Abstract
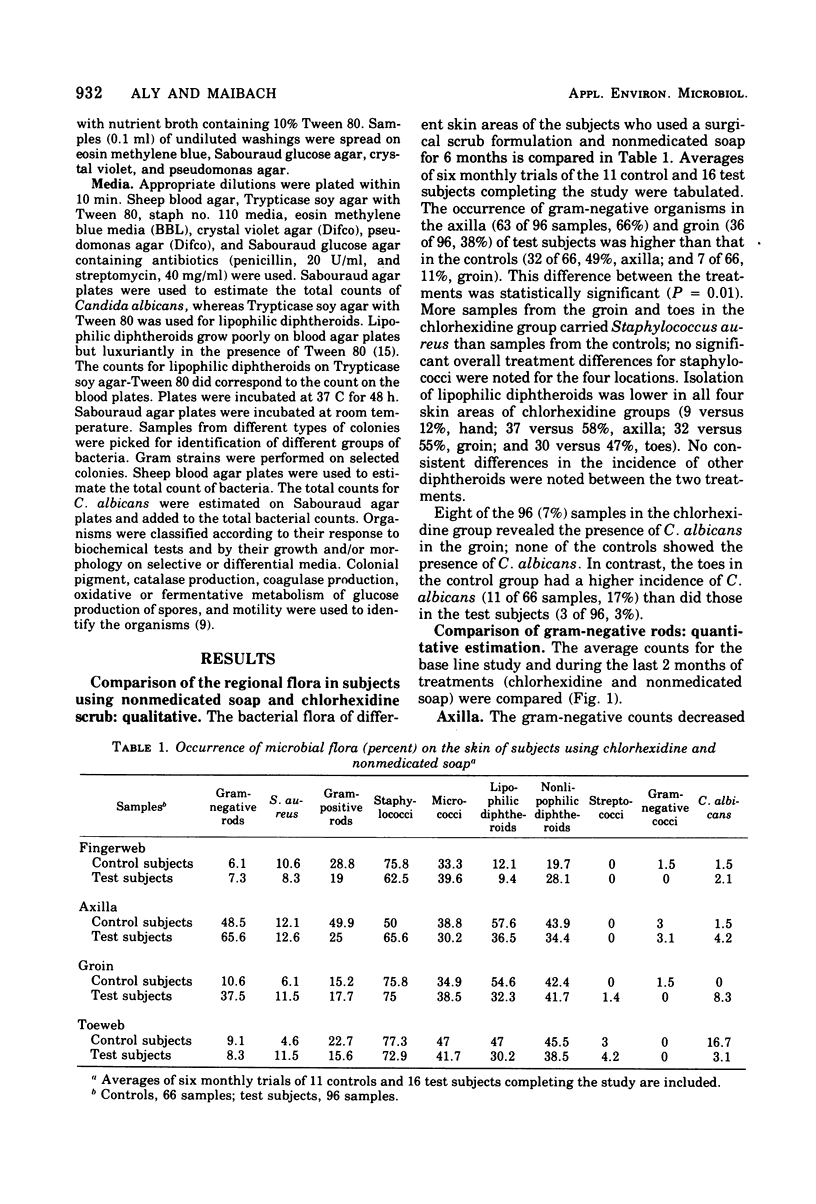
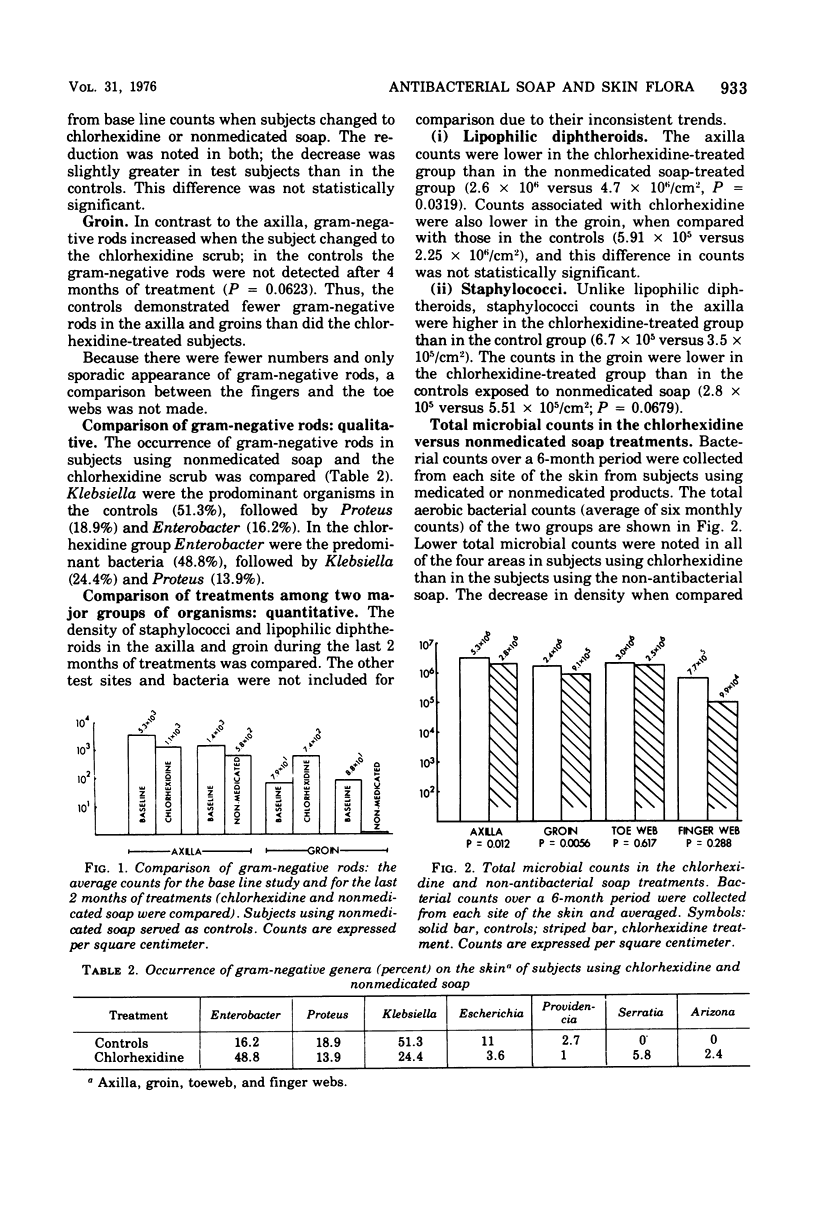
The qualitative and semiquantitative changes in the aerobic microbial flora of normal skin with the prolonged use of a chlorhexidine scrub (6 months) were investigated. More samples in the chlorhexidine scrub group had gram-negative bacilli in their axilla (63 of 96, 66%) and groin (36 of 96, 38%) than the controls (32 of 66, 49%, for axilla and 7 of 66, 11%, for groin; P = 0.01). Klebsiella and Enterobacter were the predominant organisms in the control and chlorhexidine groups, respectively. The chlorhexidine scrub produced a reduction in the total aerobic counts in the axilla, groin, and between the toes and the fingers. Fewer samples from the chlorhexidine-treated areas revealed the presence of lipophilic diphtheroids than did the controls. Lipophilic diphteroids were also reduced quantitatively in the groin and axilla with chlorhexidine treatment. No consistent pattern for the other major groups of bacteria was noted between the treatments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Rahman R., Shinefield H. R., Mandel A. D. Correlation of human in vivo and in vitro cutaneous antimicrobial factors. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):579–583. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Shinefield H. R., Strauss W. G. Survival of pathogenic microorganisms on human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Apr;58(4):205–210. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12539912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly R., Maibach H. I., Strauss W. G., Shinefield H. R. Effects of a systemic antibiotic on nasal bacterial ecology in man. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.240-244.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEEUWKES H. The use of chlorhexidine. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1958;24(1):49–62. doi: 10.1007/BF02548431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E., FRANCIS J., MARTIN A. R., ROSE F. L., SWAIN G. 1:6-Di-4'-chlorophenyldiguanidohexane (hibitane); laboratory investigation of a new antibacterial agent of high potency. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Jun;9(2):192–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00840.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forfar J. O., Gould J. C., Maccabe A. F. Effect of hexachlorophane on incidence of staphylococcal and gram-negative infection in the newborn. Lancet. 1968 Jul 27;2(7561):177–179. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92618-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyden J. J., Marples R. R., Mills O. H., Jr, Kligman A. M. Gram-negative folliculitis--a complication of antibiotic therapy in acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 1973 Jun;88(6):533–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1973.tb08015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light I. J., Sutherland J. M., Cochran M. L., Sutorius J. Ecologic relation between Staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas in a nursery population. Another example of bacterial interference. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 6;278(23):1243–1247. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806062782301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R., Williamson P. Effects of systemic demethylchlortetracycline on human cutaneous microflora. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):228–234. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.228-234.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBELL G., PILLSBURY D. M., DE SAINT PHALLE M., GINSBURG D. Factors affecting the rapid disappearance of bacteria placed on the normal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1950 Apr;14(4):247–264. doi: 10.1038/jid.1950.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. Characterization of human cutaneous lipophilic diphtheroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):433–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taplin D., Zaias N., Rebell G. Environmental influences on the microbiology of the skin. Arch Environ Health. 1965 Oct;11(4):546–550. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1965.10664255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


