Abstract
Diversity and intensity of intellectual and physical activities seem to have an inverse relationship with the extent of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To study the interaction between an active lifestyle and AD pathology, female TgCRND8 mice carrying human APPswe+ind were transferred into enriched housing. Four months of continuous and diversified environmental stimulation resulted in a significant reduction of β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques and in a lower extent of amyloid angiopathy. Neither human amyloid precursor protein (APP) mRNA/protein levels nor the level of carboxy-terminal fragments of APP nor soluble Aβ content differed between both groups, making alterations in APP expression or processing unlikely as a cause of reduced Aβ deposition. Moreover, DNA microarray analysis revealed simultaneous down-regulation of proinflammatory genes as well as up-regulation of molecules involved in anti-inflammatory processes, proteasomal degradation, and cholesterol binding, possibly explaining reduced Aβ burden by lower aggregation and enhanced clearance of Aβ. Additionally, immunoblotting against F4/80 antigen and morphometric analysis of microglia (Mac-3) revealed significantly elevated microgliosis in the enriched brains, which suggests increased amyloid phagocytosis. In summary, this study demonstrates that the environment interacts with AD pathology at dif-ferent levels.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent form of senile dementia worldwide. It is characterized by two major histological hallmarks: senile plaques, ie, extracellular deposits mainly consisting of β-amyloid (Aβ), and neurofibrillary tangles, ie, intracellular accumulations of hyperphosphorylated tau protein.1 AD patients show progressing cognitive decline as well as noncognitive behavioral symptoms such as wandering, sleep disturbance, and physical aggression.2 There are various risk factors for AD including age, family history, or apolipoprotein E ε4 genotype.3 Epidemiological studies additionally suggest that the amount of time spent on intellectual and physical activities negatively correlates with the extent of cognitive decline and even risk of developing AD.4,5 Although it cannot be excluded that lower activity levels are early subclinical symptoms, one should consider them also as a risk factor. In line with this assumption is the use of cognitive training as a rehabilitative measure resulting in deceleration of dementia progress. However, the underlying molecular pathways are essentially unknown.
In laboratory rodents cognitive, physical, and social stimulation can be regulated by altering housing conditions. It is well established that living in an enriched environment provided by additional structural or social stimuli may increase locomotor and exploratory activity, improve learning and memory performance, increase dendritic sprouting and synapse formation in the neocortex and hippocampus as well as neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus,6 and affects behavioral, endocrinological, and immunological parameters.7 Environmental enrichment also facilitates recovery from acute brain lesions, again accompanied by structural changes such as increased dendritic branching and spine density,8 tightly controlled by a complex concert of a variety of genes and proteins.9 Studies regarding the effect of enriched housing (EH) on animal models of neurodegenerative diseases have demonstrated that EH delays disease progression in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease10 or protects mice from pharmacologically induced Parkinsonism.11 Concerning AD, a few studies on the effects of environmental stimulation produced partly contradictory results. Taken together, these studies strongly suggest that EH affects both cognitive abilities12,13 and the development of an AD-like pathology13–16 in AD mouse models, although reasons for discrepant results and involved mechanisms have remained unclear. We kept female TgCRND8 mice under standard housing (SH) and EH conditions from day 30 until 5 months of age to gain insight into mechanisms underlying environmentally evoked effects on Aβ pathology. Compared to other murine models of AD, TgCRND8 mice exhibit Aβ plaques very early (∼3 months), accompanied by Aβ deposition in vessel walls, astrogliosis/microgliosis, and cognitive deficits,17,18 which are typical symptoms associated with AD.
Materials and Methods
Animals and Housing Conditions
We investigated 18 female transgenic mice of the TgCRND8 line that carries a double-mutated form of the human amyloid precursor protein 695 (APP695), the Swedish and Indiana mutations, under control of the Syrian hamster prion promoter, on a hybrid C57BL/6-C3H/HeJ background.17,18 At 30 days of age, animals were transferred to the experimental housing conditions. Nine transgenic mice were housed (together with wild-type littermates that were not further analyzed for the present study) in groups of three or four in SH conditions, nine transgenics were housed in equally composed groups in EH conditions (at least one animal of each genotype per cage). SH consisted of transparent polycarbonate cages (38 cm × 22 cm × 15 cm) with sawdust as bedding material. Enriched cages contained further nesting material, a plastic inset, and a wooden scaffolding. In addition, EH animals had access to a second, so-called stimulus cage during the dark phase that was connected to the home cage by a Plexiglas tunnel. The stimulus cage contained different stimulus objects divided in five categories: 1) permanently, a sisal rope and gnawing wood were available. In addition, one object of the categories 2) tunnels, 3) balls, 4) soft materials, and 5) varied locomotive substrates including wooden ramps and ladders, plastic stairs, as well as runningwheels were inside. Every day, one stimulus object of a daily switching category was exchanged to expose EH mice to novel environmental stimulation. A photoperiod of a 12-hour light/dark cycle was maintained. All experimental procedures were in accordance with the guidelines of the local animal care commission.
Brain Tissue Preparation
Mice were decapitated at 150 days of age. Brains were removed and one hemisphere was fixed in 4% buffered formaldehyde for 24 hours followed by dehydration and paraffin embedding. The other hemisphere was immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total RNA and subsequently protein were extracted from the same homogenized tissue of the whole cerebral hemisphere (without cerebellum and brain stem) using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was DNase-treated and cleaned. RNA quality was assessed by Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA). Proteins were dissolved in 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Because of loss of one pellet, the number of SH mice was eight for RNA and protein analyses.
