Abstract
1. Splenic arterial flow and splenic weight were recorded in cats anaesthetized with sodium pentobarbitone. The responses of the spleen to catecholamines, angiotensin and vasopressin were investigated.
2. Catecholamines caused responses mediated by α- and β-adrenoceptors in the arteriolar smooth muscle, but only insignificant β-adrenoceptor responses could be elicited from the capsular smooth muscle. The difficulties in elucidating the mechanism of action of catecholamines on arteriolar smooth muscle are discussed.
3. Angiotensin caused marked vasoconstriction, but contraction of the capsular smooth muscle was less marked. Vasopressin caused vasoconstriction but had no effect on capsular smooth muscle. Thus these peptides constrict the resistance vessels but produce much weaker contraction of the capsule.
4. These responses are discussed in relation to the splenic responses to acute haemorrhage.
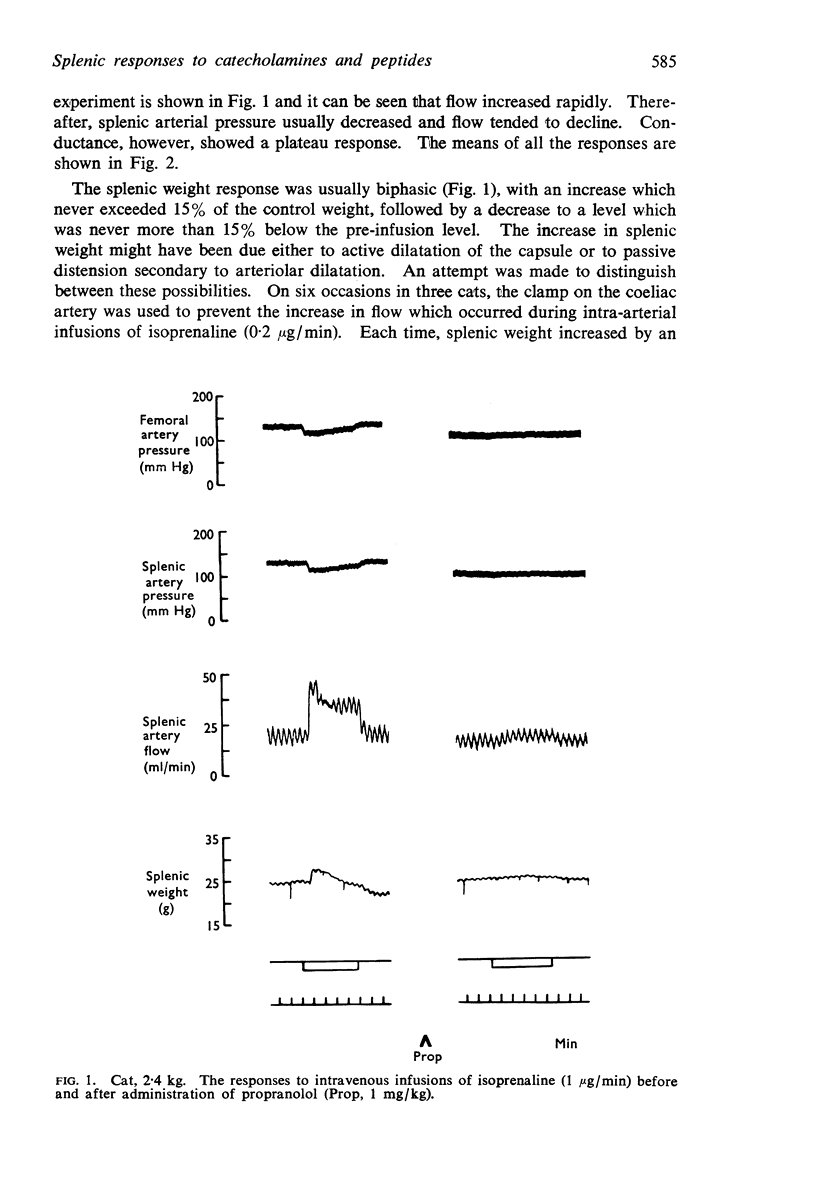
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHLQUIST R. P., TAYLOR J. P., RAWSON C. W., Jr, SYDOW V. L. Comparative effects of epinephrine and levarterenol in the intact anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Mar;110(3):352–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENELLI G., DELLABELLA D., GANDINI A. ANGIOTENSIN AND PERIPHERAL SYMPATHETIC NERVE ACTIVITY. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Feb;22:211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BICKERTON R. K. THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED STRIPS OF CAT SPLEEN TO SYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS AND THEIR ANTAGONISTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Oct;142:99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOATMAN D. L., BRODY M. J. ANALYSIS OF VASCULAR RESPONSES IN THE SPLEEN. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:155–161. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELANDER O. The range of control exercised by the sympathico-adrenal system; a quantitative study on blood vessels and other smooth muscle effectors in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1954;32(116):1–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. J., Silva MR Jr E. An afferent pathway for the selective release of vasopressin in response to carotid occlusion and haemorrhage in the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):529–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresel P., Wallentin I. Effects of sympathetic vasoconstrictor fibres, noradrenaline and vasopressin on the intestinal vascular resistance during constant blood flow or blood pressure. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Apr;66(4):427–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., LEWIS G. P. THE ACTION OF PEPTIDES ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA. RELEASE OF ADRENALINE BY BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN. J Physiol. 1964 May;171:98–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. A critical study of some methods used in investigations on the blood circulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;27(2-3):118–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., OBERG B., RUBINSTEIN E. H. A PROPOSED DIFFERENTIATED NEURO-EFFECTOR ORGANIZATION IN MUSCLE RESISTANCE VESSELS. Angiologica. 1964;1:197–208. doi: 10.1159/000157582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAVIANO V. V., BASS N., NYKIEL F. Adrenal medullary secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine in dogs subjected to hemorrhagic hypotension. Circ Res. 1960 May;8:564–571. doi: 10.1161/01.res.8.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H. D., OTTIS K., KITCHEN T. Autonomic stimulation and blockade on canine splenic inflow, outflow and weight. