Abstract
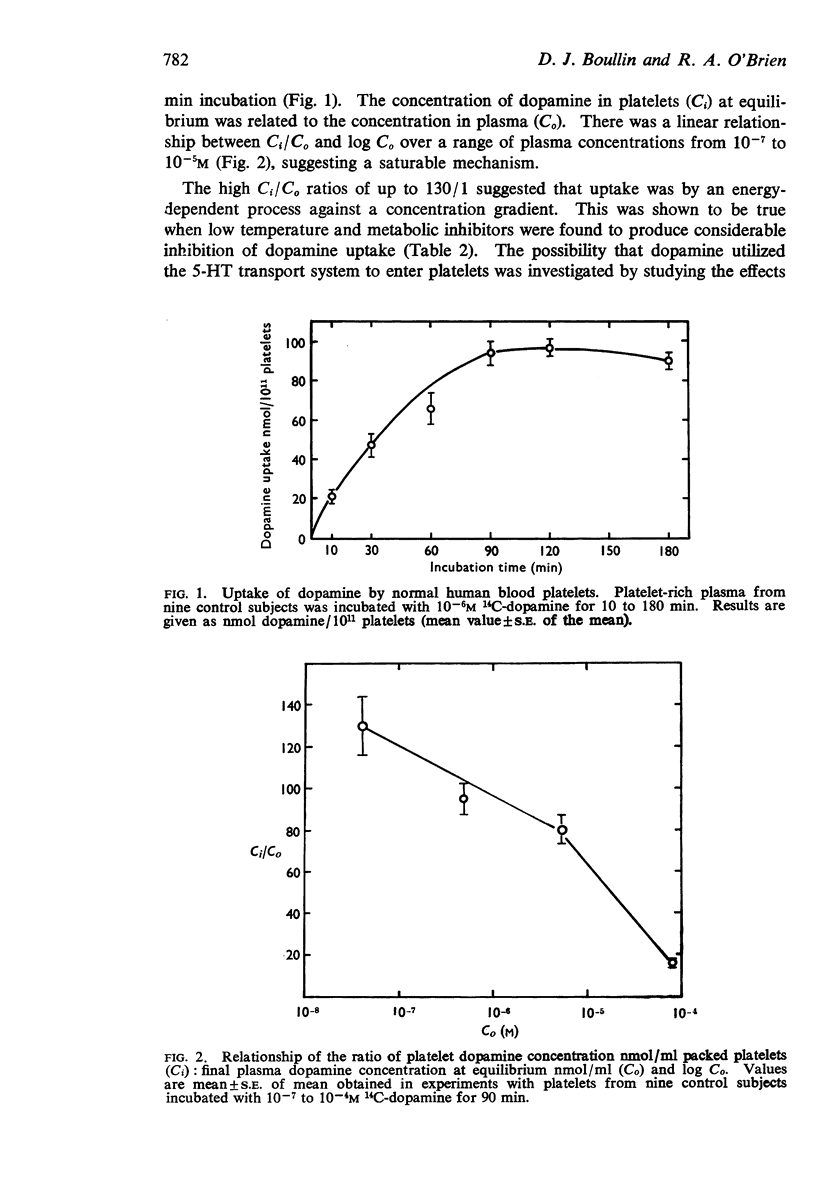
1. Human blood platelets have been shown to take up dopamine by an energy-dependent, saturable process that is inhibited by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), desipramine and other drugs.