Immunohistochemistry
For Aβ staining three pairs of 2-μm sagittal brain sections of each transgenic animal were pretreated with formic acid and automatically stained in a TechMate instrument (DAKO, Hamburg, Germany) with 6F/3D anti-Aβ monoclonal antibody to residues 8 to 17 (1:100, DAKO) followed by the DAKO StreptABC complex-horseradish peroxidase conjugated Duet anti-mouse/rabbit antibody kit and development with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. For Mac-3 staining two pairs of slices were pretreated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid buffer (pH 8.5) in a vegetable steamer for 30 minutes. Primary anti-Mac-3 antibody (1:100, BD Biosciences, Heidelberg, Germany) was incubated overnight at 4°C and developed using the biotin/avidin technique. Counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. The pairs of sections (10 μm distance) were situated between 100 and 300 μm lateral from the mid-sagittal fissure. Each staining was performed in two consecutive procedures making sure that brains of both experimental groups were equally distributed in all procedures.
Quantitative Evaluation of Aβ and Mac-3 Immunoreactivity
To quantify Aβ plaque burden, neocortices and hippocampi of all stained sections were digitized (Olympus BX50, ColorView II, charge-coupled device camera; Olympus, Hamburg, Germany) under constant light and filter settings. Color images were converted to grayscale by extracting blue to gray values to obtain best contrast between positive immunoreactivity and background. A constant threshold was chosen for all images to detect immunoreactive staining (analySIS 5; Soft Imaging System, Münster, Germany). Plaque number, size, and total area were determined in total neocortex and hippocampus. Absolute values of plaque burden were related to the investigated area.
The severity of amyloid angiopathy was assessed semiquantitatively in the whole cerebral hemisphere by light microscopy at ×400 magnification. Leptomeningeal and intracerebral blood vessels with a visible lumen and being at least 0.01 mm in diameter were considered positive when Aβ immunoreactivity was present in a circumferential or patchy pattern within the vessel walls. The percentage of Aβ-positive vessels was acquired in relation to total counted vessels. The observer was blind to experimental condition.
The total number of Mac-3-positive microglia/macrophages was counted in the whole neocortical and hippocampal area using ×200 magnification with a morphometrical lattice. In average 15 ± 2 optical fields per slice were examined. The number of microglial cells is given as cells per mm2. Microglia were counted by two raters who were blind to experimental condition.
Protein Analysis
Protein concentration was assessed by the DC Protein Assay (Bio-Rad, Munich, Germany). Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 peptide levels of each animal were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Biosource, Solingen, Germany). For Western blot analysis of Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42, samples were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as previously reported.19 Tris/Tricine sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of full-length APP and C-terminal fragments was performed as described by Schägger and von Jagow.20 Subsequently proteins were electrophoretically transferred onto nitrocellulose, and Western blot was performed with the antibodies 6E10 (1:1000, directed against Aβ1-16; Signet Laboratories, Dedham, MA), anti-APP C-terminal (no. 171610, 1:10,000, raised against the C-terminal 20 residues of human APP; Calbiochem/EMD Biosciences, Darmstadt, Germany), or anti-α-tubulin CP06 (1:1000, Calbiochem), followed by incubation with appropriate horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Amersham, Freiburg, Germany). Detection was done by the use of ECL-Advance (Amersham), band intensity was analyzed with QuantityOne software (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy).
F4/80 antigen and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) levels were also assessed by Western blot analysis. Protein (20 or 5 μg) of each animal was loaded on a 7.5% or 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel for F4/80 and GFAP, respectively. After electrophoresis and wet blotting, membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk in phosphate-buffered saline buffer (containing 0.5% Tween 20) for F4/80 Western blot or in TST buffer (10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 0.05% Tween 20) for GFAP Western blot and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with F4/80 antibody (MCAP497, 1:500; Serotec, Düsseldorf, Germany) or overnight at 4°C with GFAP antibody (Z0334, 1:7500; DAKO) followed by secondary antibody [401416, 1:5000 (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) for F4/80; A2074, 1:15000 (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany) for GFAP] and peroxidase-catalyzed enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL-Plus; Amersham Biosciences, Freiburg, Germany). β-Actin was used for normalization (primary and secondary antibody 1:10,000 each; Sigma-Aldrich). Protein expression levels were determined by a densitometry software Gel-Pro analyzer (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD). All samples were analyzed in duplicate.
Corticosterone Assay
Trunk blood was collected from each animal in heparinized capillaries directly after decapitation (within 3 minutes from disturbing the animals’ cage). Plasma corticosterone concentrations were determined in duplicate by radioimmunoassay without chromatography using corticosterone antiserum (C8784, Sigma-Aldrich) with the following cross-reactivity: progesterone, 15.7%; 11-deoxycorticosterone, 20%; 20α-hydroxyprogesterone, 8.8%; cortisol, 4.5%; 20β-hydroxyprogesterone, 5.2%; testosterone, 7.9%; 17-hydroxyprogesterone, 1.8%; androstenedione, 2.6%; aldosterone, 4.4%; 11-deoxycortisol, 1.3%; 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 1.4%; cortisone, 3.2%; and androsterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, estrone, 17β-estradiol, estriol, <0.1%. All samples were run in a single assay. The intra-assay coefficient of variation was <4%. Further details of assay performance have been described elsewhere.21
DNA Microarray
Isolated RNA from animals of the same housing condition was pooled, receiving four pools consisting of two biological duplicates termed standard 1 (four animals), standard 2 (four animals), enriched 1 (four animals), and enriched 2 (five animals), each pool containing 20 μg of RNA. Mouse genome 430A 2.0 array hybridization was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Affymetrix, Wooburn Green, United Kingdom).
