Abstract
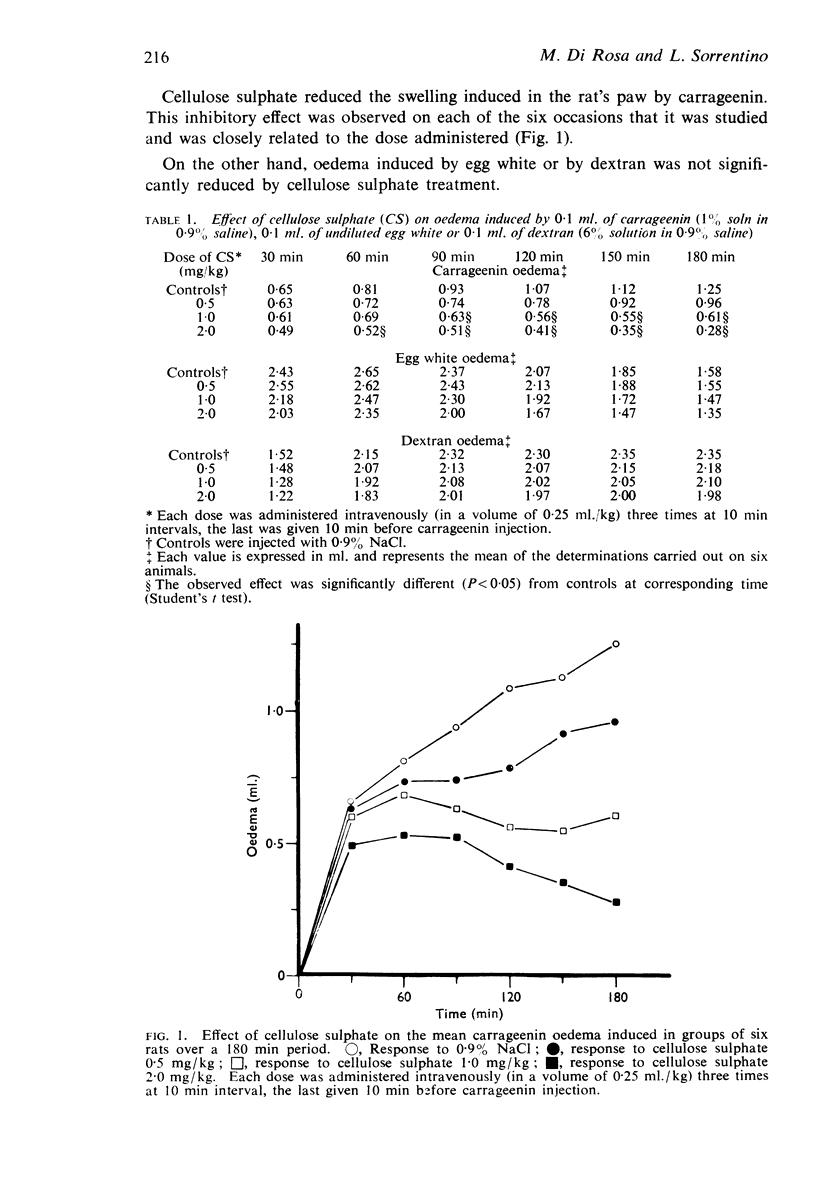
1. Carrageenin oedema is suppressed by pre-treating the rats with cellulose sulphate, a kininogen depleting agent. This inhibition is closely related to the dose of cellulose sulphate and to the time course of kininogen depletion.
2. Oedema induced by egg white or by dextran, in which the mediators are histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine, is quite unaffected by cellulose sulphate treatment.
