Abstract
1. Tubular size and lissamine green transit times were measured in rat kidneys undergoing a diuretic response to angiotensin II (0·5 μg/kg per min), and compared with the changes observed during diuresis induced by osmotic diuretics, noradrenaline and chlorothiazide.
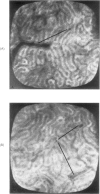
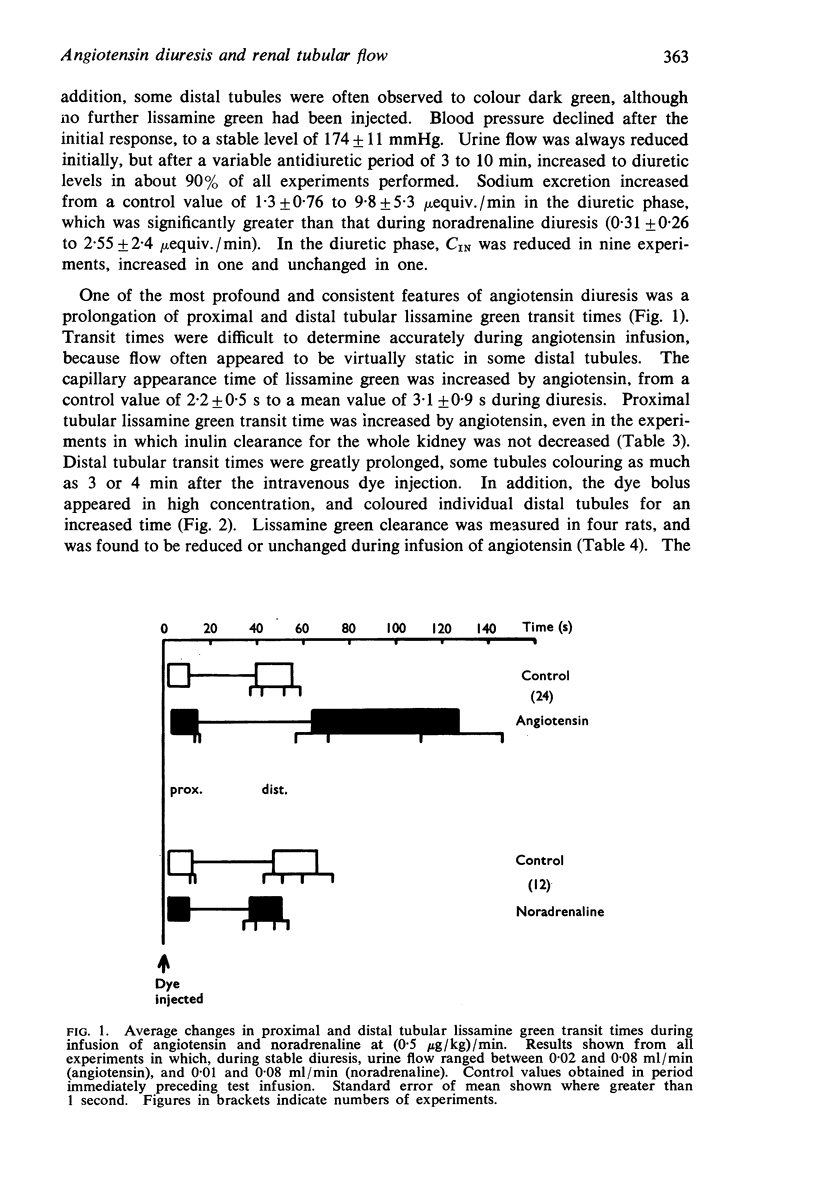