Raw expression data were accumulated by GeneChip Operating System software (Gecos v1.2; Affymetrix). CEL-files were then imported to the software package CoBi/Expressionist Pro 1.0 (GeneData, Basel, Switzerland). Before analysis, signal values were normalized to the logarithmic mean with a reference value of 1000 to ensure comparability. Expressionist’s internal quality control was set to P = 0.05. The mean expression values received from biological duplicates in EH versus SH groups were used to accomplish pair-wise comparison and assess fold changes. Only genes with a mean expression value greater than 100 in one of the two groups and a 1.5-fold differential expression between the groups were used for further investigations. Differences of P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test) were considered significant. Genes showing significant different regulation between the two experimental conditions were categorized according to their biological function by means of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software (Ingenuity Systems, Redwood City, CA) and via literature survey (PubMed).
Quantitative Real-Time PCR (TaqMan Assay)
To assess human APP transgene expression levels, cDNA was synthesized from 2 μg of RNA of each animal using Omniscript RT kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. To verify expression levels of the microarray experiment, RNA was pooled before reverse transcription corresponding to the four pools used for the microarray analysis. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers and TaqMan probes were designed using Primer Express software (version 2.0, Applied Biosystems). Specificity of each amplicon was controlled by BLAST search. GAPDH was used for normalization. All assays were run in triplicate. Primers and cycling conditions are available on request.
Statistical Analysis
Normal distribution of all data sets was confirmed by one-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. As all data were normally distributed, SH and EH groups were compared using an unpaired t-test. All tests were applied two-tailed except for the morphometrical analysis of microglia (as the confirmation for Western blot data) using the software package SPSS (version 12.0.1). When necessary, Bonferroni correction was calculated for multiple testing. Differences were considered significant at P < 0.05.
Results
Reduced Aβ Deposition in EH Mice
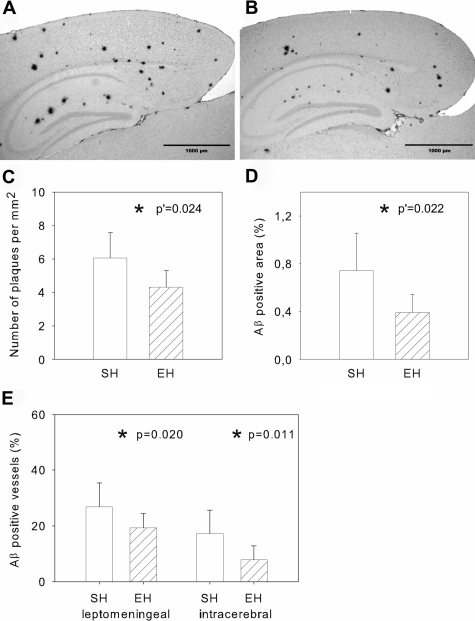
We first investigated the effect of EH on Aβ deposition by immunohistochemical staining and digital image analysis (Figure 1, A and B). The number of Aβ plaques in the neocortex and hippocampus together was significantly reduced (by 28.8%, P′ = 0.024, P′: Bonferroni corrected) in EH animals compared to SH mice (Figure 1C). In addition, there was a 47.3% reduction in the total Aβ-positive area (Figure 1D, P′ = 0.022). The mean size of plaques was 25% smaller in EH mice (P′ = 0.024). In neocortex alone, plaque number was significantly reduced by 29.2% (P′ = 0.026), Aβ-positive area by 45.3% (P′ = 0.020) and the mean size of plaques by 24.3% (P′ = 0.016). In hippocampus, there was only a slight but statistically not significant reduction in plaque number by 19.6% (P′ = 0.308), Aβ-positive area (by 42.9%, P′ = 0.122) and mean plaque size (by 28.7%, P′ = 0.134). The extent of amyloid angiopathy was also significantly reduced in EH mice. The percentage of amyloid laden leptomeningeal vessels decreased by 30% (P = 0.020), and that of intracerebral vessels by 59% (Figure 1E, P = 0.011). Paraffin sections of two wild-type mice were stained as control. None of these animals showed any Aβ deposits.
Figure 1-6942.
A and B: Representative figures of SH (A) and EH (B) plaque burden after immunohistochemical staining against Aβ with 6F/3D antibody, digitization and subsequent extraction of blue to gray values to obtain the best contrast between immunopositive plaques and background. C and D: Number of neocortical and hippocampal plaques and the percentage of Aβ-positive area related to total area of the neocortex and hippocampus. E: Percentage of Aβ-positive vessel walls related to the total amount of counted vessels. Data are given as mean ± SD; statistics, t-test; P′, Bonferroni corrected.
