Abstract
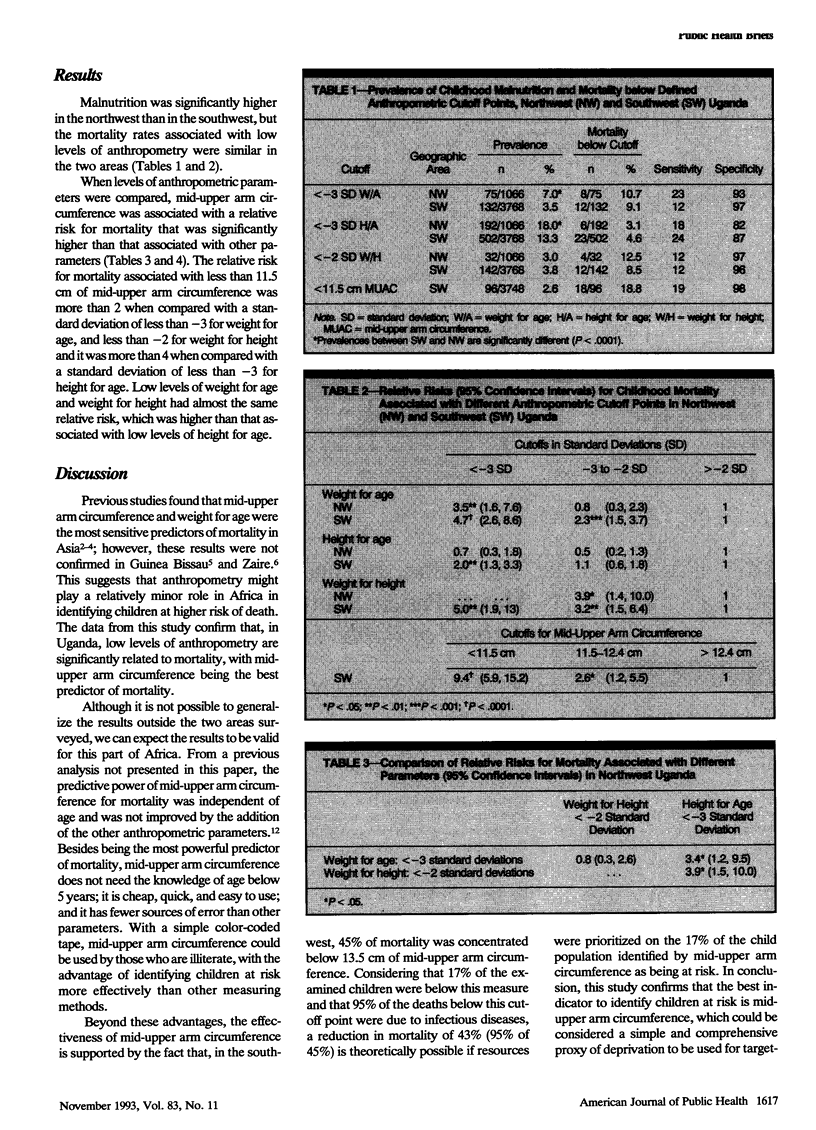
Two longitudinal studies were carried out in northwest and southwest Uganda to examine the relationship between anthropometry and childhood mortality. Although the prevalence of malnutrition was significantly different between the two geographic areas, the relative risk for mortality associated with low levels of anthropometry was similar. When the anthropometric parameters were compared among each other, mid-upper arm circumference was found to be the most powerful predictor of mortality. The findings of this study confirm that mid-upper arm circumference is the indicator of choice to identify children at higher risk of death.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bairagi R. Why the mortality discriminating power of anthropometric indicators differs among populations. J Trop Pediatr. 1985 Feb;31(1):63–64. doi: 10.1093/tropej/31.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briend A., Wojtyniak B., Rowland M. G. Arm circumference and other factors in children at high risk of death in rural Bangladesh. Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):725–728. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Chowdhury A., Huffman S. L. Anthropometric assessment of energy-protein malnutrition and subsequent risk of mortality among preschool aged children. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Aug;33(8):1836–1845. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.8.1836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielmann A. A., McCord C. Weight-for-age as an index of risk of death in children. Lancet. 1978 Jun 10;1(8076):1247–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedman L., Sterky G., Mellander L., Wall S. Anthropometry and subsequent mortality in groups of children aged 6-59 months in Guinea-Bissau. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 Aug;46(2):369–373. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/46.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


