Abstract
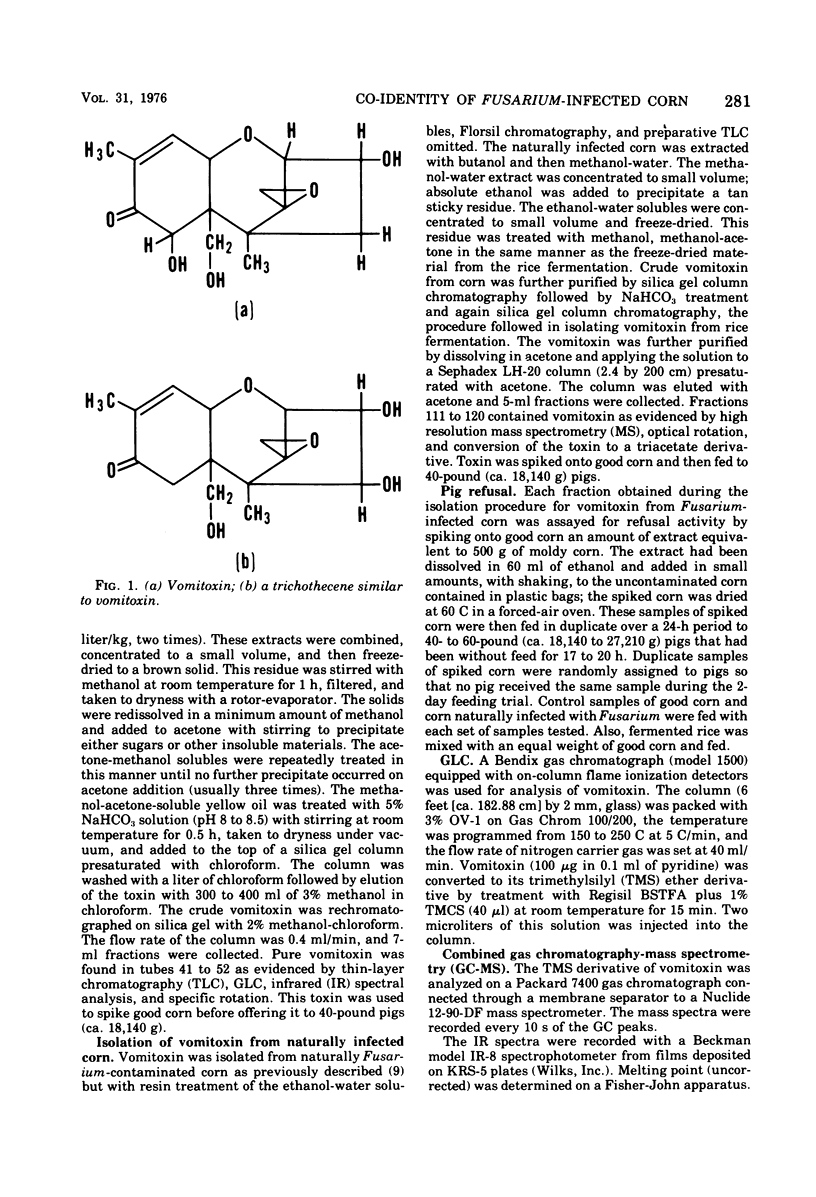
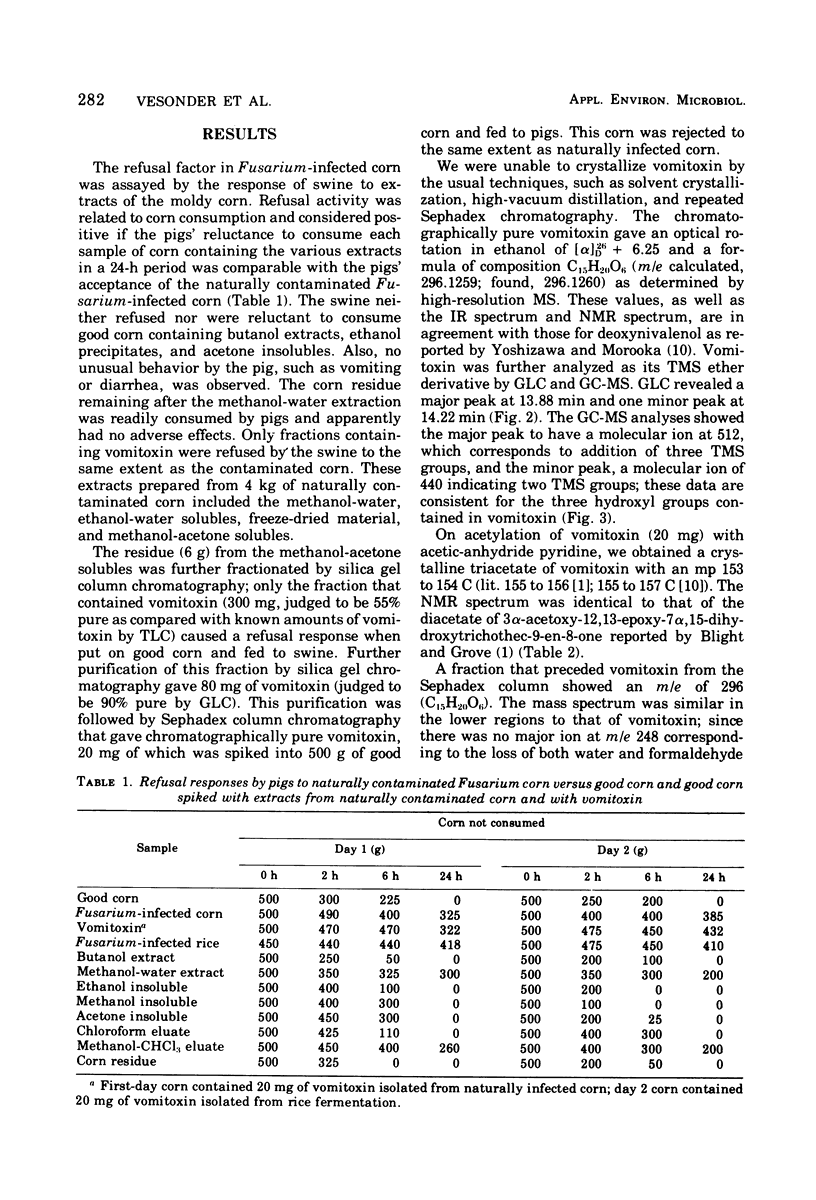
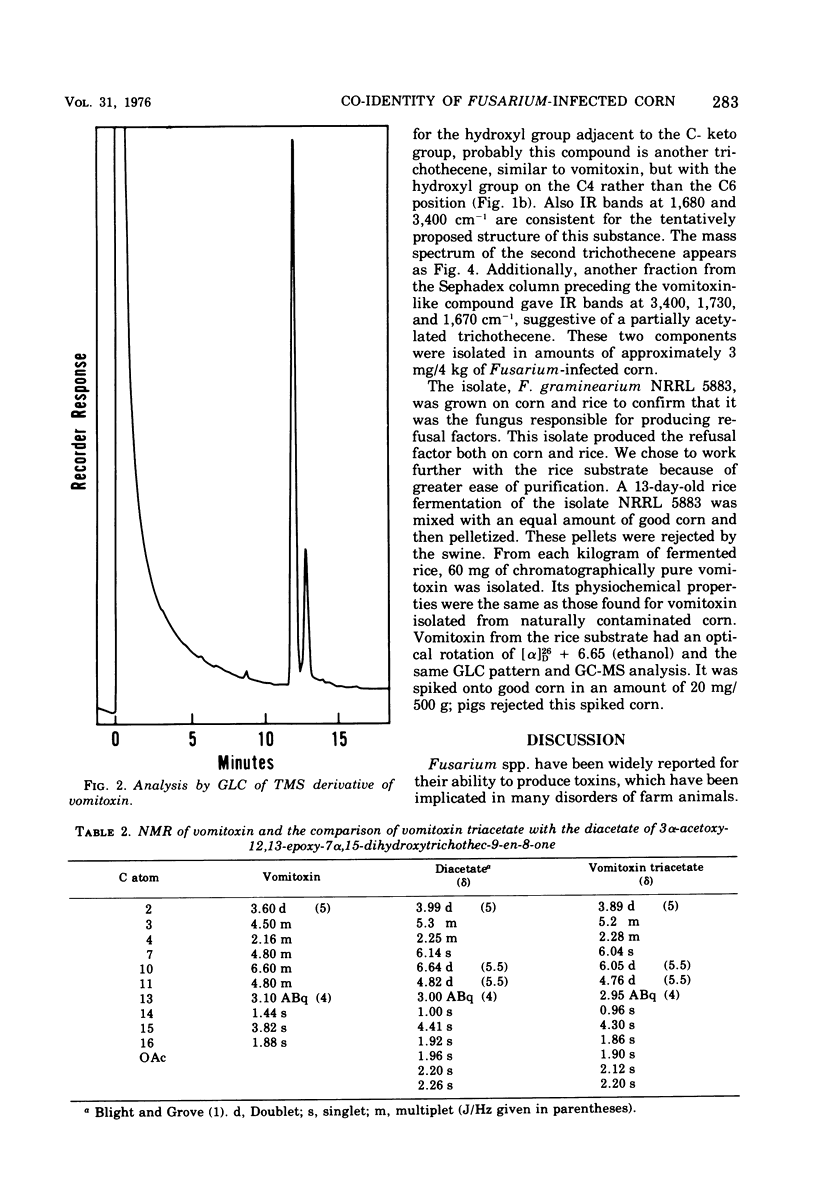
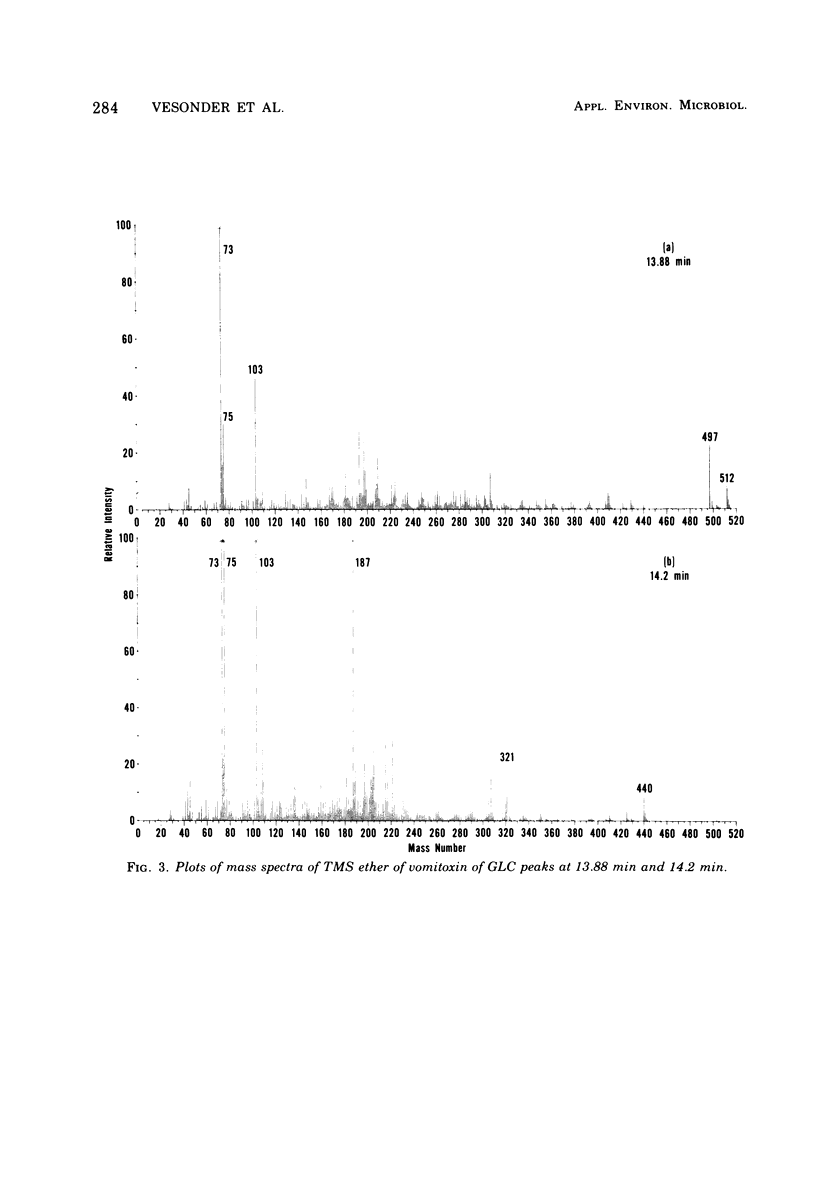
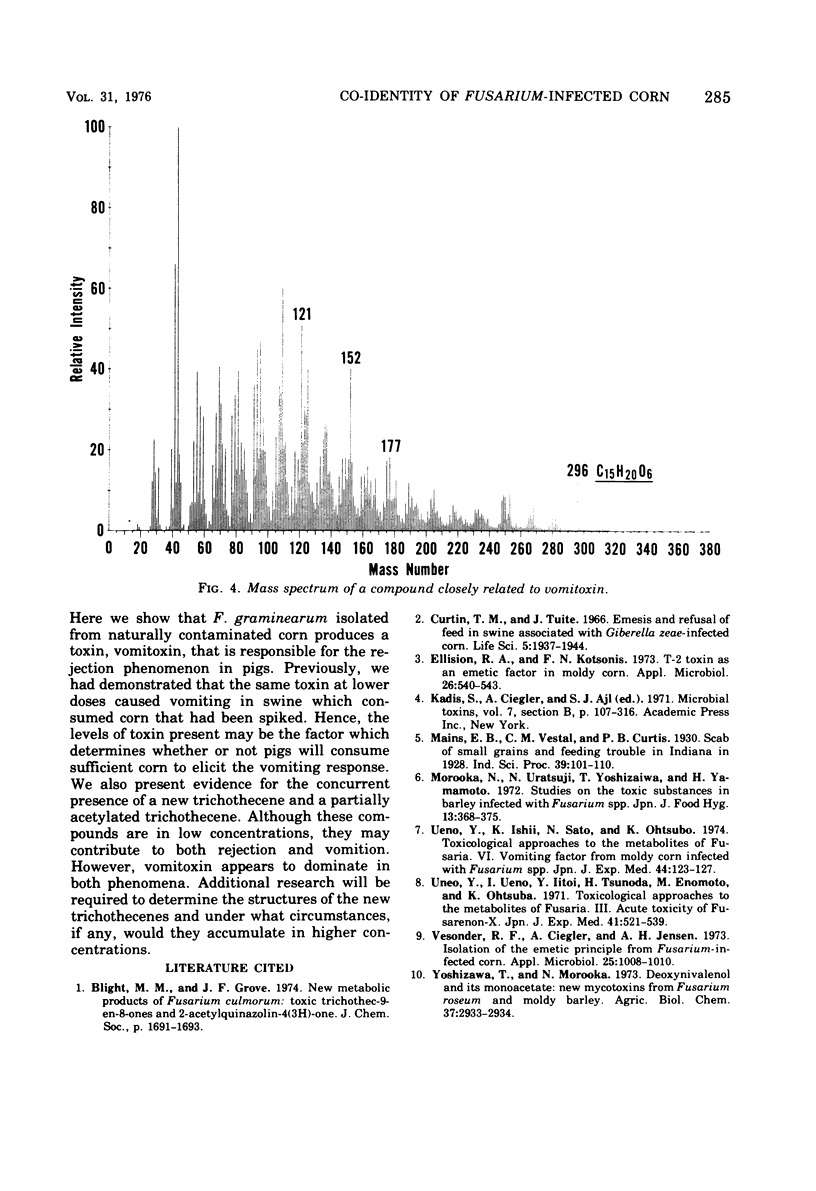
The structure of vomitoxin isolated from Fusarium-contaminated corn was proved to be 3,7,15-trihydroxy-12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-en-8-one. This same toxin is responsible for the "refusal phenomenon" exhibited by swine fed contaminated corn. In addition, two new substances believed to be trichothecenes were isolated from naturally infected corn. Vomitoxin was also isolated from rice inoculated with F. graminearium NRRL 5883.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blight M. M., Grove J. F. New metabolic products of Fusarium culmorum: toxic trichothec-9-en-8-ones and 2-acetylquinazolin-4(3h)-one. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1974;0(14):1691–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. A., Kotsonis F. N. T-2 toxin as an emetic factor in moldy corn. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.540-543.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Ishii K., Sato N., Otsubo K. Toxicological approaches to the metabolites of Fusaria. VI. Vomiting factor from moldy corn infected with Fusarium spp. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Feb;44(1):123–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Ueno I., Iitoi Y., Tsunoda H., Enomoto M. Toxicological approaches to the metabolites of Fusaria. 3. Acute toxicity of fusarenon-X. Jpn J Exp Med. 1971 Dec;41(6):521–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesonder R. F., Ciegler A., Jensen A. H. Isolation of the emetic principle from Fusarium-infected corn. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):1008–1010. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.1008-1010.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