Soluble Aβ Levels as Well as APP Expression and Processing Did Not Differ Between Housing Conditions
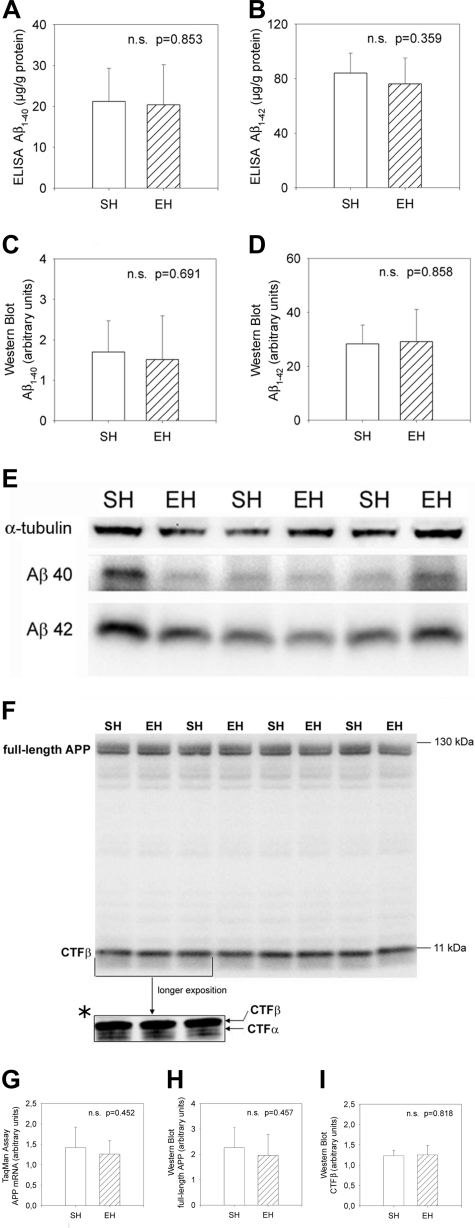
There was no significant difference in the levels of soluble Aβ1-40 or Aβ1-42 between EH and SH mice as measured by ELISA (Figure 2, A and B; P = 0.853 and P = 0.359, respectively). The relation between Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 levels did not differ between the two housing conditions (P = 0.743). Similar results could be obtained by Western blot analysis (Figure 2, C–E). There were again no differences between EH and SH mice in Aβ1-40 (Figure 2C, P = 0.691), Aβ1-42 levels (Figure 2D, P = 0.858), as well as in the relation between Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 (P = 0.333).
Figure 2-6942.
APP expression and processing. A–D: Steady state levels of soluble Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 as measured by ELISA and Western blot. E: Representative Western blot with antibody specific for Aβ (6E10). There are slight variations in levels of detergent-soluble Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42, but these are fully consistent with the variations observed with a protein loading control, α-tubulin. F: Representative Western blot data showing no differences in full-length APP and in proteolytic fragments of APP (CTFβ). A faint CTFα fragment was only detectable after a longer exposition duration (F*). G–I: Steady state levels of APP mRNA and protein as well as CTFβ stub. No differences were seen in EH versus SH mice. Data are given as means ± SD; statistics, t-test.
To assess the expression levels of human APP transgene as a possible reason of altered plaque burden, we performed quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR as well as Western blot analysis against APP (Figure 2F, top row). No differences between EH and SH mice could be detected, neither at transcriptional nor translational levels (Figure 2, G and H; P = 0.452 and P = 0.457, respectively). Additionally, the level of the proteolytic fragment APP-CTFβ was measured to evaluate whether alteration in APP processing could account for reduction of Aβ deposition (Figure 2F, bottom row). Again, there was no significant difference in CTFβ levels between EH and SH mice (Figure 2I, P = 0.818). A weak CTFα band was detectable after a longer exposition duration (Figure 2F*). A densitometric quantification of this band was hampered because of its faintness, although it appeared virtually unchanged in all examined animals.
Housing Conditions Did Not Influence Glucocorticoid Levels
Corticosterone as main glucocorticoid in mice was measured to determine the stress level of the animals. Plasma corticosterone levels did also not differ between EH and SH mice (P = 0.567).
Enhanced Microgliosis in EH Mice
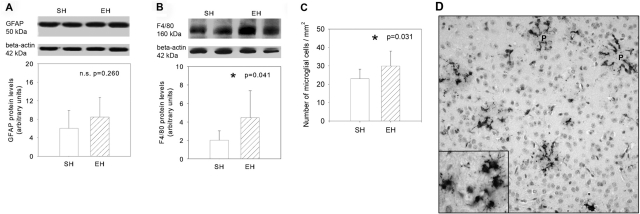
To determine the extent of activated microglia and astroglia, the expression of cell-type-specific markers was assessed by Western blot analysis. Levels of the astrocytic marker GFAP did not differ between brains from EH and SH conditions (Figure 3A, P = 0.260). In contrast, levels of F4/80 antigen, a 160-kd glycoprotein specifically expressed in microglia,22 were significantly elevated by 118% in EH brains (Figure 3B, P = 0.041). To confirm this result, we performed morphometrical analysis using immunohistochemical staining against Mac-3. EH mice showed an enhancement of 30% in number of activated microglia per mm2 (Figure 3, C and D; P = 0.032). Interestingly, we could very often observe that ramifications of microglial cells appear to infiltrate the core of amyloid plaques (Figure 3D).
Figure 3-6942.
A and B: Levels of GFAP and F4/80 antigen in SH and EH mice as measured by Western blot analysis. In contrast to astrocytic marker GFAP, F4/80 antigen was significantly elevated in EH when compared with SH mice. C: Additionally, the number of microglial cells per mm2 that were counted after immunohistochemistry against Mac-3 was also increased in EH mice. D: Representative picture of Mac-3 immunostaining (P, plaque) showing ring formation of ramified and elongated microglial cells surrounding and infiltrating the amyloid plaques. Data are given as means ± SD; statistics, t-test. Original magnifications: ×200; ×400 (inset).
Microarray Analysis Revealed Multiple Pathways that May Be Involved in Aβ Burden Reduction
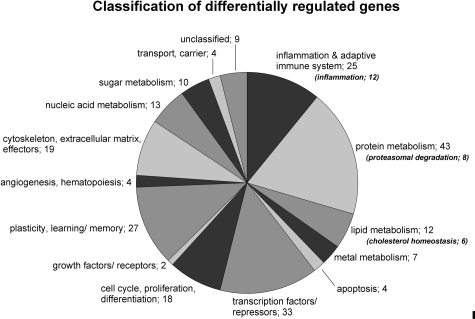
Expression levels of the housekeeping genes GAPDH and β-actin showed no significant differences between the four arrays (range: 1.005-fold to 1.01-fold). Two hundred thirty genes revealed different expression values between the two experimental conditions (P < 0.05). Two hundred twenty-one of these genes could be categorized into 14 groups concerning the main function of the protein products in a biological context based on Ingenuity Pathway Analysis and literature survey (PubMed; Figure 4). Nine genes remained unclassified. The entire list of all 230 genes can be found as Supplementary Table 1 (see http://ajp.amjpathol.org).