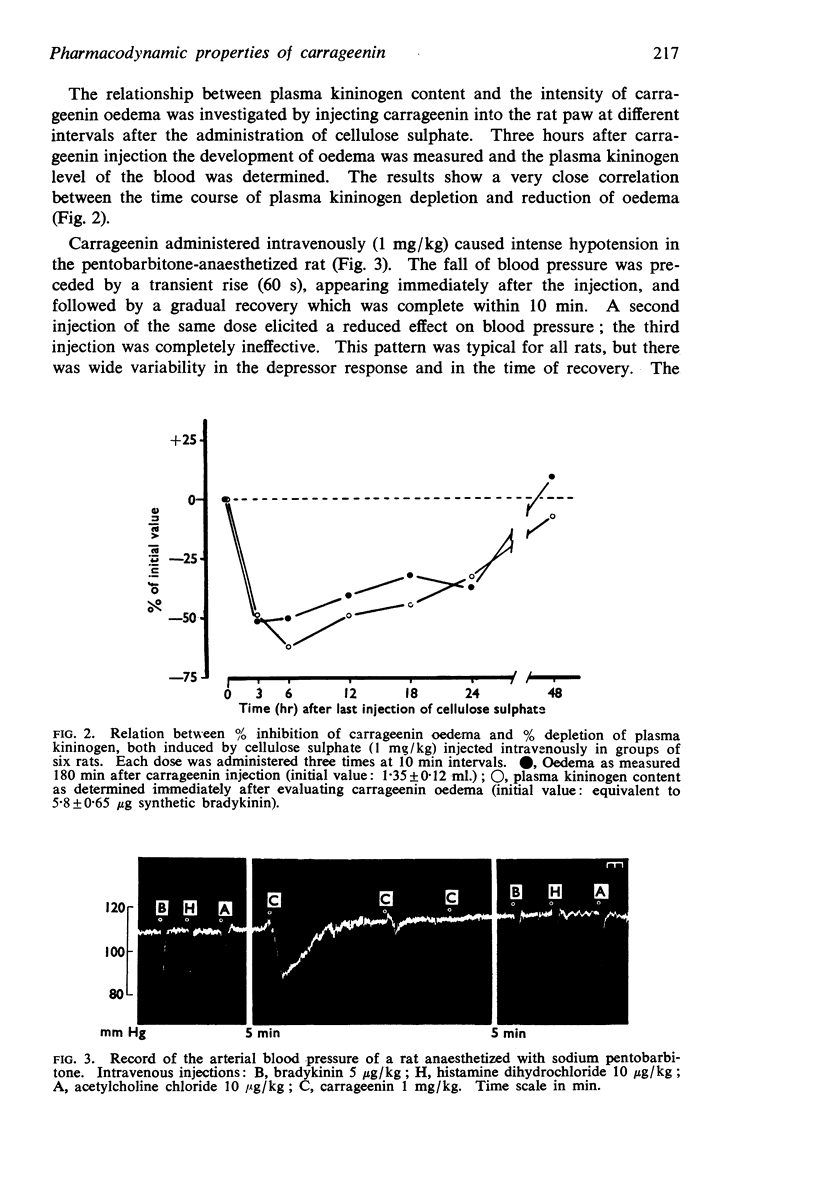
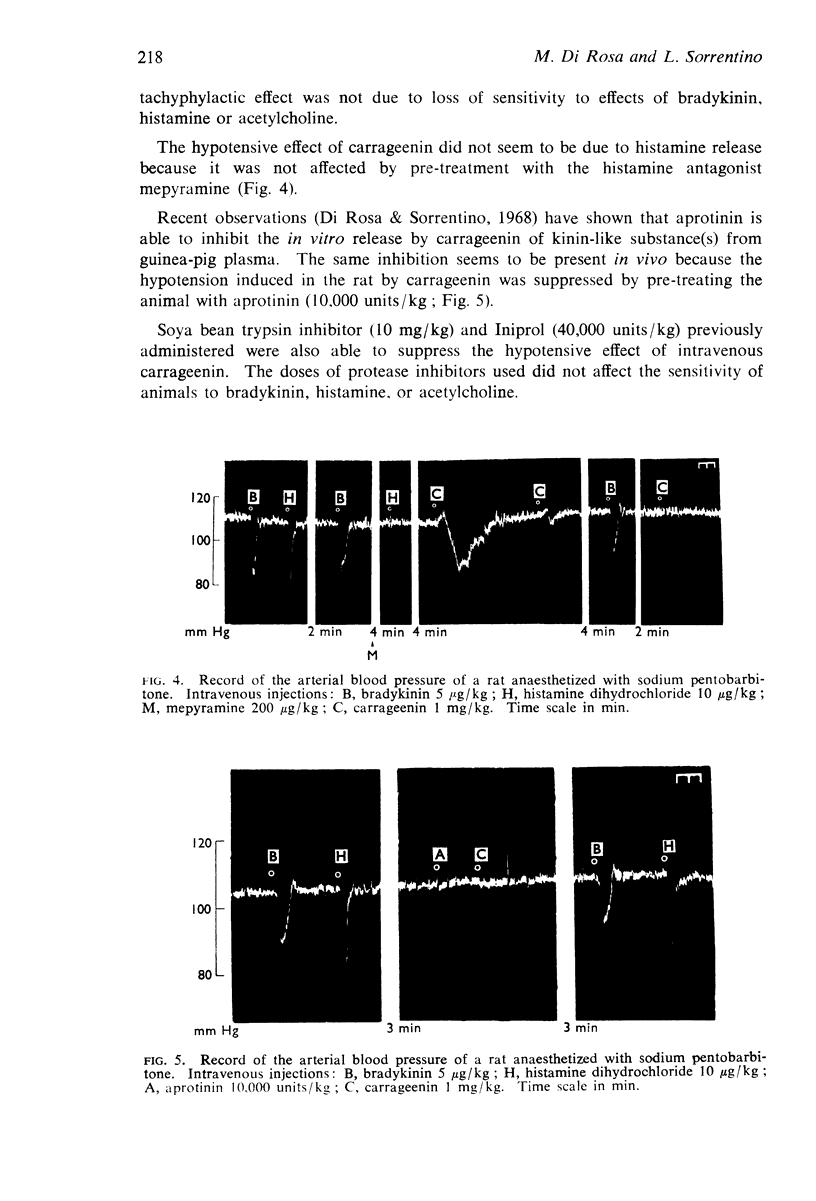
3. Carrageenin injected intravenously lowers the arterial blood pressure of rats. This hypotensive effect is unaffected by histamine antagonists and is abolished by protease inhibitors and thus seems to be due to kinin release from plasma substrates.