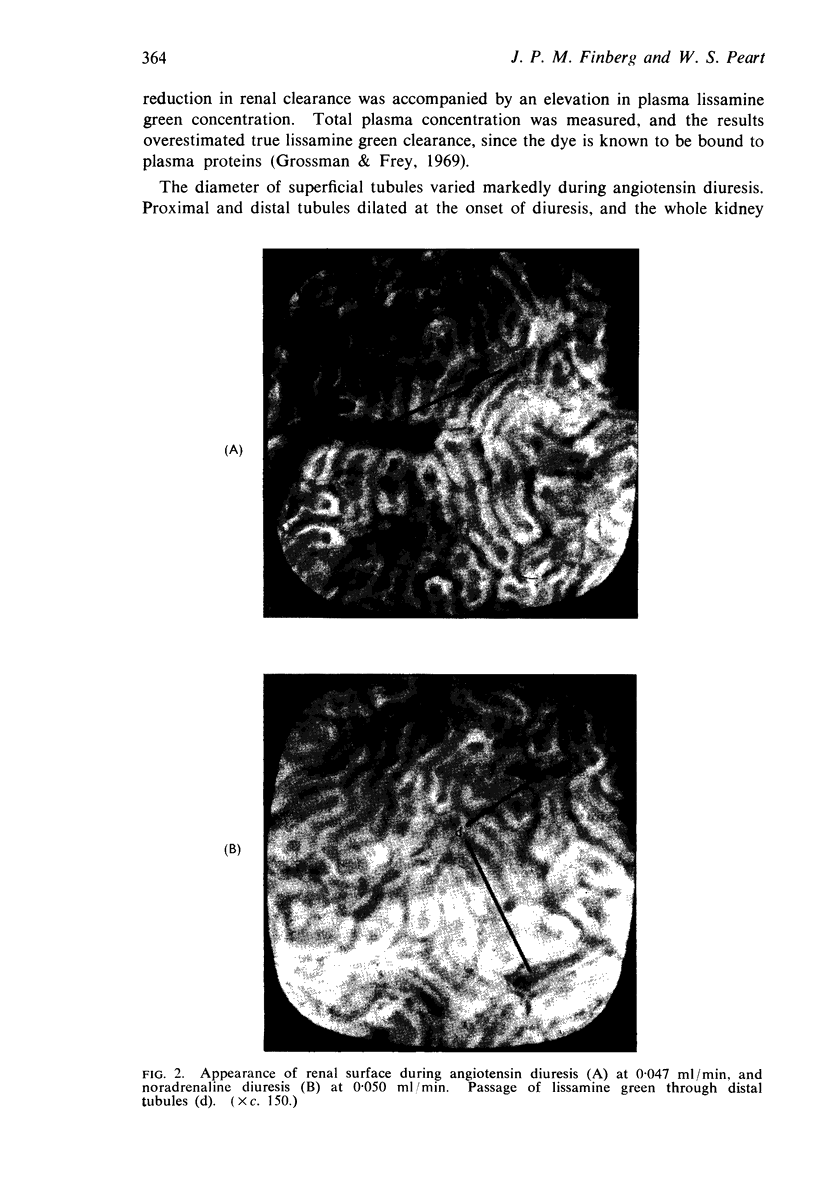
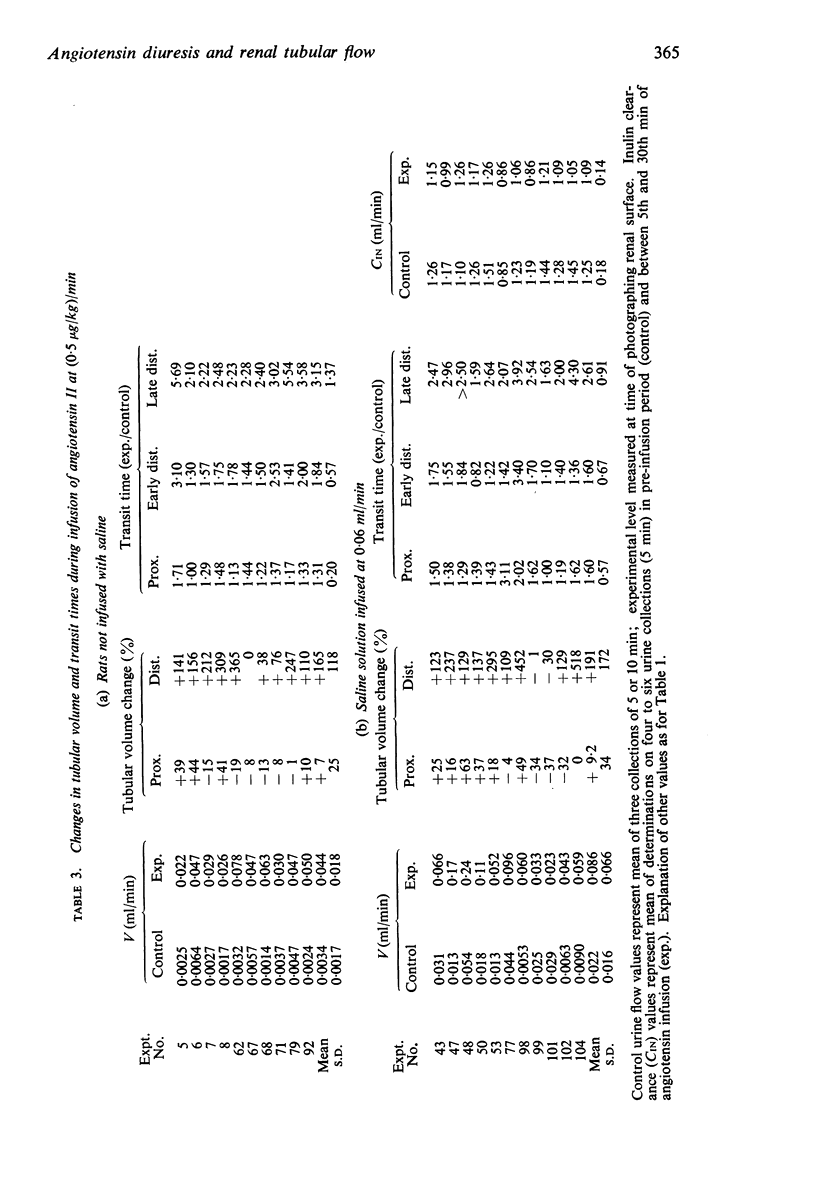
2. Angiotensin always caused a marked prolongation in proximal and distal tubular transit times; individual distal convolutions