Figure 4-6942.
Number of genes categorized into different classes concerning their biological function based on Ingenuity Pathway Analysis and literature survey.
Table 1.
Differentially Regulated Genes Being Associated with 1, Inflammation; 2, Proteasomal Degradation; and 3, Cholesterol Metabolism
| Probe ID | Gene symbol | Gene name | Accession | P value | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Inflammation | |||||
| A: Anti-inflammatory | |||||
| 1419768_at | Cd22 | CD22 antigen | NM 009845 | 0.024 | +1.9 |
| 1425198_at | Ptpn2 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 2 | NM 008977 | 0.037 | +6.5 |
| 1438562_a_at | Ptpn2 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 2 | NM 008977 | 0.046 | +2.4 |
| 1431791_a_at | Ptpn13 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 13 | AK014577 | 0.019 | +1.5 |
| 1451593_at | H2-Q1 | Histocompatibility 2, Q region locus 1 | BC018402 | 0.022 | +2.9 |
| B: Proinflammatory | |||||
| 1450157_a_at | Hmmr | Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) | NM 013552 | 0.042 | −9.1 |
| 1454184_a_at | Ikbkb | Inhibitor of κB kinase β | NM 010546 | 0.022 | −2.8 |
| 1420380_at | Ccl2 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 | NM 011333 | 0.016 | −3.0 |
| 1422349_at | Ccr1l1 | Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 1-like 1 | NM 007718 | 0.044 | −2.9 |
| 1452424_at | Gpr23 | G Protein-coupled receptor 23 | NM 175271 | 0.043 | −1.6 |
| 1449310_at | Ptger2 | Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2) | NM 008964 | 0.022 | −1.5 |
| 1448870_at | Ltbp1 | Latent transforming growth factor β-binding protein 1 | AF022889 | 0.010 | −10.2 |
| 1419132_at | Tlr2 | Toll-like receptor 2 | NM 011905 | 0.044 | −1.6 |
| 2. Proteasomal degradation | |||||
| A: Ubiquitin E3 ligases | |||||
| 1427625_a_at | Herc2 | Hect (homologous to the E6-AP (UBE3A) carboxyl terminus) domain and RCC1 (CHC1)-like domain (RLD) 2 | NM 010418 | 0.032 | −5.0 |
| 1456375_x_at | Trim27 | Tripartite motif protein 27 | NM 009054 | 0.039 | −1.6 |
| 1417453_at | Cul4b | Cullin 4B | NM 028288 | 0.001 | −1.8 |
| 1426135_a_at | Park2 | Parkin | NM 016694 | 0.007 | −4.5 |
| 1416681_at | Ube3a | Ubiquitin protein ligase E3A | NM 173010 | 0.019 | −1.9 |
| B: Scaffold protein in ubiquitin-cycle | |||||
| 1450849_at | Hnrpu | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U | BC018353 | 0.030 | −1.7 |
| C: Proteasomal activator and subunit | |||||
| 1416290_a_at | Psmc4 | Proteasome (prosome macropain) 26S subunit. ATPase. 4 | NM 011874 | 0.001 | +3.5 |
| 1452211_at | Psme4 | Proteasome (prosome macropain) activator subunit 4 | BC024484 | 0.044 | +1.7 |
| 3. Cholesterol homeostasis | |||||
| 1449145_a_at | Cav | Caveolin, caveolae protein | NM 007616 | 0.020 | +1.6 |
| 1452803_at | Glipr2 | GLI pathogenesis-related 2 | NM 027450 | 0.027 | +4.2 |
| 1455820_x_at | Scarb1 | Scavenger receptor class B, member 1 | NM 016741 | 0.048 | +1.5 |
| 1449457_at | Cach | Cytosolic acetyl-CoA hydrolase | NM 028790 | 0.024 | −1.8 |
| 1421500_at | Sts | Steroid sulfatase | NM 009293 | 0.038 | −1.7 |
| 1456011_x_at | Acaa1 | Acetyl-coenzyme A acyltransferase 1 | NM 130864 | 0.026 | −3.2 |
+, N-Fold up-regulation in enriched; −, N-fold down-regulation in enriched.
For explaining reduced plaque burden, genes categorized into the three groups, inflammation, proteasomal degradation, and cholesterol homeostasis, strongly associated with plaque formation and degradation were chosen for further investigation (Table 1). Genes related to inflammation revealed transcriptional down-regulation of eight proinflammatory genes in EH mice and up-regulation of four genes suppressing inflammation activities. Among the eight proteasome-related genes, five ubiquitin-ligase-encoding genes were down-regulated in animals under EH, whereas two genes representing a proteasomal subunit or activator, respectively, showed significant up-regulation. The 12 differentially regulated genes related to lipid metabolism revealed six gene products involved in cholesterol homeostasis.
To affirm the validity of the microarray data, four genes related to inflammation (Ptpn2), proteasomal degradation (Psmc4, Psme4), and iron chelation (Hba-a1) were selected and quantitatively analyzed by real-time PCR. In all cases, the microarray data could be verified as the changes in mRNA abundance between EH and SH mice measured by microarray analysis and real-time PCR reached approximately same values (data not shown).