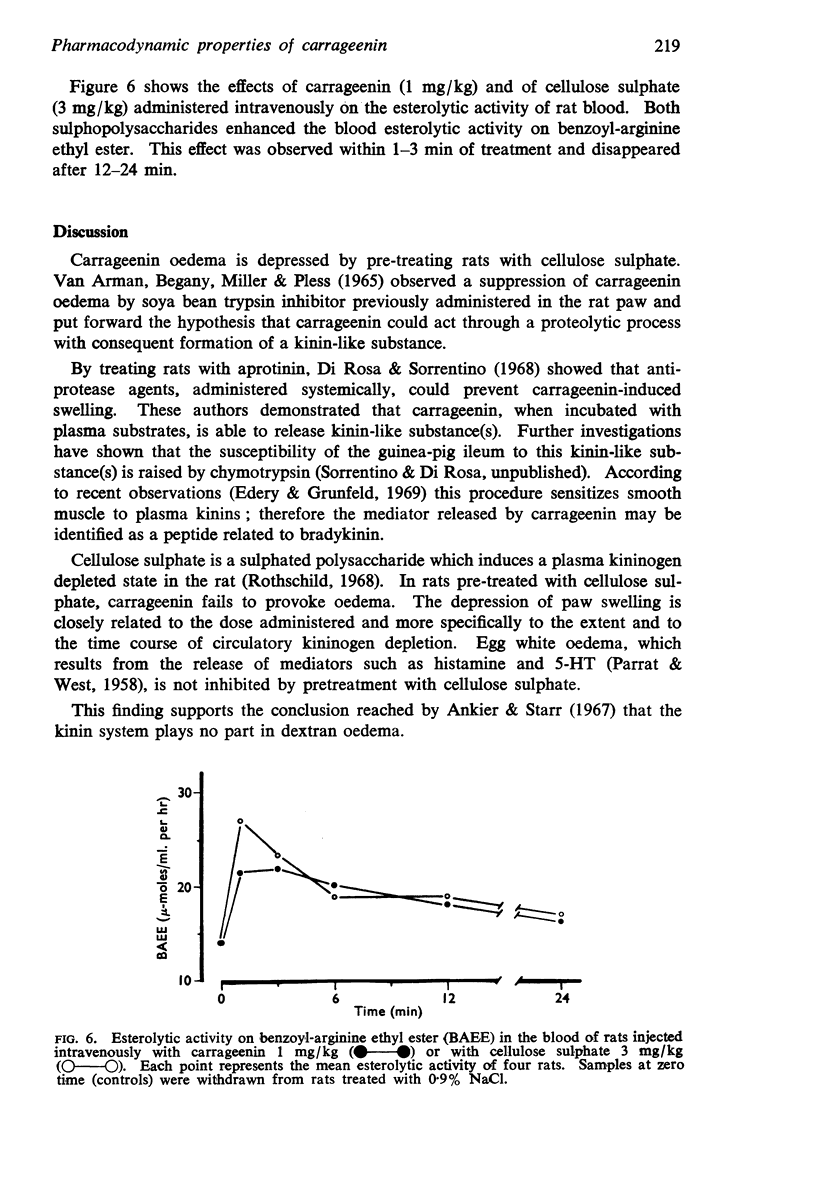
4. Like cellulose sulphate, carrageenin enhances the esterolytic activity of the blood from treated rats when incubated with benzoyl-arginine ethyl ester.
5. The ability of carrageenin to activate the kinin-forming system could account for both its inflammatory and hypotensive effects.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DINIZ C. R., CARVALHO I. F. A micromethod for determination of bradykininogen under several conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:77–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Sorrentino L. The mechanism of the inflammatory effect of carrageenin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Oct;4(3):340–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery H., Grunfeld Y. Sensitization of smooth muscle to plasma kinins: effects of enzymes and peptides on various preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):51–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRATT J. R., WEST G. B. Inhibition by various substances of oedema formation in the bind-paw of the rat induced by 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine, dextran, egg-white and compound 48/80. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Mar;13(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild A. M., Gascon L. A. Sulphuric esters of polysaccharides as activators of a bradykinin-forming system in plasma. Nature. 1966 Dec 17;212(5068):1364–1364. doi: 10.1038/2121364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild A. M. Some pharmacodynamic properties of cellulose sulphate, a kininogen-depleting agent in the rat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jul;33(3):501–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., RISLEY E. A., NUSS G. W. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AND ANTIPYRETIC ACTIVITIES OF INDOMETHACIN, 1-(P-CHLOROBENZOYL)-5-METHOXY-2-METHYLINDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Sep;141:369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., RISLEY E. A., NUSS G. W. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiiflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:544–547. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A., Coote E., Turk J. L. Complement in acute inflammation. J Pathol. 1969 Feb;97(2):295–305. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


