Abstract
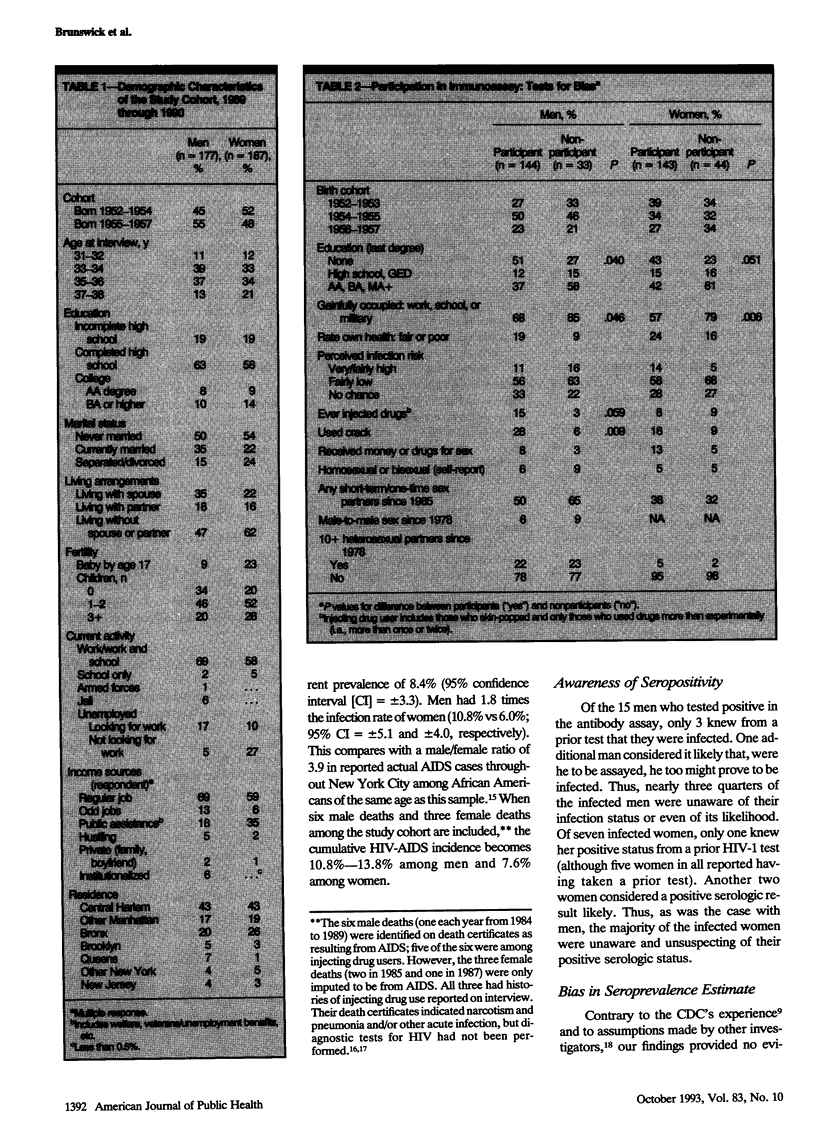
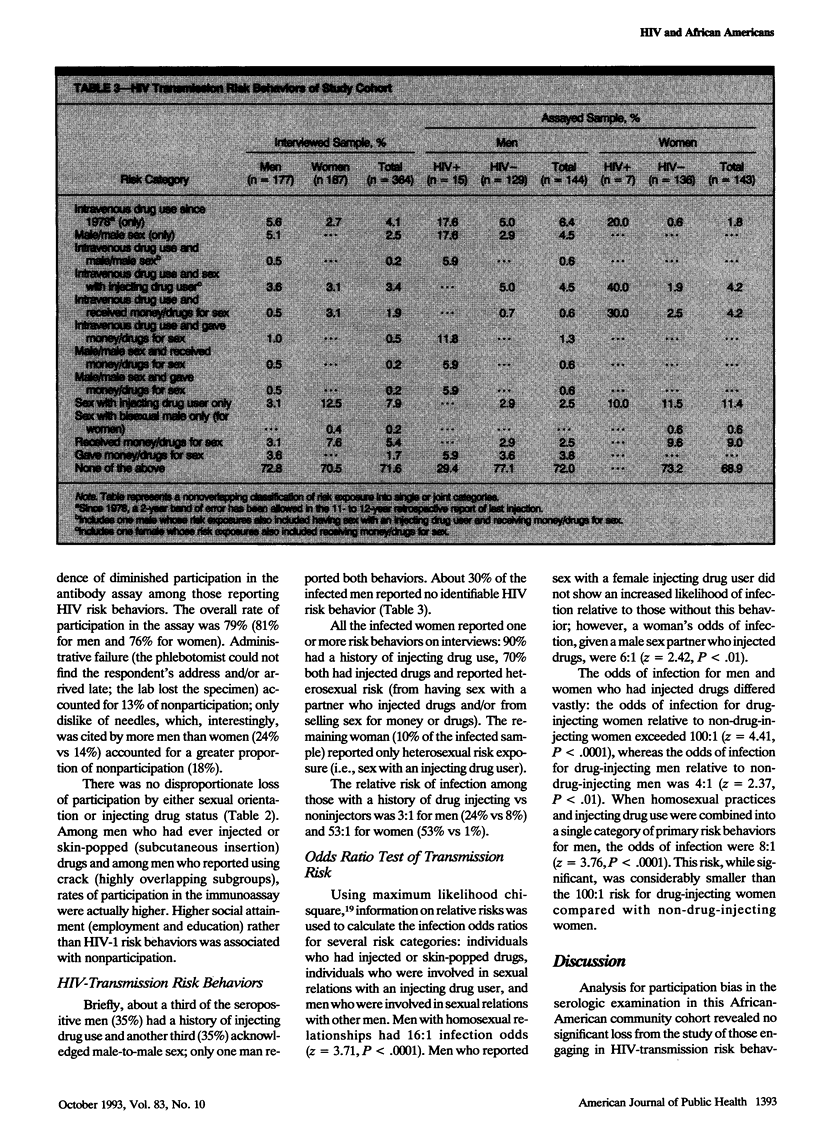
OBJECTIVES. Previous attempts at obtaining population estimates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) seroprevalence have been beset by problems of cooperation bias. As part of the fourth round of study with an urban African-American community cohort, the following investigation was aimed at assessing HIV-1 prevalence and the relative importance of sex and drug injection as risk factors in infection. METHODS. Personal interviews were conducted in the home with 364 respondents, followed by voluntary blood sample collection from 287 of these individuals. RESULTS. Blood assays showed a point prevalence of 8.4% HIV-1 seropositivity in this community cross section, with a higher female-to-male ratio than appears among acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) case reports. Most infected persons were unaware and unsuspecting of their infection. CONCLUSIONS. First, findings underscore the need to focus on risk behaviors rather than on risk groups. Second, the smaller than 2:1 ratio of infected men to women suggests that current AIDS case reports seriously underestimate HIV-1 infection among certain cohorts of African-American women. Finally, widespread ignorance of own infected status and inaccurate risk assessment signal the substantial task for community health educators in reaching inner-city African-American men and women at risk.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunswick A. F. Health and substance use behavior: the longitudinal Harlem Health Study. J Addict Dis. 1991;11(1):119–137. doi: 10.1300/j069v11n01_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W., Jaffe H. W., Hardy A. M., Morgan W. M., Selik R. M., Dondero T. J. Epidemiology of HIV infection and AIDS in the United States. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):610–616. doi: 10.1126/science.3340847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerichs R. R., Htoon M. T., Eskes N., Lwin S. Comparison of saliva and serum for HIV surveillance in developing countries. Lancet. 1992 Dec 19;340(8834-8835):1496–1499. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Parry J. V., Best S. J., Smith A. M., de Silva M., Mortimer P. P. HIV surveillance by testing saliva. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):369–371. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198810000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padian N. S., Shiboski S. C., Jewell N. P. Female-to-male transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. JAMA. 1991 Sep 25;266(12):1664–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry J. V., Perry K. R., Mortimer P. P. Sensitive assays for viral antibodies in saliva: an alternative to tests on serum. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):72–75. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92737-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoneburner R. L., Des Jarlais D. C., Benezra D., Gorelkin L., Sotheran J. L., Friedman S. R., Schultz S., Marmor M., Mildvan D., Maslansky R. A larger spectrum of severe HIV-1--related disease in intravenous drug users in New York City. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.3187532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


