Abstract
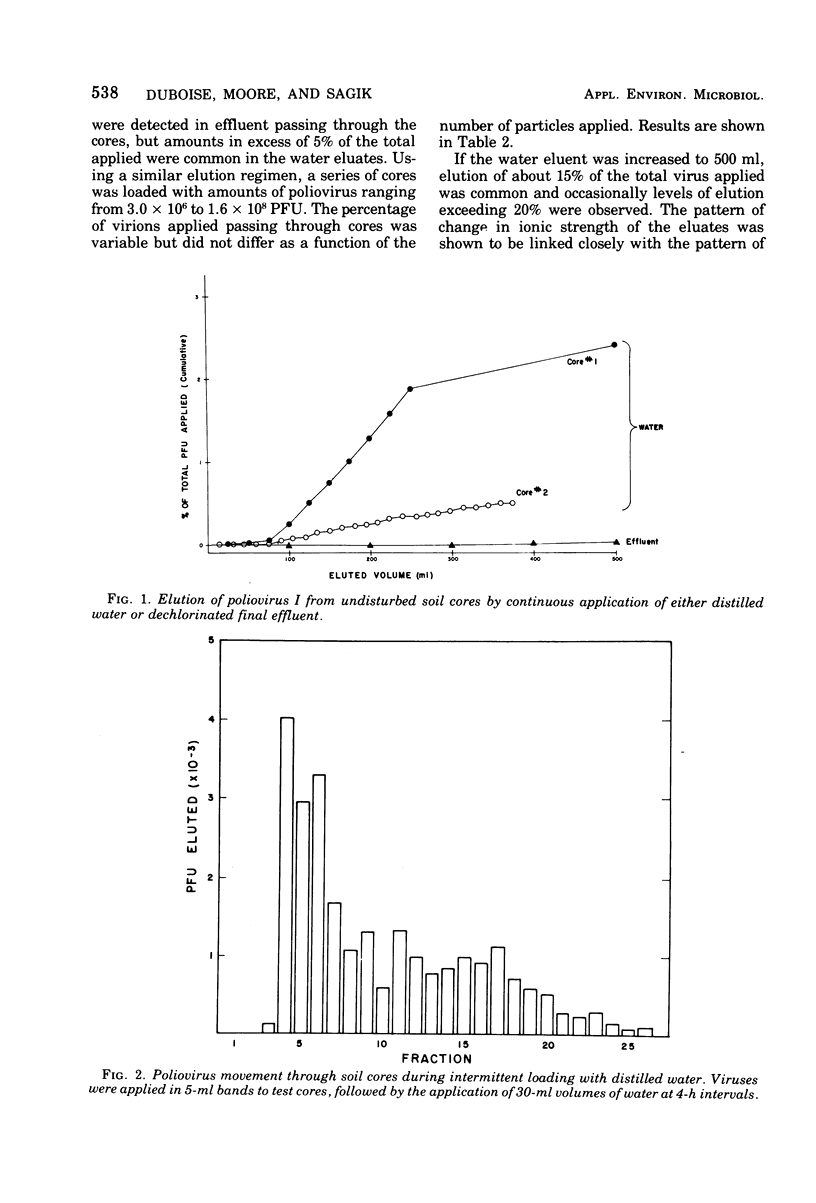
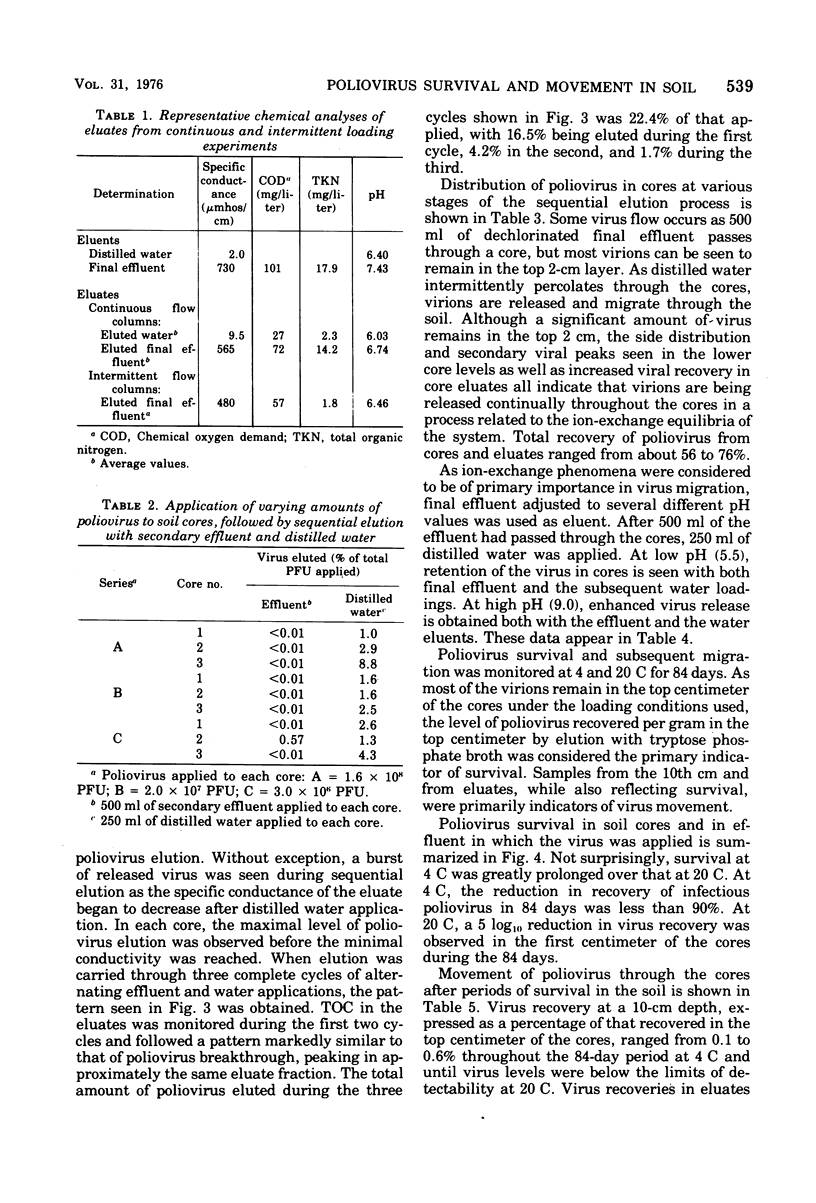
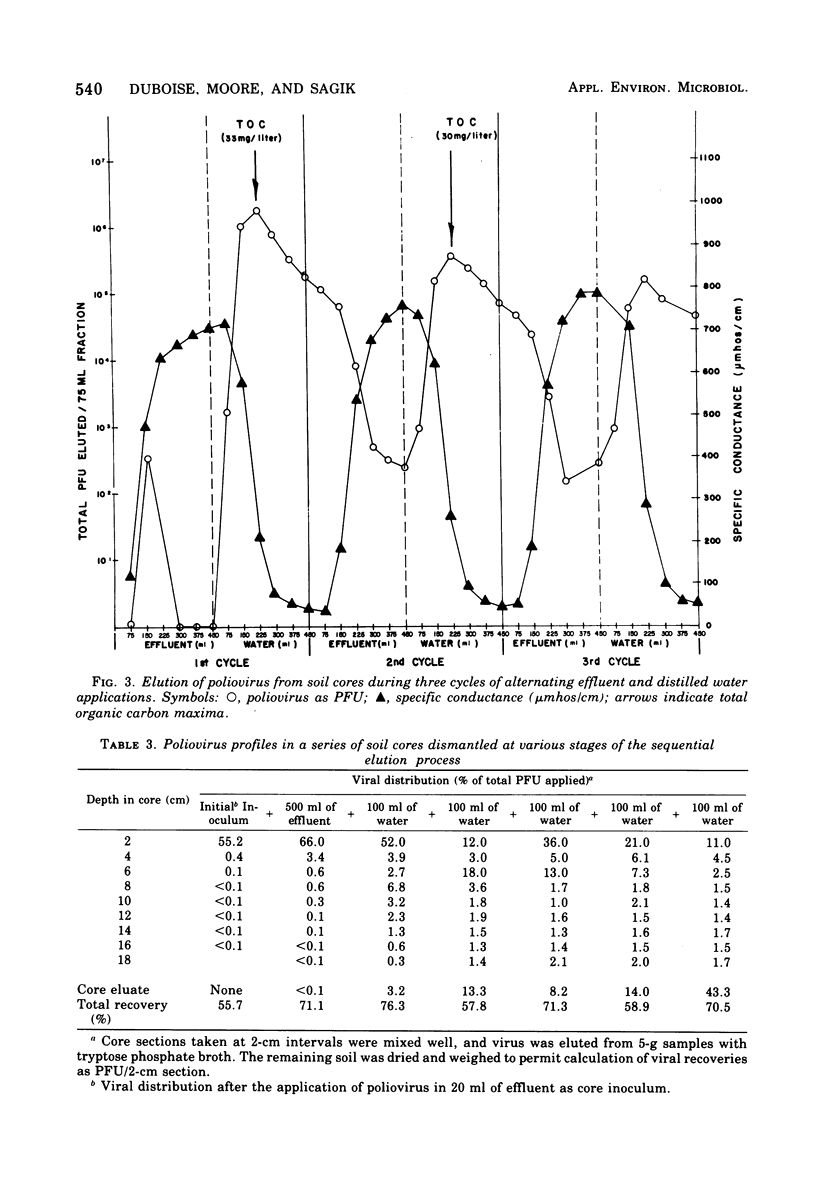
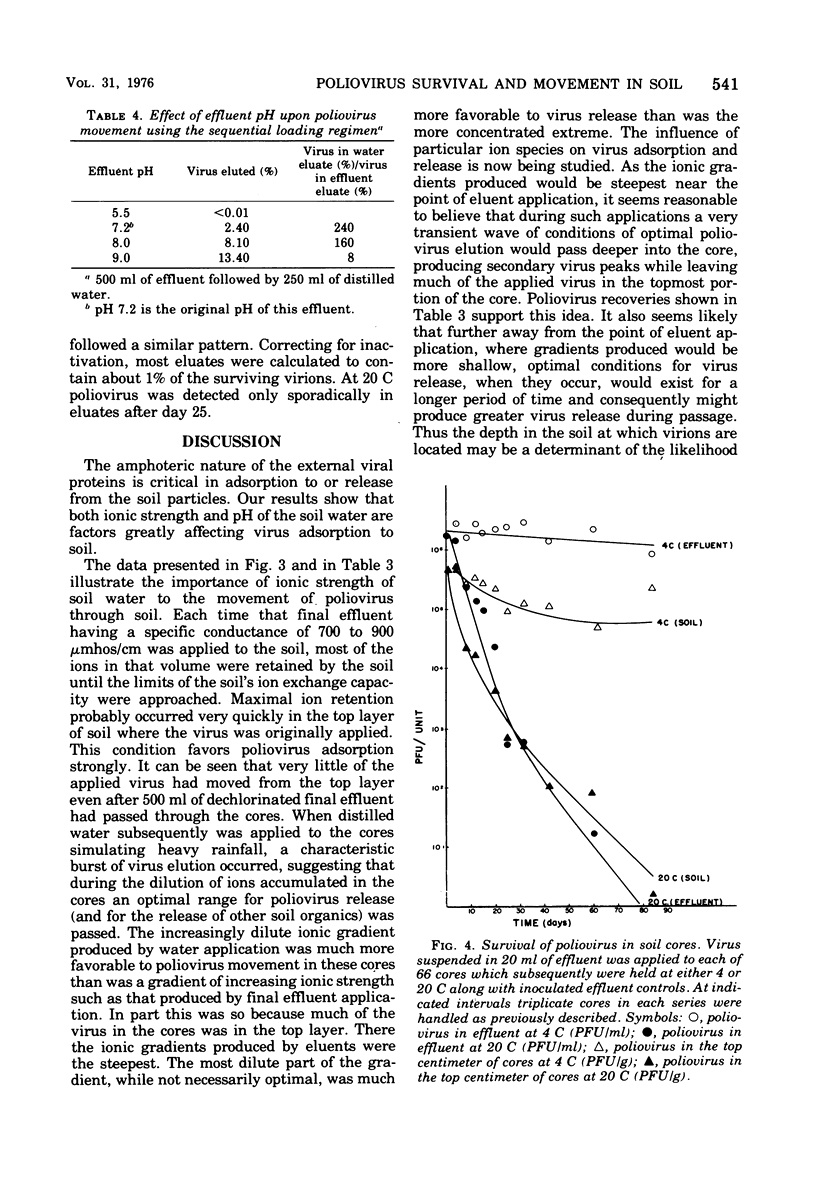
Movement of poliovirus I (Chat) through nonsterile core samples of a sandy forest soil was monitored, using several regimens of loading with either dechlorinated final effluent from an operating activated sludge treatment plant or distilled water. Stimulated cycles of rainfall and effluent applications, resulting in ionic gradients, were shown to affect virus movement. Such studies indicate that poliovirus applied in effluents may move considerable distances through this soil after rainfall. Survival of poliovirus in the soil at 4 and 20 C has been monitored for 84 days. During this period, the capacity of the virus to migrate is unchanged.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malina J. F., Jr, Ranganathan K. R., Sagik B. P., Moore B. E. Poliovirus inactivation by activated sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1975 Aug;47(8):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub S. A., Sagik B. P. Association of enteroviruses with natural and artificially introduced colloidal solids in water and infectivity of solids-associated virions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):212–222. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.212-222.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W., Pierce L. V. Demonstration of virus in groundwater after effluent discharge onto soil. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):751–757. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.751-757.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



