Abstract
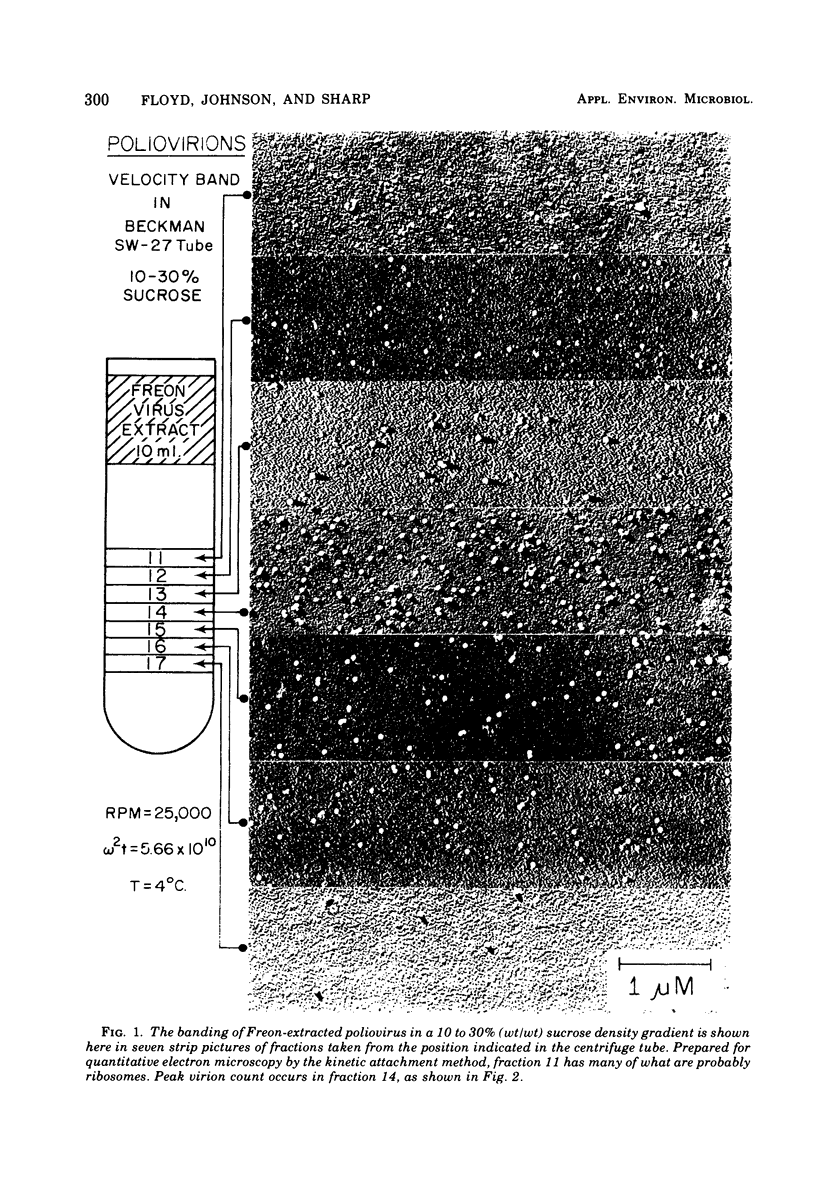
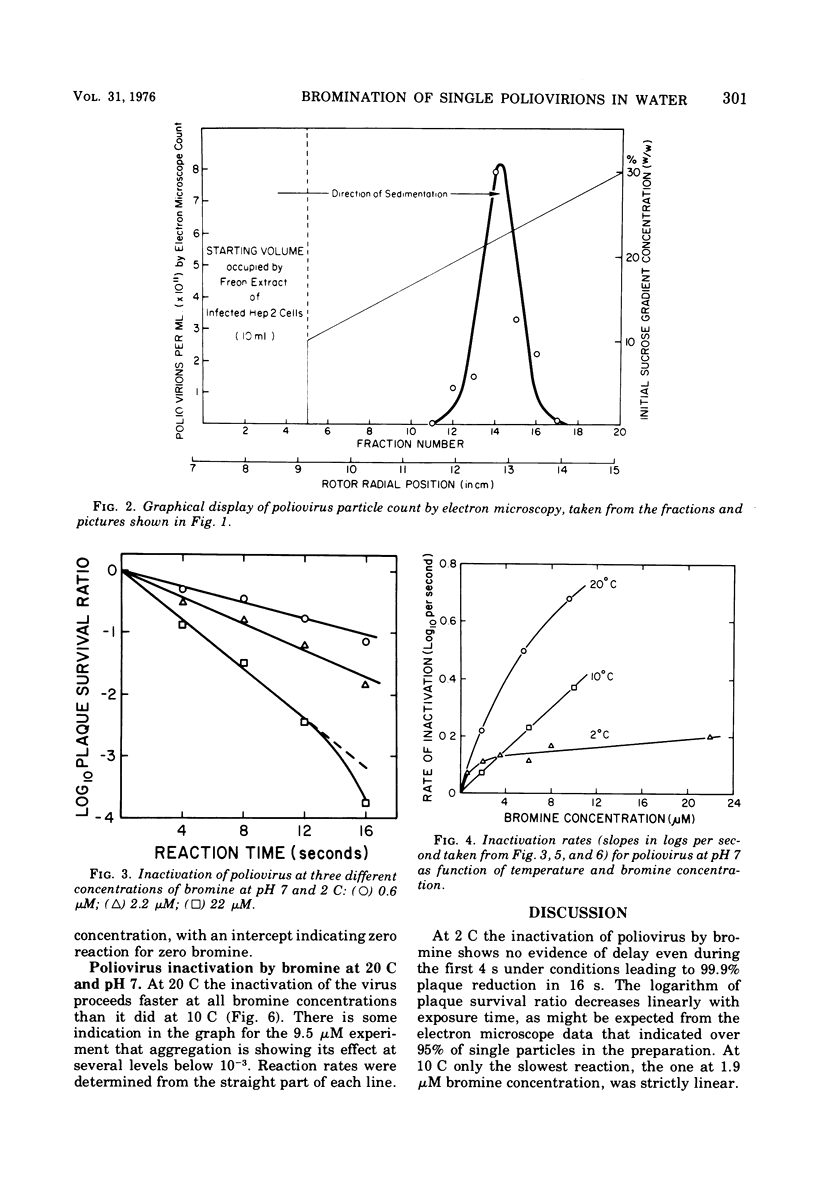
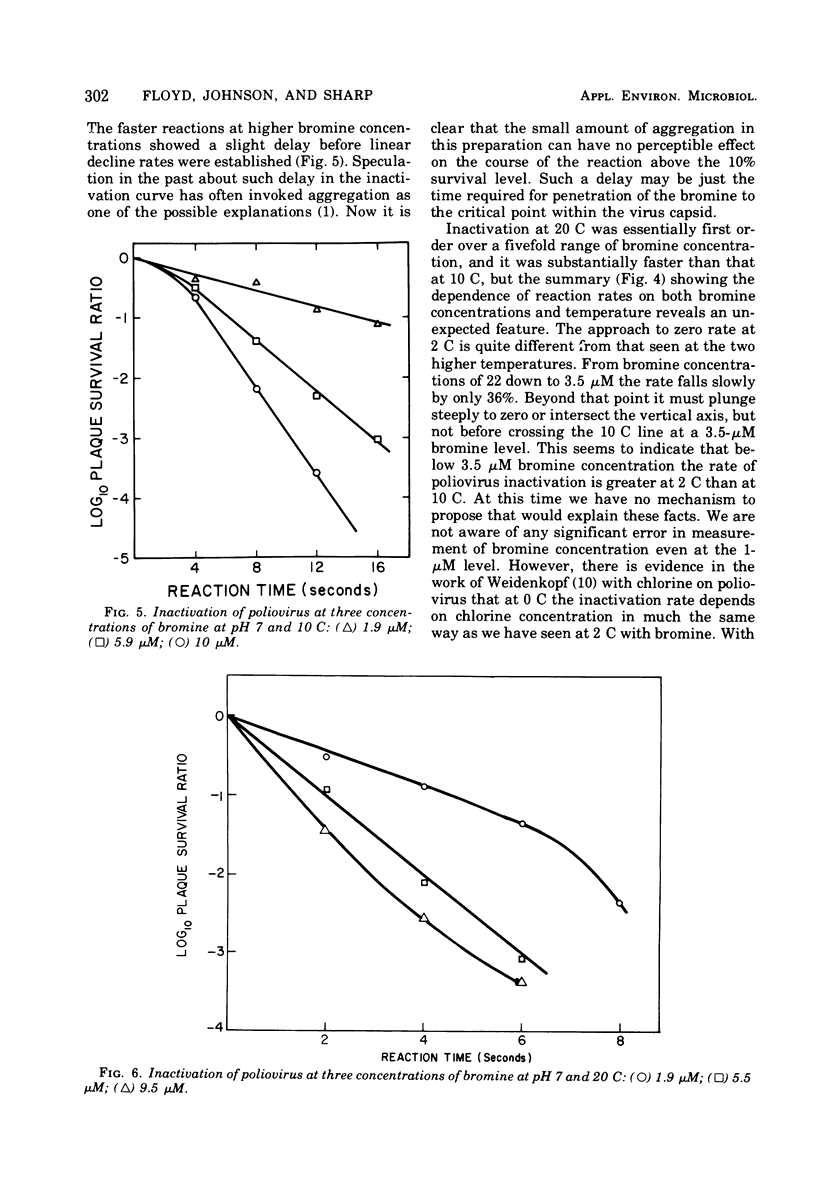
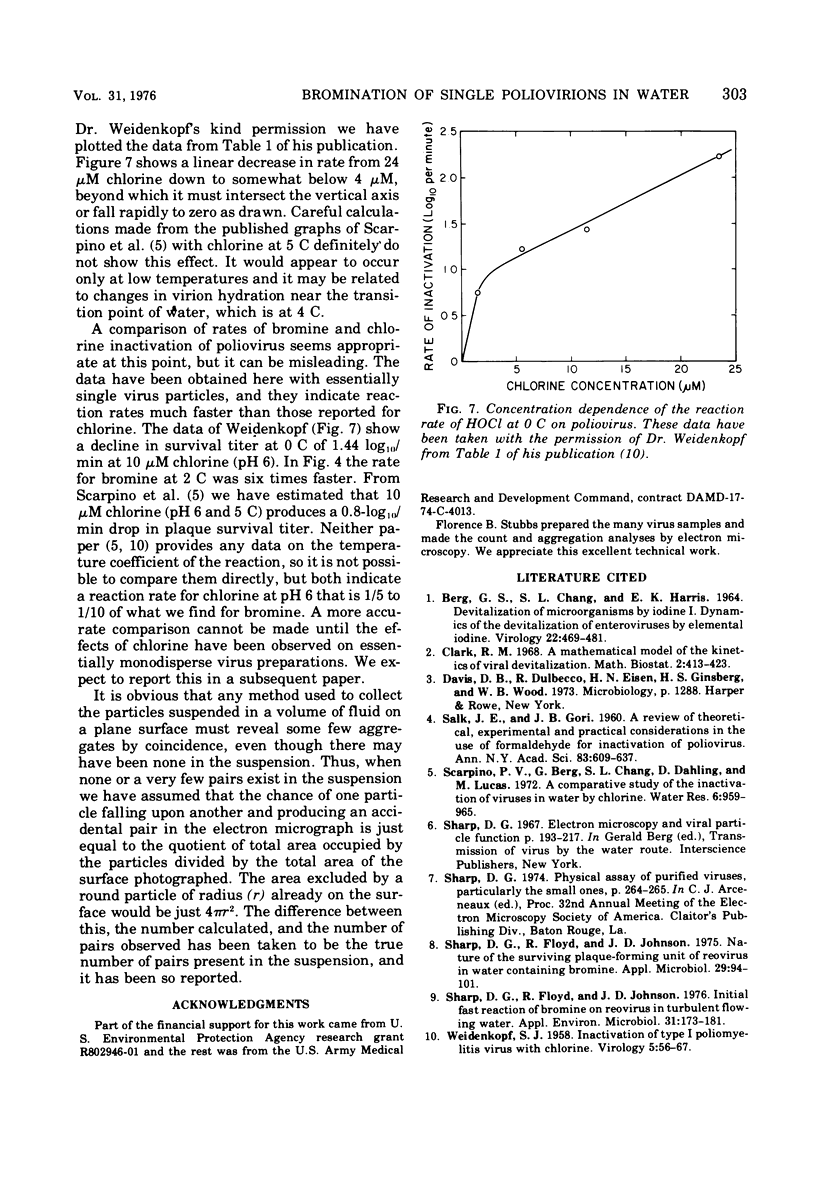
Quantitative electron microscopy shows that Freon-extracted poliovirus, velocity banded in a sucrose gradient, contains over 95% single particles. This well-dispersed virus reacts quite rapidly with bromine in turbulent flowing water, losing plaque titer at the rate of one log10 unit in 10s at pH 7, 2 C, and at a bromine concentration of 2.2 muM. At 10 and 20 C the rate of disinfection (log10 plaque-forming units per second) is faster, and at both temperatures it increases in approximately linear fashion with increasing bromine concentration. At 2 C such a linear relationship is not observed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG G., CHANG S. L., HARRIS E. K. DEVITALIZATION OF MICROORGANISMS BY IODINE. I. DYNAMICS OF THE DEVITALIZATION OF ENTEROVIRUSES BY ELEMENTAL IODINE. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:461–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALK J. E., GORI J. B. A review of theoretical, experimental, and practical considerations in the use of formaldehyde for the inactivation of poliovirus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 13;83:609–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb40933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. G., Floyd R., Johnson J. D. Initial fast reaction of bromine on reovirus in turbulent flowing water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):173–181. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.173-181.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. G., Floyd R., Johnson J. D. Nature of the surviving plaque-forming unit of reovirus in water containing bromine. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.94-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDENKOPF S. J. Inactivation of type 1, poliomyelitis virus with chlorine. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):56–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



