Abstract
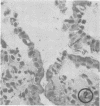
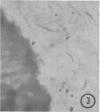
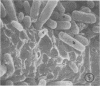
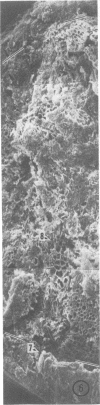
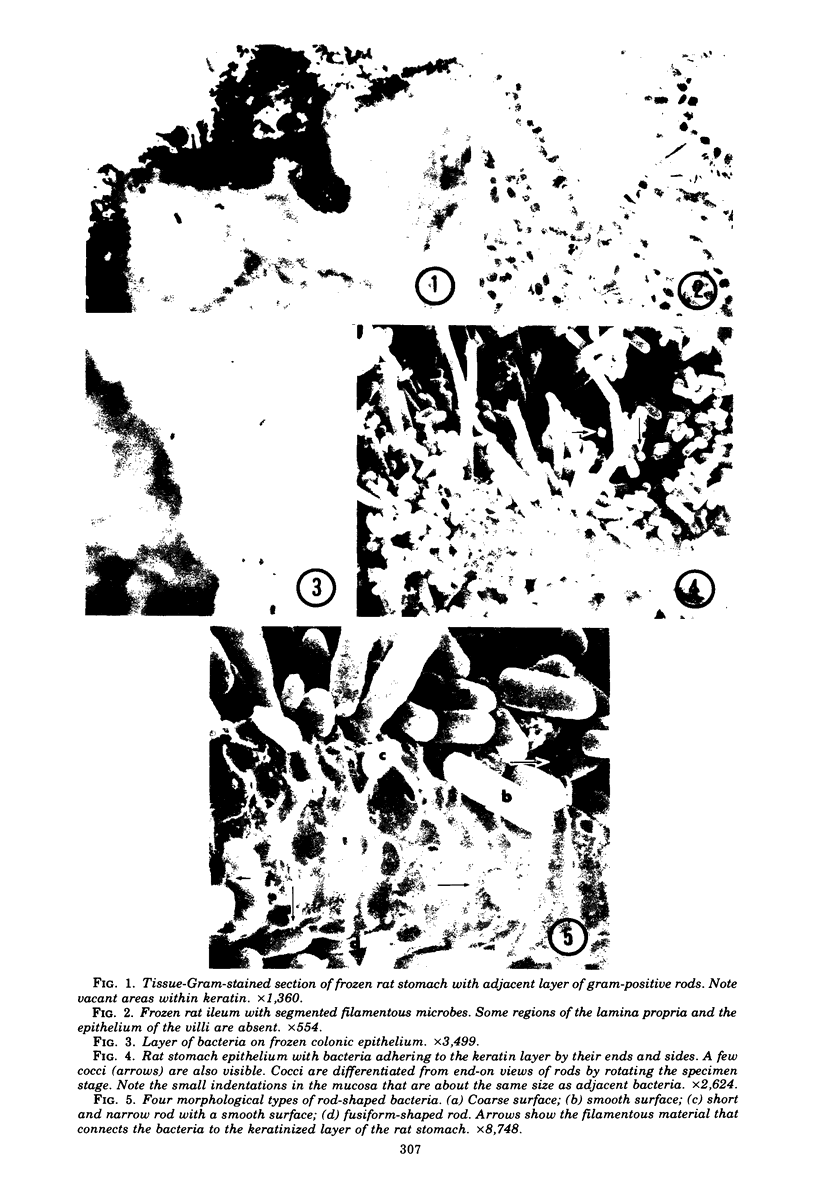
The use of frozen rat gastrointestinal tissue samples for both the recovery of viable bacteria and for observation of microbial communities associated with the tissue was investigated. A decrease of 1 log in lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, and anaerobes was observed when the numbers of bacteria recoverable from frozen tissue (stored 7 to 9 days) were compared to those recoverable from fresh nonfrozen tissue (zero time control). However, freezing did not appear to decrease the numbers of recoverable coliforms. Tissues, cleaved with razor blades after being frozen and stored for 7 to 9 days, showed bacterial communities situated on the mucosa and in the lumen of gastrointestinal specimens. This freezing technique preserved structures not previously observed in the gastrointestinal tract. This indicates that freezing is a good method to use to study such fragile microenvironments.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., McAllister J. S., Savage D. C. Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.666-672.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Mulcahy D., Takeuchi A., Savage D. C. Location and description of spiral-shaped microorganisms in the normal rat cecum. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.184-192.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Savage D. C. Habitat, succession, attachment, and morphology of segmented, filamentous microbes indigenous to the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):948–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.948-956.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach W. D., Lee A., Stubbs R. P. Localization of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract: a possible explanation of intestinal spirochaetosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):961–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.961-972.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson H., Irvin R., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Ultrastructure and adhesion properties of Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):278–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.278-287.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M. Lysis of blue-green algae by myxobacter. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):453–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.453-461.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Kawal Y., Mutai M. Behavior of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of the rat stomach in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.173-179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]