Abstract
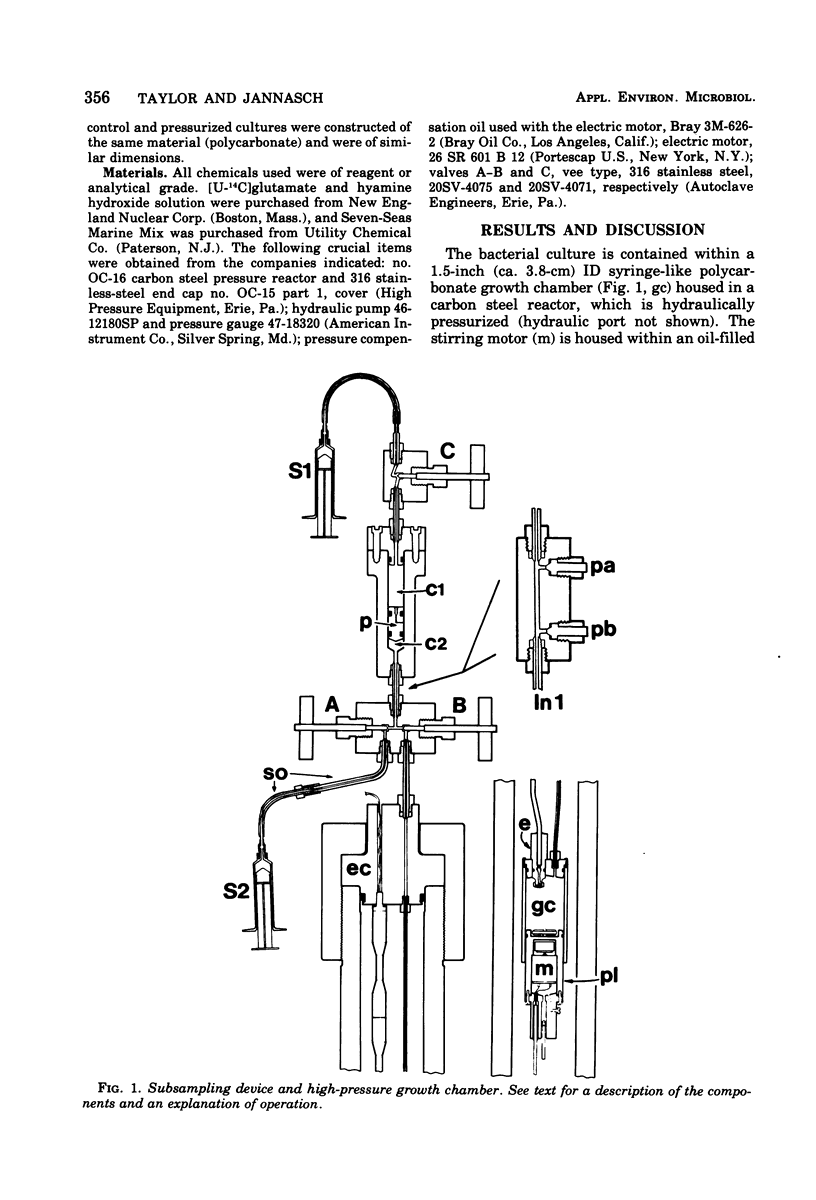
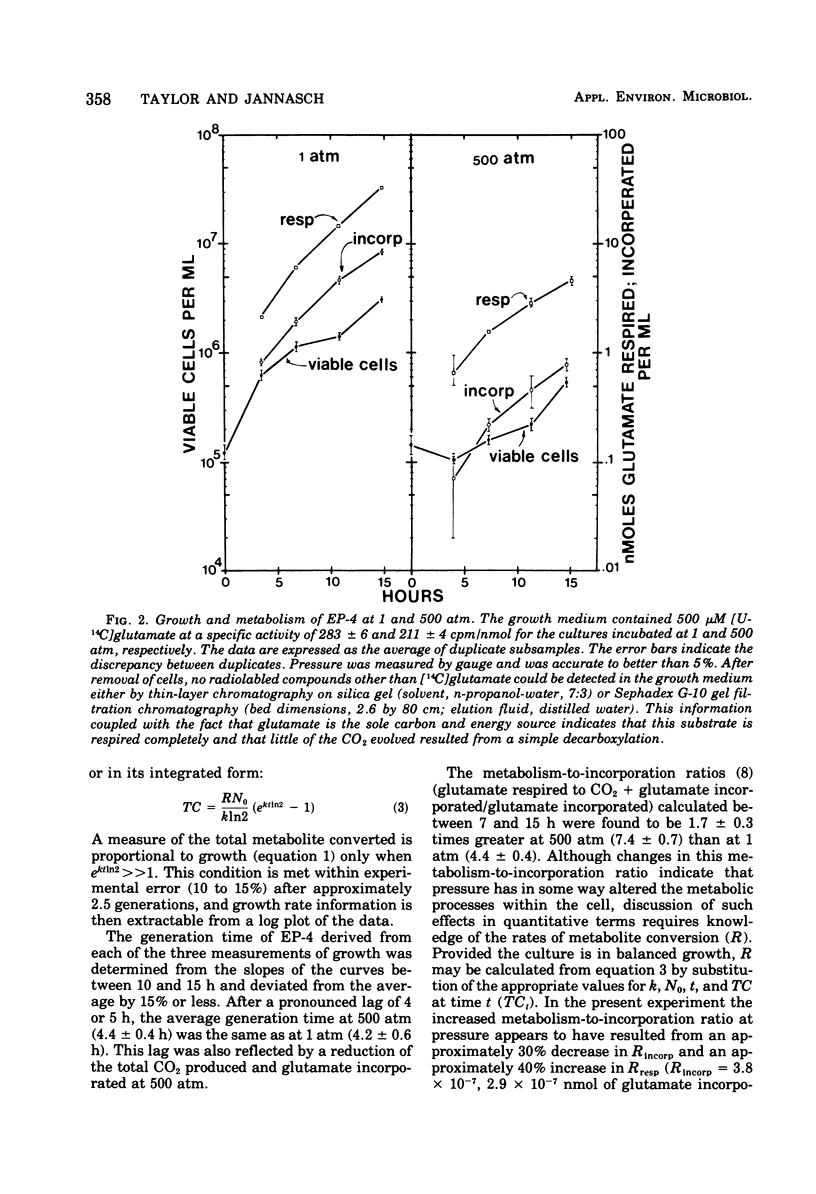
A method is presented for measuring growth of bacteria under high hydrostatic pressure in subsamples taken without pressure change in the incubation vessel. Subsamples may be withdrawn rapidly (5 s) and are not subjected to shear forces. Vice versa, nutrient media, labeled substrates, etc., may be introduced into the culture while under pressure. Chemical fixation of subsamples for electron microscopy or adenosine 5'-triphosphate determinations under pressure is also possible without affecting the growing culture. Data are given of growth experiments demonstrating the feasibility of the method. Problems of oxygen depletion are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carey F. G., Teal J. M. Responses of oxygen electrodes to variables in construction, assembly, and use. J Appl Physiol. 1965 Sep;20(5):1074–1077. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1965.20.5.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope D. H., Berger L. R. An apparatus to measure the rate of oxygen evolution while maintaining pO2 constant during photosynthetic growth in closed culture vessels capable of operation at increased hydrostatic pressures. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1973 May;15(3):505–518. doi: 10.1002/bit.260150307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope D. H., Connors N. T., Landau J. V. Stability of Escherichia coli polysomes at high hydrostatic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):753–758. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.753-758.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A. A technique for studying biological reaction rates at high pressure. Rev Sci Instrum. 1969 Jul;40(7):961–963. doi: 10.1063/1.1684124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A. Stimulatory effect of hydrostatic pressure on cell division in cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 12;392(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


