effect. METHODS. The subjects were blood donors who had been notified of HIV infection by the New York Blood Center. A nurse elicited a medical history, performed a limited medical examination, and asked the subjects to complete a questionnaire that included questions about drug use, sexual behavior, and psychological characteristics. The subjects completed another questionnaire approximately 2 weeks later. RESULTS. The average depressive symptom scores for both men and women were substantially higher than scores typically found in representative population samples. More than a quarter of the men and more than a third of the women reported seeking psychological or psychiatric services in the first few weeks following notification. CONCLUSIONS. Anticipating and meeting individuals' psychological needs may be necessary if HIV screening programs are to address effectively the needs of persons infected with HIV.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd J. H., Weissman M. M., Thompson W. D., Myers J. K. Screening for depression in a community sample. Understanding the discrepancies between depression symptom and diagnostic scales. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Oct;39(10):1195–1200. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290100059010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang H. T., Devins G. M., Hunsley J., Gill M. J. Psychosocial distress and well-being among gay and bisexual men with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Psychiatry. 1989 Jul;146(7):876–880. doi: 10.1176/ajp.146.7.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. D., Rogers T. F., Singer E., Avorn J., van Devanter N., Perry S., Pindyck J. Health education about AIDS among seropositive blood donors. Health Educ Q. 1986 Winter;13(4):317–329. doi: 10.1177/109019818601300404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. D., Singer E., Rogers T. F., Avorn J., Van Devanter N., Soumerai S., Perry S., Pindyck J. Sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics of HIV antibody-positive blood donors. Am J Public Health. 1988 Aug;78(8):953–957. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.8.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. D., Van Devanter N., Rogers T. F., Singer E., Avorn J., Pindyck J. Trends in sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics of HIV antibody-positive blood donors. AIDS Educ Prev. 1991 Spring;3(1):60–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dew M. A., Ragni M. V., Nimorwicz P. Infection with human immunodeficiency virus and vulnerability to psychiatric distress. A study of men with hemophilia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;47(8):737–744. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1990.01810200045006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. W., Kessler L. G. Rates of symptoms of depression in a national sample. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Oct;114(4):528–538. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S., Riccio M., Harlow P., Oretti R., Thompson C. Psychosis associated with HIV infection. Br J Psychiatry. 1988 Nov;153:618–623. doi: 10.1192/bjp.153.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jette A. M., Davies A. R., Cleary P. D., Calkins D. R., Rubenstein L. V., Fink A., Kosecoff J., Young R. T., Brook R. H., Delbanco T. L. The Functional Status Questionnaire: reliability and validity when used in primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 1986 May-Jun;1(3):143–149. doi: 10.1007/BF02602324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. C., O'Brien K., Joseph J. G., Ostrow D. G., Phair J. P., Chmiel J. S., Wortman C. B., Emmons C. A. Effects of HIV infection, perceived health and clinical status on a cohort at risk for AIDS. Soc Sci Med. 1988;27(6):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. S., Tendler C., VanDevanter N., Cleary P. D. A group intervention model for individuals testing positive for HIV antibody. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1990 Jul;60(3):452–459. doi: 10.1037/h0079192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maj M. Psychiatric aspects of HIV-1 infection and AIDS. Psychol Med. 1990 Aug;20(3):547–563. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700017050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic D., Cleary P. D. Factors associated with the maintenance of positive health behavior. Prev Med. 1980 Nov;9(6):805–814. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(80)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton J. M., Stempel R. R., Bacchetti P., Temoshok L., Moss A. R. Results of a one year longitudinal study of HIV antibody test notification from the San Francisco General Hospital cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(8):787–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow D. G., Joseph J. G., Kessler R., Soucy J., Tal M., Eller M., Chmiel J., Phair J. P. Disclosure of HIV antibody status: behavioral and mental health correlates. AIDS Educ Prev. 1989 Spring;1(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow D. G., Monjan A., Joseph J., VanRaden M., Fox R., Kingsley L., Dudley J., Phair J. HIV-related symptoms and psychological functioning in a cohort of homosexual men. Am J Psychiatry. 1989 Jun;146(6):737–742. doi: 10.1176/ajp.146.6.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. W., Jacobsberg L. B., Fishman B., Weiler P. H., Gold J. W., Frances A. J. Psychological responses to serological testing for HIV. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):145–152. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S., Jacobsberg L., Fishman B. Suicidal ideation and HIV testing. JAMA. 1990 Feb 2;263(5):679–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindyck J., Waldman A., Zang E., Oleszko W., Lowy M., Bianco C. Measures to decrease the risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome transmission by blood transfusion. Evidence of volunteer blood donor cooperation. Transfusion. 1985 Jan-Feb;25(1):3–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1985.25185116497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A. AIDS: what is now known. IV. Psychosocial aspects, treatment prospects. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1986 Oct 15;21(10):125-30, 133, 137-8 passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tross S., Hirsch D. A. Psychological distress and neuropsychological complications of HIV infection and AIDS. Am Psychol. 1988 Nov;43(11):929–934. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.43.11.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallston K. A., Wallston B. S., DeVellis R. Development of the Multidimensional Health Locus of Control (MHLC) Scales. Health Educ Monogr. 1978 Spring;6(2):160–170. doi: 10.1177/109019817800600107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