Discussion
We studied the effect of environmental enrichment on the AD-like pathology of female TgCRND8 mice. Exposure of transgenic animals to EH from day 30 until the age of 5 months resulted in a significant reduction of Aβ plaque burden in the brain when compared to SH mice. Furthermore, we could show for the first time a significant reduction of amyloid angiopathy in cerebral and leptomeningeal vessels of EH animals. In principle, reduction of Aβ deposition (as found in our study) can be the consequence of changes in APP expression, APP processing, Aβ oligomerization/aggregation, or Aβ clearance/degradation.23 Because APP transcriptional and translational expression levels did not differ between EH and SH mice, decreased APP expression probably does not account for lower plaque burden in EH mice. Furthermore, unchanged levels of soluble Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 as well as unaltered secretase activity (as indicated by unvaried carboxy-terminal fragments) make it unlikely that alterations in proteolytic cleavage of APP were responsible for decreased Aβ deposition. In accordance with this result and based on the microarray data, we could find no differences in the expression levels of genes associated with APP cleavage such as presenilin 1, presenilin 2, nicastrin, Bace 1/2, or Adam10 between animals of the two housing conditions.
Because of the protein extraction method used in this study we were not able to measure insoluble Aβ peptides in the brain samples. Hence, we cannot exclude that insoluble Aβ levels (in contrast to soluble Aβ levels) were reduced on environmental enrichment. Based on our microarray data, we favor decreased aggregation as well as increased clearance of Aβ as the cause for reduced Aβ deposition after EH. At least three biological functional processes seem to be involved: 1) inflammation, 2) proteasomal degradation, and 3) cholesterol homeostasis (Table 1).
Inflammation
Remarkably, genes products that are involved in the proinflammatory response such as chemokine [C–C motif] ligand 2 (Ccl2 or MCP-1)24 or prostaglandin E receptor 2 (EP2 or Ptger2)25 were down-regulated, whereas anti-inflammatory associated genes such as Cd2226 or protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 2 (Ptpn2)27 were up-regulated in brains of EH mice. Inflammation processes in AD brains lead to both enhanced cytotoxicity as well as enhanced Aβ aggregation.28 Thus our data suggest that enrichment might reduce the release of cytotoxic agents and lower Aβ aggregation. It remains unclear to what extent the up-regulation of anti-inflammatory and down-regulation of proinflammatory mediators in enriched brains are primary cause or secondary phenomena to Aβ burden reduction. In both cases (no matter if cause or consequence) this anti-inflammatory microenvironment could interfere in the amyloid cascade and inhibit the vicious circle of inflammation↔ amyloidogenesis.
Furthermore, the down-regulation of EP2 and Ccl2 suggests enhanced microglial phagocytotic activity24,29 in absence of neurotoxicity.30 Our data on elevated levels of the microglia-specific glycoprotein F4/80 antigen (Western blot) as well as an increased number of microglial cells (immunohistochemistry against Mac-3) suggest an increased microglial activation/phagocytotic activity after EH. Interestingly, an increased microglial proliferation has been previously shown as a result of physical exercise (by wheel running) in the brains of wild-type healthy mice.31 In different experiments with APP transgenics in which microglial activation has been triggered by varying methods (eg, passive and active Aβ vaccine, lipopolysaccharide injection), amyloid deposition has been consistently reduced.32,33 In fact, microglial activation and plaque clearance after application of Aβ antibody have been monitored in vivo using multiphoton microscopy.34 A recent work by Simard and colleagues35 suggests that the prevailing part of microglia with the ability to eliminate amyloid deposits are blood-derived and not their resident counterparts. The role of microglia in the AD brain remains at the end controversial. It seems to propagate the formation of amyloid plaques by expressing inflammatory mediators but also to remove plaques by phagocytosis.36,37 This study suggests for the first time that EH can possibly cause a shift from neurotoxic into phagocytotic microglia, hence evoking Aβ clearance.
Proteasomal Degradation
Recent findings indicate that the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is involved in several neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and prion diseases.38 In AD brains, a region-specific reduction in proteasomal activity has been found.39 Regarding Aβ clearance it has been shown that Aβ can be degraded by the proteasome and it has been proposed that the normal proteolytic removal of Aβ could be affected in AD.40 Hence, the up-regulation of a subunit of the 26S proteasome (Psmc4) and an activator of the 20S proteasome (Psme4) may have improved the ability to remove a greater portion of aggregated Aβ in EH mice. The down-regulation of five genes (Herc2, Trim27, Cul4b, Park2, Ube3a) encoding for ubiquitin E3 ligases could have resulted in less tagged substrates for proteasomal degradation and therefore enhanced the capacity of the proteasome for ubiquitin-independent Aβ degradation.
Cholesterol Homeostasis
The microarray data revealed differentially regulated genes such as caveolin or scavenger receptor B1 that are involved in cholesterol metabolism. A number of epidemiological studies suggest an increased brain cholesterol turnover during neurodegeneration.41 The apolipoprotein E ε4 allele, which exacerbates hypercholesterolemia, is considered as a major genetic risk factor,42 and transgenic mice modeling AD that are fed with a high cholesterol diet develop elevated Aβ levels as well as increased plaque deposition.43 Recently it has been shown that oxidative cholesterol metabolites covalently modify Aβ, thereby dramatically accelerating its amyloidogenesis.44 Because genes whose products bind cholesterol, like caveolin or scavenger receptor-B1,45 were up-regulated in EH mice, and steroid sulfatase (Sts)46 involved in synthesis of cholesterol was down-regulated, we hypothesize that altered cholesterol homeostasis or distribution took part in reducing Aβ deposition as a result of EH.