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:424–428. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick G., Epstein S. E., Wechsler A. S., Braunwald E. Physiological differences between the effects of neuronally released and bloodborne norepinephrine on beta adrenergic receptors in the arterial bed of the dog. Circ Res. 1967 Aug;21(2):217–227. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Lawson A. E. Beta-adrenergic receptors in the hepatic arterial bed of the anesthetized cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1969 May;47(5):415–419. doi: 10.1139/y69-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Lawson A. E., Mellander S. The effects of stimulation of the hepatic nerves, infusions of noradrenaline and occlusion of the carotid arteries on liver blood flow in the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):21–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Lawson A. E., Stark R. D. Vascular responses of the spleen to nerve stimulation during normal and reduced blood flow. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):421–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Stark R. D. Vascular responses of the spleen to rapid haemorrhage in the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):169–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge R. L., Lowe R. D., Vane J. R. The effects of alteration of blood-volume on the concentration of circulating angiotensin in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):613–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANGER W. M., BOLLMAN J. L., MAHER F. T., BERKSON J. Plasma concentration of epinephrine and norepinephrine in hemorrhagic and anaphylactic shock. Am J Physiol. 1957 Aug;190(2):310–316. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.190.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTTIS K., DAVIS J. E., Jr, GREEN H. D. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic drugs on splenic inflow and outflow before and during adrenergic blockade. Am J Physiol. 1957 Jun;189(3):599–604. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton D. M. The evidence for different types of beta-adrenergic receptors. Am Heart J. 1969 May;77(5):707–709. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(69)90560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Vane J. R. The continuous estimation of angiotensin formed in the circulation of the dog. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):513–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. Effects of catecholamines on splenic blood flow in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Nov;213(5):1079–1083. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.5.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. D. Conductance or resistance? Nature. 1968 Feb 24;217(5130):779–779. doi: 10.1038/217779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOENEN H., HUERLIMANN A., HAEFELY W. REMOVAL OF INFUSED NOREPINEPHRINE BY THE CAT'S SPLEEN; MECHANISM OF ITS INHIBITION BY PHENOXYBENZAMINE. Experientia. 1963 Nov 15;19:601–602. doi: 10.1007/BF02151014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Hürlimann A., Haefely W. Dual site of action of phenoxybenzamine in the cat's spleen; blockade of alpha-adrenergic receptors and inhibition of re-uptake of neurally released norepinephrine. Experientia. 1964 May 15;20(5):272–273. doi: 10.1007/BF02151802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Garlick D. G., Renkin E. M. Sympathetic beta adrenergic vasodilatation in skeletal muscle of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1218–1225. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



