Abstract
1. In the neuronally isolated cortex of the cat, local application of diphenhydramine, promethazine, gammahydroxybutyrate, gammabutyrolactone, gamma aminobutyric acid, hyoscine and pethidine, and the intravenous injection of diazepam and meprobamate depressed or abolished the surface negative and surface positive response to direct stimulation and raised the stimulus threshold of the positive burst response. These effects were the same as previously demonstrated for general and local anaesthetics on the same preparation.
2. Chlorpromazine produced a similar depression in small concentrations but caused spontaneous activity in higher concentrations.
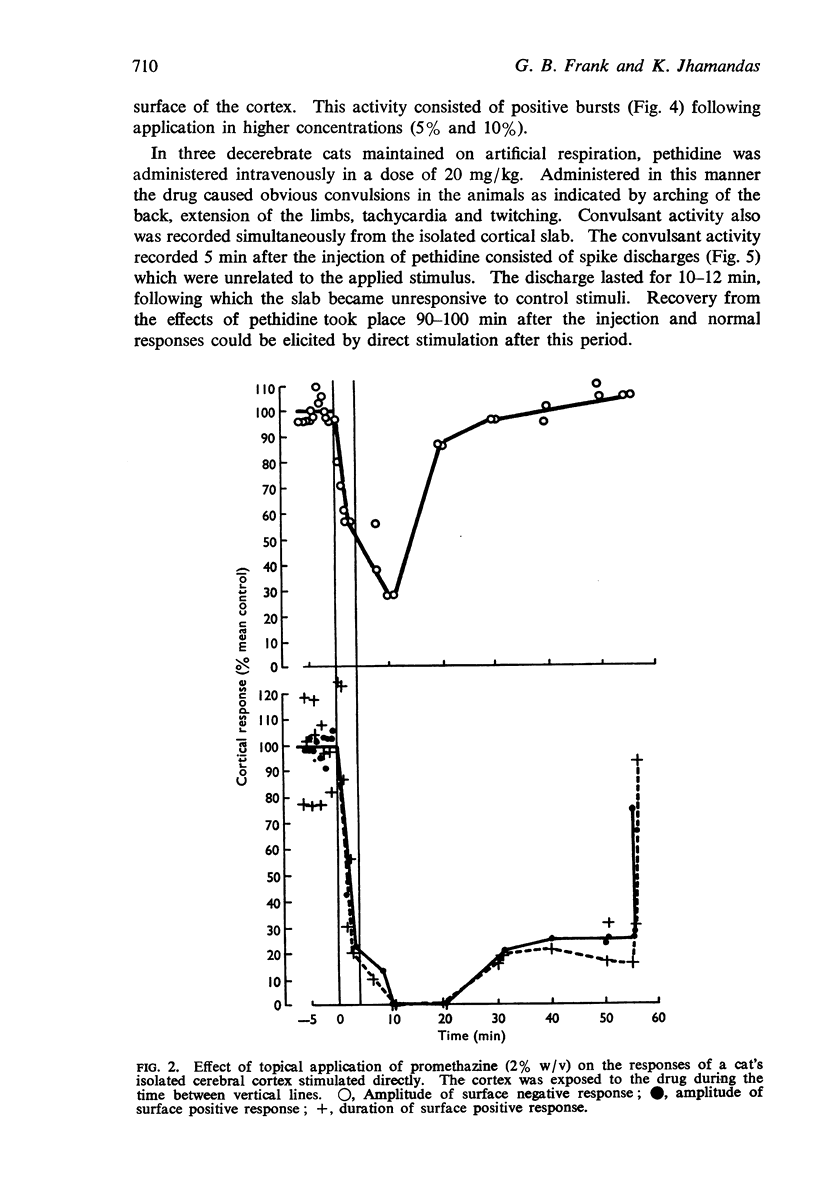
3. In contrast to local application, pethidine when given by intravenous injection in a high dose produced convulsant activity in the isolated cortical slab. The possibility was suggested that the convulsant activity was produced by a metabolite of pethidine.
4. The results of this investigation suggest that the central depression produced by a number of structurally unrelated drugs is indicative of an anaesthetic-like property of these drugs.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNS B. D., GRAFSTEIN B. The function and structure of some neurones in the cat's cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):412–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns B. D. Some properties of the cat's isolated cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1950 Apr 15;111(1-2):50–68. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK G. B., SANDERS H. D. A PROPOSED COMMON MECHANISM OF ACTION FOR GENERAL AND LOCAL ANAESTHETICS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Aug;21:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B. Drugs which modify membrane excitability. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):132–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B., Jhamandas K. Effects of drugs acting alone and in combination on the motor activity of intact mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Aug;39(4):696–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. B., Pinsky C. Tetrodotoxin-induced central nervous system depression. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Feb;26(2):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. The effect of methyl, ethyl and n-propyl alcohol on neuromuscular transmission in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Nov;150(2):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue F., Frank G. B. Effects of ethyl alcohol on excitability and on neuromuscular transmission in frog skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 May;30(1):186–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINALDI F., HIMWICH H. E. Drugs affecting psychotic behavior and the function of the mesodiencephalic activating system. Dis Nerv Syst. 1955 May;16(5):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. The effect of anesthetic agents on skeletal muscle membrane. Acta Physiol Scand. 1956 Nov 5;37(4):335–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1956.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