As another main result, we found a reduction of amyloid angiopathy in EH mice. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is an important feature of AD probably leading to faulty clearance of Aβ peptide across the blood-brain barrier. This vascular dysfunction may cause vessel regression, brain hypoperfusion, and neurovascular inflammation.47,48 Hence, the reduction of Aβ peptide deposition in the vessel walls of enriched brains is potentially a very important contributor counteracting the destructive effects of AD pathology.
Until now four groups have published on the effects of environmental stimulation in transgenic AD models reporting partly contradictory results.12–16 Particularly, it has been hypothesized that EH in large groups with altering populations as used by Jankowsky and colleagues induced social stress resulting in off-setting positive effects.15 In our experimental setting, we could not find differences in glucocorticoid levels between SH and EH animals, suggesting that EH mice did not experience more stress than SH mice. Future studies have to investigate the effect of single environmental factors such as composition and stability of the group, cage size, the structural setting, number of animals per running wheel (as component of EH) as well as genetic background, sex, and age of animals at the start of enrichment to determine those factors that have positive effects on the AD brain.
In conclusion, we show that the environment in form of EH is able to reduce Aβ plaque burden as well as amyloid angiopathy in mice with AD-like pathology. This effect was independent from APP expression or processing and rather associated with reduced aggregation and enhanced clearance of Aβ. The mechanism appears to be mediated by multiple pathways, in particular a reduced inflammatory response, enhanced microglial phagocytosis, proteasomal degradation, as well as reduced cholesterol levels. Thorough knowledge on these self-protecting pathways represents the first steps toward a pharmacological intervention for supporting the restorative processes in the AD brain.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank David Westaway for giving us the possibility to work with the TgCRND8 mice; and Diane Kosters, Maria Leisse, Susanne Peetz-Dienhart, and Andrea Wagner for excellent technical support.
Footnotes
Address reprint requests to Kathy Keyvani, M.D., University Hospital Münster, Institute of Neuropathology, Domagkstr. 19, D-48149, Münster, Germany. E-mail: keyvani@uni-muenster.de.
Supported by Innovative Medical Research (grant KE520401) and the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes.
Supplementary material for this article can be found on http://ajp.amjpathol.org.
References
- Mattson M. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2004;430:631–639. doi: 10.1038/nature02621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel SI. Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Clin Geriatr Med. 2003;19:799–824. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0690(03)00046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie K, Lovestone S. The dementias. Lancet. 2002;360:1759–1766. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11667-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland RP, Fritsch T, Smyth KA, Koss E, Lerner AJ, Chen CH, Petot GJ, Debanne SM. Patients with Alzheimer’s disease have reduced activities in midlife compared with healthy control-group members. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:3440–3445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.061002998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson RS, Mendes De Leon CF, Barnes LL, Schneider JA, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Bennett DA. Participation in cognitively stimulating activities and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. JAMA. 2002;287:742–748. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.6.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:191–198. doi: 10.1038/35044558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marashi V, Barnekow A, Ossendorf E, Sachser N. Effects of different forms of environmental enrichment on behavioral, endocrinological, and immunological parameters in male mice. Horm Behav. 2003;43:281–292. doi: 10.1016/s0018-506x(03)00002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson BB, Belichenko PV. Neuronal plasticity and dendritic spines: effect of environmental enrichment on intact and postischemic rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:89–96. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200201000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyvani K, Sachser N, Witte OW, Paulus W. Gene expression profiling in the intact and injured brain following environmental enrichment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004;63:598–609. doi: 10.1093/jnen/63.6.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dellen A, Blakemore C, Deacon R, York D, Hannan AJ. Delaying the onset of Huntington’s in mice. Nature. 2000;404:721–722. doi: 10.1038/35008142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faherty CJ, Raviie Shepherd K, Herasimtschuk A, Smeyne RJ. Environmental enrichment in adulthood eliminates neuronal death in experimental Parkinsonism. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;134:170–179. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendash G, Garcia M, Costa D, Cracchiolo J, Wefes I, Potter H. Environmental enrichment improves cognition in aged Alzheimer’s transgenic mice despite stable beta-amyloid deposition. Neuroreport. 2004;15:1751–1754. doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000137183.68847.4e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowsky JL, Melnikova T, Fadale DJ, Xu GM, Slunt HH, Gonzales V, Younkin LH, Younkin SG, Borchelt DR, Savonenko AV. Environmental enrichment mitigates cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2005;25:5217–5224. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5080-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowsky JL, Xu G, Fromholt D, Gonzales V, Borchelt DR. Environmental enrichment exacerbates amyloid plaque formation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003;62:1220–1227. doi: 10.1093/jnen/62.12.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarov O, Robinson J, Tang YP, Hairston IS, Korade-Mirnics Z, Lee VMY, Hersh LB, Sapolsky RM, Mirnics K, Sisodia SS. Environmental enrichment reduces Abeta levels and amyloid deposition in transgenic mice. Cell. 2005;120:701–713. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adlard PA, Perreau VM, Pop V, Cotman CW. Voluntary exercise decreases amyloid load in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2005;25:4217–4221. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0496-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chishti MA, Yang DS, Janus C, Phinney AL, Horne P, Pearson J, Strome R, Zuker N, Loukides J, French J, Turner S, Lozza G, Grilli M, Kunicki S, Morissette C, Paquette J, Gervais F, Bergeron C, Fraser PE, Carlson GA, St. George-Hyslop P, Westaway D. Early-onset amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice expressing a double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21562–21570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100710200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janus C, Pearson J, McLaurin J, Mathews PM, Jiang Y, Schmidt SD, Chishti MA, Horne P, Heslin D, French J, Mount HT, Nixon RA, Mercken M, Bergeron C, Fraser PE, St. George-Hyslop P, Westaway D. Aβ peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2000;408:979–982. doi: 10.1038/35050110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klafki HW, Wiltfang J, Staufenbiel M. Electrophoretic separation of betaA4 peptides (1-40) and (1-42) Anal Biochem. 