Abstract
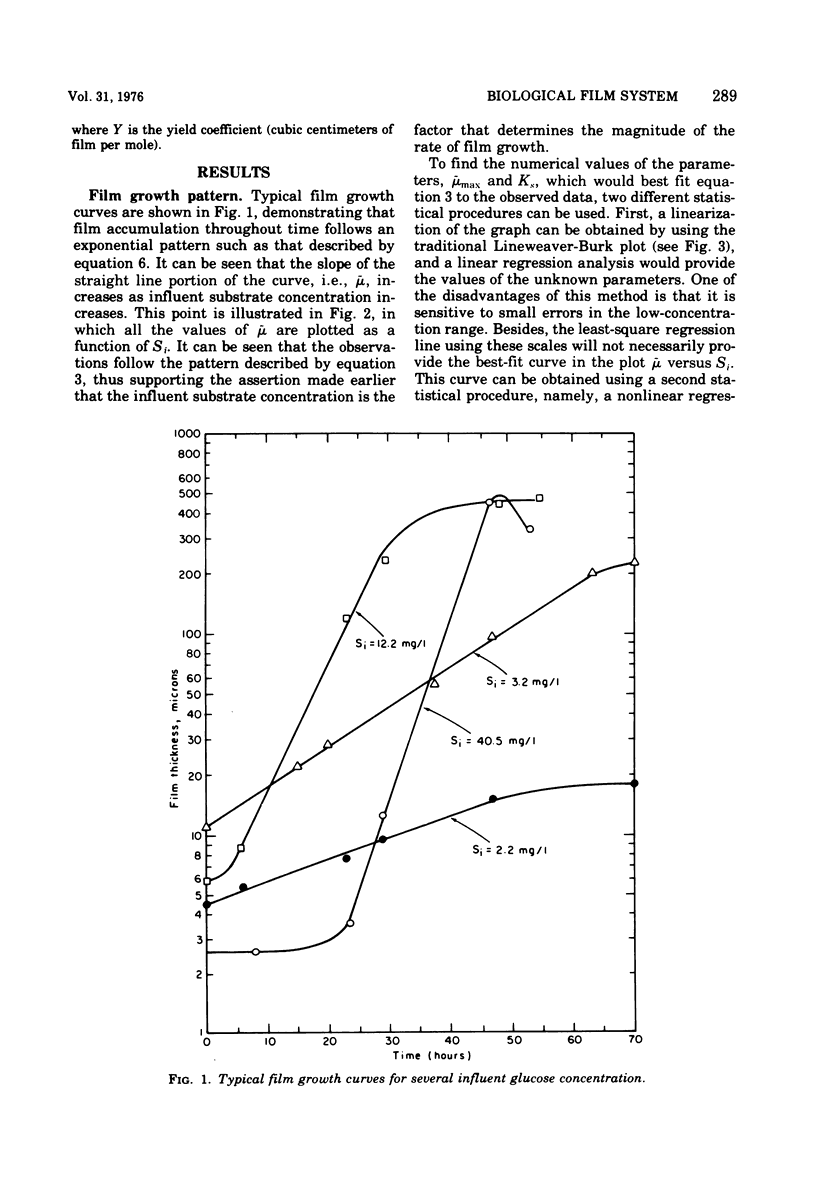
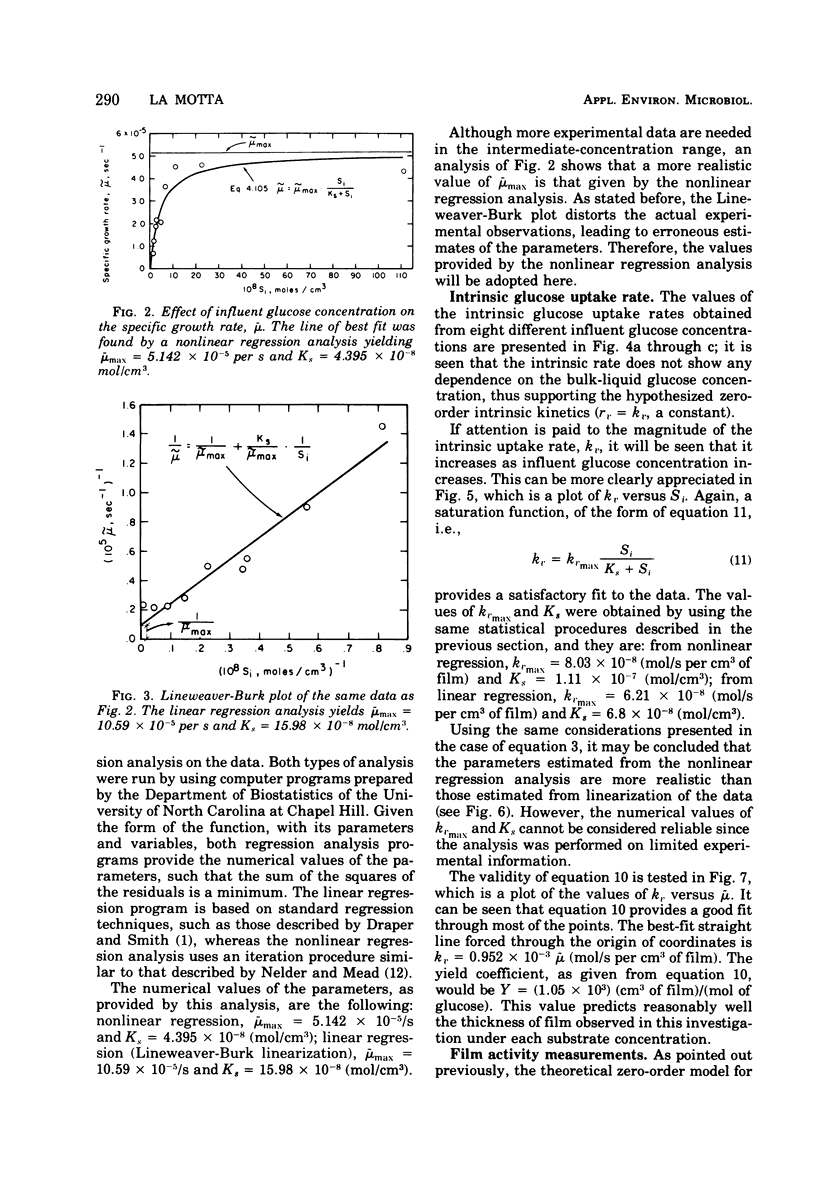
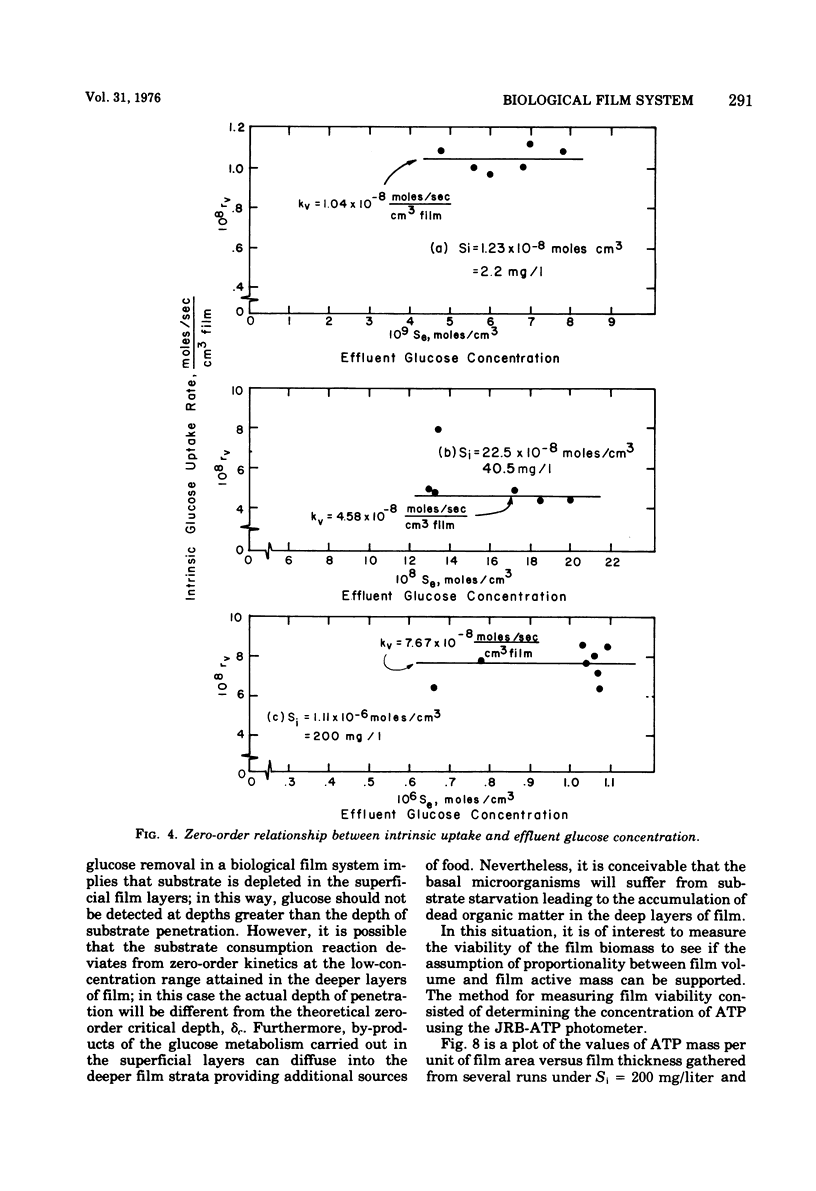
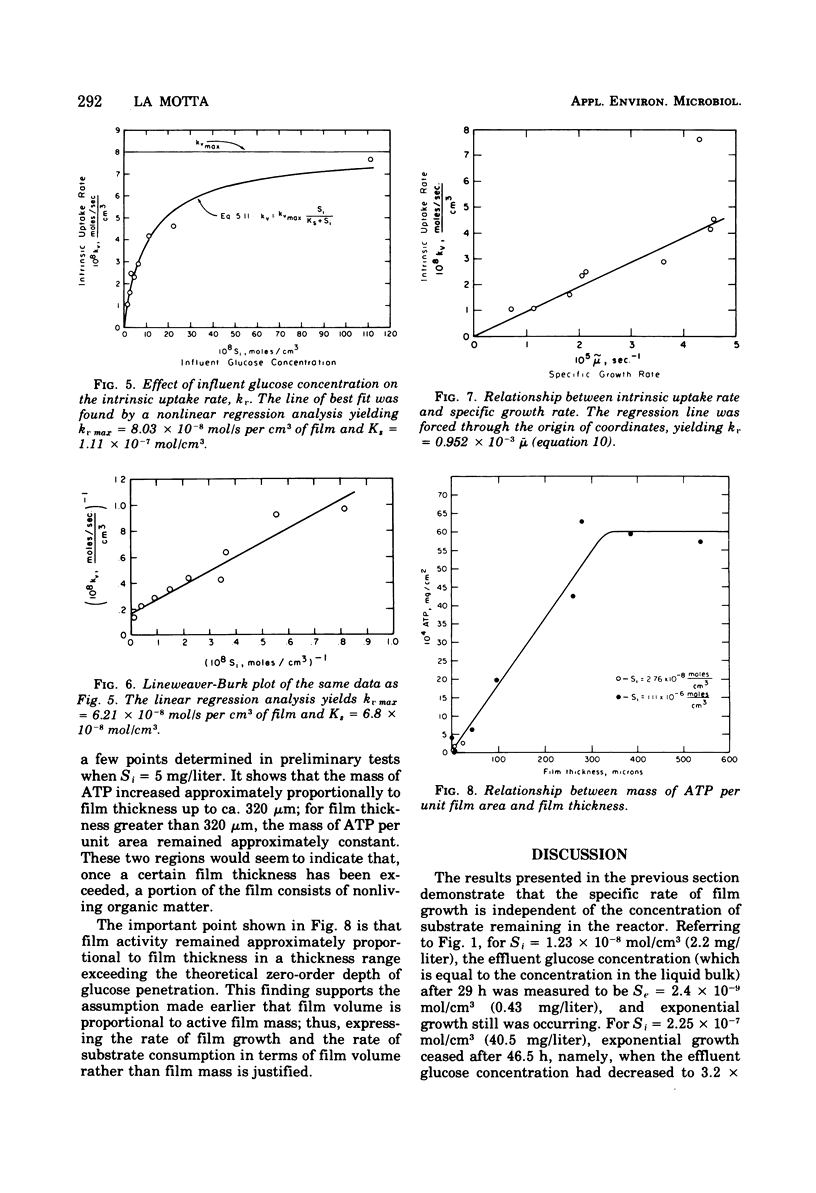
The rates of growth and substrate uptake in a biological film continuous-flow reactor were studied. The experiments were performed with high fluid velocities to bring the reactor operation to the reaction-controlled regime, thus avoiding external diffusional resistances. The glucose uptake experiments were performed with small film thicknesses so that full substrate penetration within the entire film thickness could be obtained. In this way, the catalyst effectiveness factor was 1.0 and the observed rate was the true, or intrinsic, rate. The results of the experiments indicate that both the intrinsic rate of substrate uptake and the rate of film growth are independent of the substrate concentration remaining in the reactor (zero-order reactions). However, the value of the initial substrate concentration when the film is in the early stages of growth defines the magnitude of both the rate of uptake and growth. This effect of the initial substrate concentration follows a saturation-function pattern.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaudy A. F., Jr, Obayashi A., Gaudy E. T. Control of growth rate by initial substrate concentration at values below maximum rate. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1041-1047.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann L. Influence of turbulence on the activity of bacterial slimes. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1967 Jun;39(6):958–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn R. C., Ray A. D. Effects of thickness on bacterial film. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1973 Nov;45(11):2302–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Ven Dedem G., Moo-Young M. Oxygen transfer into mycelial pellets. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1973 Jan;15(1):27–45. doi: 10.1002/bit.260150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson T. G., Snaddon D. M. Biological oxidation of sewage by films of microorganisms. Air Water Pollut. 1966 Nov-Dec;10(11):865–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