2. Platelets from parkinsonian subjects receiving oral L-DOPA also took up dopamine.
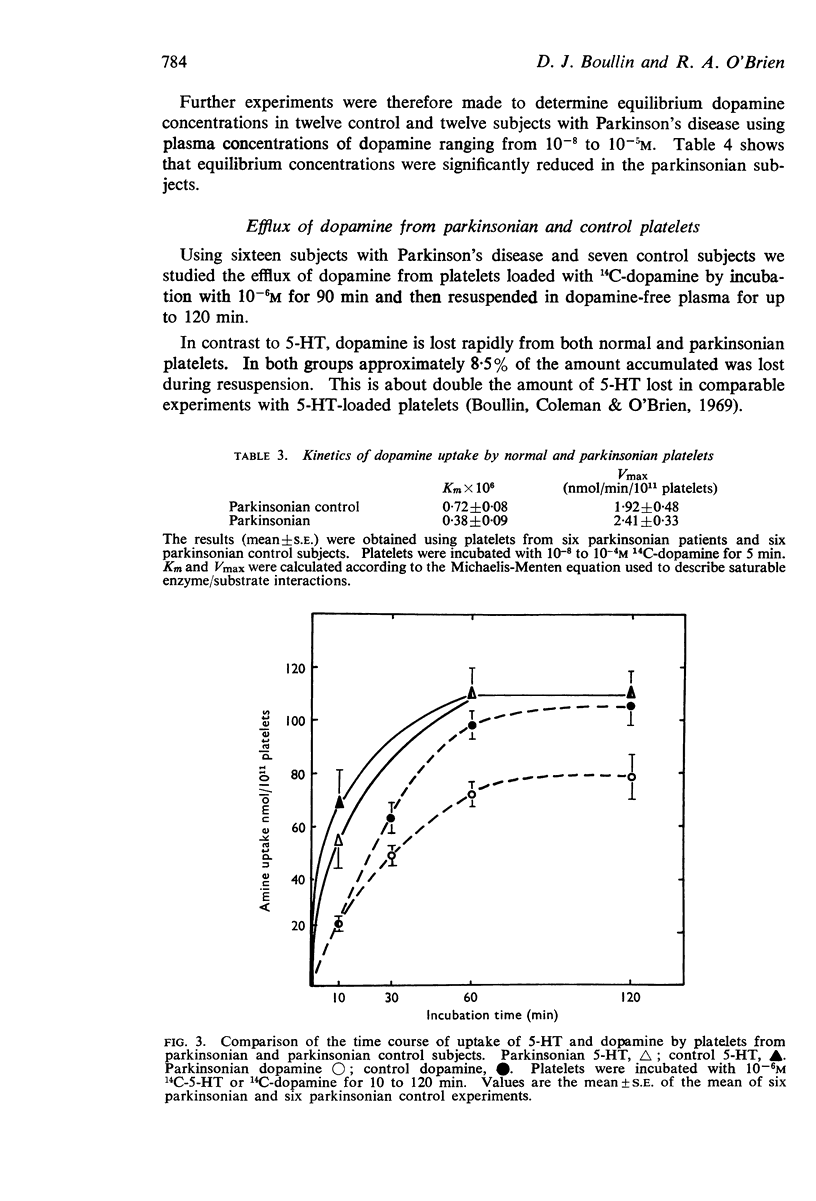
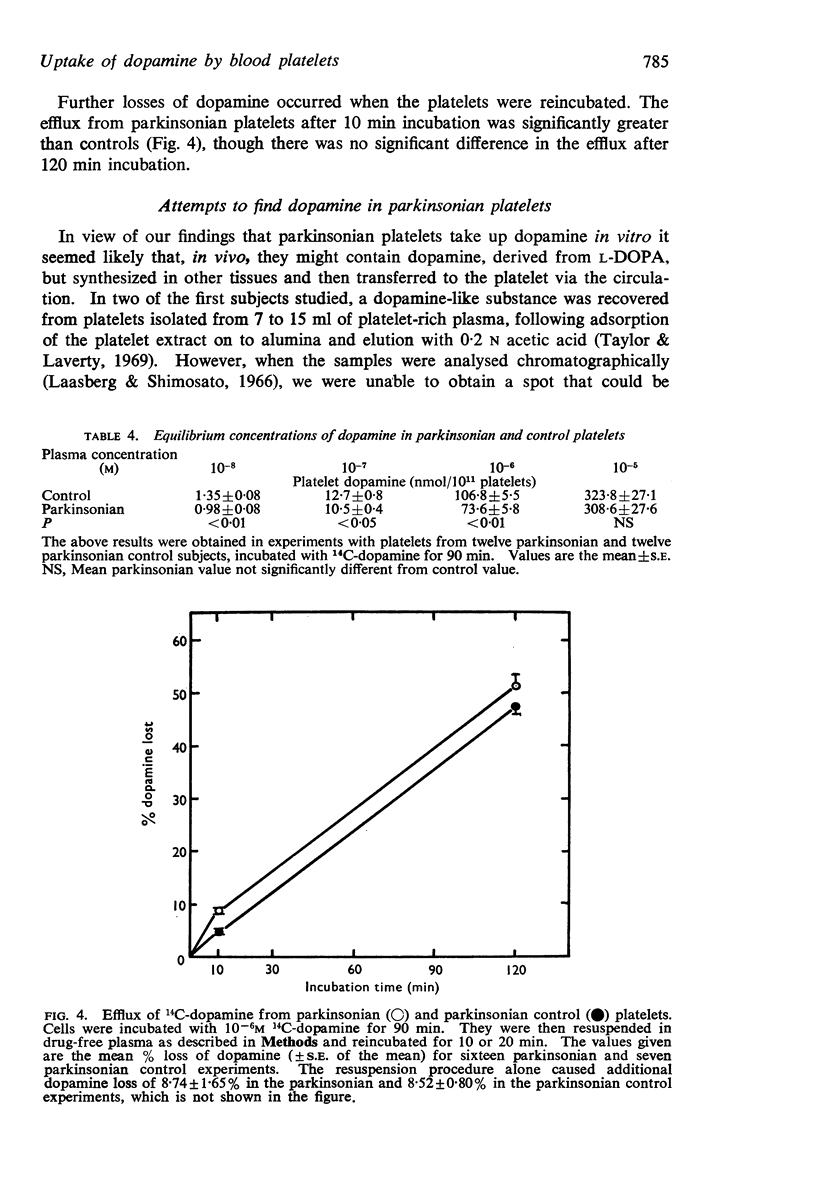
3. When the responses of normal and parkinsonian platelets were compared, the parkinsonian cells showed the following differences: increased affinity for the dopamine transport process; decreased equilibrium concentrations of dopamine after incubation for 90 min, and greater efflux of dopamine from loaded platelets during a 10 min incubation.
4. There were no differences in the uptake of 5-HT by parkinsonian platelets, but endogenous 5-HT was significantly reduced; ATP was normal.
5. In two out of three samples of platelets from parkinsonian subjects, traces of a dopamine-like substance were detected, but this finding requires confirmation.
6. If the platelet is a valid model for dopaminergic brain neurones, then the results described would suggest that dopamine uptake and storage may be abnormal in brain neurones in Parkinson's disease.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOGDANSKI D. F., PLETSCHER A., BRODIE B. B., UNDENFRIEND S. Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., HORNYKIEWICZ O., STAFFORD A. The uptake of adrenaline and noradrenaline by blood platelets of the pig. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Dec;13(4):411–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berneis K. H., Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Micelle formation between 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine triphosphate in platelet storage organelles. Science. 1969 Aug 29;165(3896):913–914. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3896.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berneis K. H., Pletscher A., Da Prada M. Metal-dependent aggregation of biogenic amines: a hypothesis for their storage and release. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):281–282. doi: 10.1038/224281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullin D. J., O'Brien R. A. The accumulation of guanethidine by human blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):90–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Differential uptake of biogenic amines by isolated 5-hydroxytryptamine organelles of blood platelets. Life Sci. 1969 Jan 1;8(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., STACEY R. S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine in normal human platelets. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):711–720. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., TOH C. C. Absorption of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) and histamine by dog platelets. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):300–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Holmsen I., Bernhardsen A. Microdetermination of adenosine diphosphate and adenosine triphosphate in plasma with firefly luciferase system. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):456–473. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laasberg L. H., Shimosato S. Paper chromatographic identification of catecholamines. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Nov;21(6):1929–1934. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.6.1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paasonen M. K. Platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine as a model in pharmacology. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1968;46(3):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletscher A. Metabolism, transfer and storage of 5-hydroxytryptamine in blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. M., Laverty R. The metabolism of tritiated dopamine in regions of the rat brain in vivo. I. The separation of catecholamines and their metabolites. J Neurochem. 1969 Sep;16(9):1361–1366. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