1996;237:24–29. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H, von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987;166:368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser S, Kirtzeck M, Hornschuh G, Sachser N. Sex-specific difference in social support—a study in female guinea pigs. Physiol Behav. 79:297–303. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(03)00091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn JM, Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981;11:805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C, Beyreuther K. Molecular pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Dickson D, editor. ISN Neuropathology Press,; Basel: The Molecular Pathology of Dementia and Movement Disorders. 2003:pp 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M, Horiba M, Buescher JL, Huang D, Gendelman HE, Ransohoff RM, Ikezu T. Overexpression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CCL2 in beta-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice show accelerated diffuse beta-amyloid deposition. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1475–1485. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62364-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan JW. EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptor signaling. Life Sci. 2003;74:143–153. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott RT, Ait-Ghezala G, Town T, Mori T, Vendrame M, Zeng J, Ehrhart J, Mullan M, Tan J. Neuronal expression of CD22: novel mechanism for inhibiting microglial proinflammatory cytokine production. Glia. 2004;46:369–379. doi: 10.1002/glia.20009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdeau A, Dube N, Tremblay ML. Cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatases, regulation and function: the roles of PTP1B and TC-PTP. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasko I, Stampfer-Kountchev M, Robatscher P, Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. How chronic inflammation can affect the brain and support the development of Alzheimer’s disease in old age: the role of microglia and astrocytes. Aging Cell. 2004;3:169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shie FS, Breyer RM, Montine TJ. Microglia lacking E prostanoid receptor subtype 2 have enhanced Abeta phagocytosis yet lack Abeta-activated neurotoxicity. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:1163–1172. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62336-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shie FS, Montine KS, Breyer RM, Montine TJ. Microglial EP2 as a new target to increase amyloid beta phagocytosis and decrease amyloid beta-induced damage to neurons. Brain Pathol. 2005;15:134–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2005.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehninger D, Kempermann G. Regional effects of wheel running and environmental enrichment on cell genesis and microglia proliferation in the adult murine neocortex. Cereb Cortex. 2003;13:845–851. doi: 10.1093/cercor/13.8.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Nguyen M, Soriano F, Vasquez N, Weiss K, Welch B, Seubert P, Schenk D, Yednock T. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. doi: 10.1038/78682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCarlo G, Wilcock D, Henderson D, Gordon M, Morgan D. Intrahippocampal LPS injections reduce Abeta load in APP+PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2001;22:1007–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(01)00292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacskai BJ, Kajdasz ST, Christie RH, Carter C, Games D, Seubert P, Schenk D, Hyman BT. Imaging of amyloid-beta deposits in brains of living mice permits direct observation of clearance of plaques with immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2001;7:369–372. doi: 10.1038/85525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard AR, Soulet D, Gowing G, Julien JP, Rivest S. Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2006;49:489–502. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss-Coray T, Mucke L. Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease—a double-edged sword. Neuron. 2002;35:419–432. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00794-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J, Strohmeyer R, Kovelowski CJ, Li R. Microglia and inflammatory mechanisms in the clearance of amyloid beta peptide. Glia. 2002;40:260–269. doi: 10.1002/glia.10153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A, Brundin P. The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron. 2003;40:427–446. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00606-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller JN, Hanni KB, Markesbery WR. Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2000;75:436–439. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Salon M, Pasquini L, Besio Moreno M, Pasquini JM, Soto E. Relationship between beta-amyloid degradation and the 26S proteasome in neural cells. Exp Neurol. 2003;180:131–143. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(02)00060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss AB, Siller KA, Rahman MM, Chan ESL, Ghiso J, de Leon MJ. Cholesterol in neurologic disorders of the elderly: stroke and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:977–989. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglielli L, Tanzi RE, Kovacs DM. Alzheimer’s disease: the cholesterol connection. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:345–351. doi: 10.1038/nn0403-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refolo LM, Malester B, LaFrancois J, Bryant-Thomas T, Wang R, Tint GS, Sambamurti K, Duff K, Pappolla MA. Hypercholesterolemia accelerates the Alzheimer’s amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7:321–331. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2000.0304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q, Powers ET, Nieva J, Huff ME, Dendle MA, Bieschke J, Glabe CG, Eschenmoser A, Wentworth PJ, Lerner RA, Kelly JW. Metabolite-initiated protein misfolding may trigger Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:4752–4757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400924101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assanasen C, Mineo C, Seetharam D, Yuhanna IS, Marcel YL, Connelly MA, Williams DL, de la Llera-Moya M, Shaul PW, Silver DL. Cholesterol binding, efflux, and a PDZ-interacting domain of scavenger receptor-BI mediate HDL-initiated signaling. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:969–977. doi: 10.1172/JCI200523858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias PM, Crumrine D, Rassner U, Hachem JP, Menon GK, Man W, Choy MHW, Leypoldt L, Feingold KR, Williams ML. Basis for abnormal desquamation and permeability barrier dysfunction in RXLI. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;122:314–319. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.22258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:202–208. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attems J. Sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: pathology, clinical implications, and possible pathomechanisms. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2005;110:345–359. doi: 10.1007/s00401-005-1074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.