were coloured for prolonged periods, and lissamine green appeared in high concentration in distal tubules.
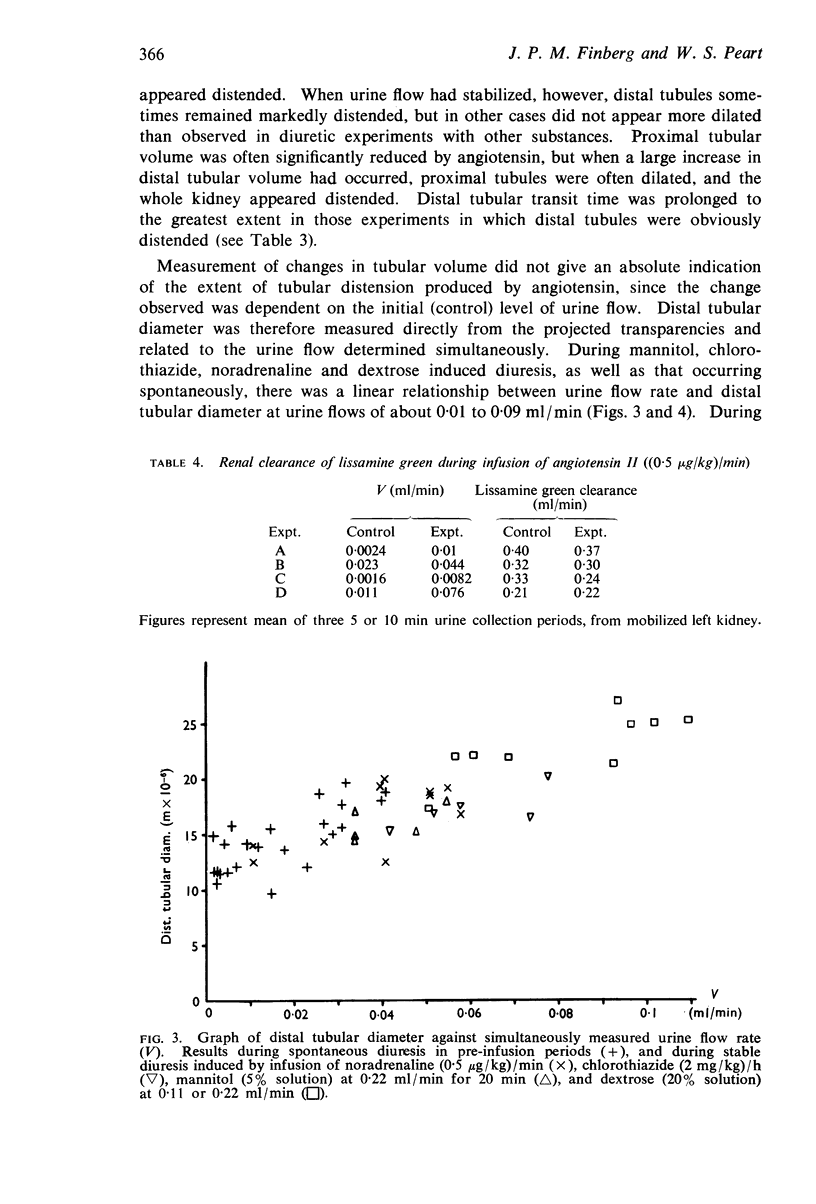
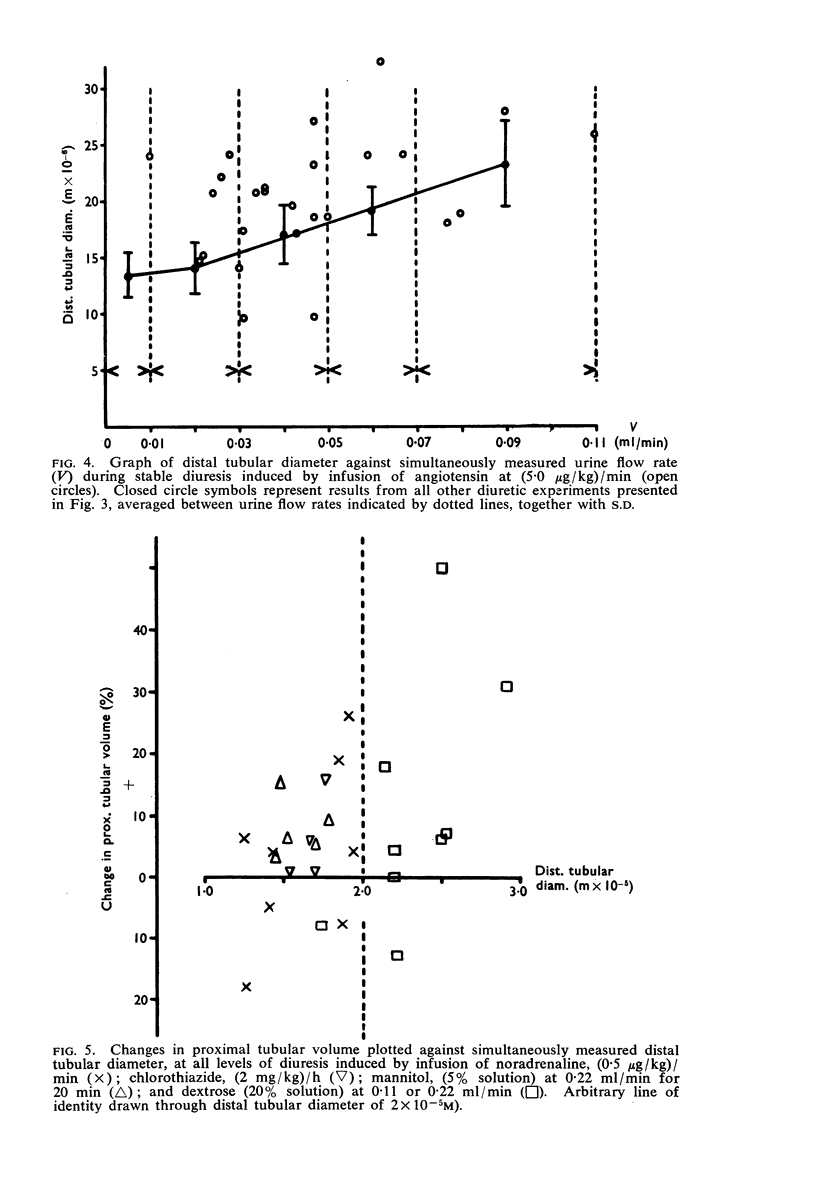
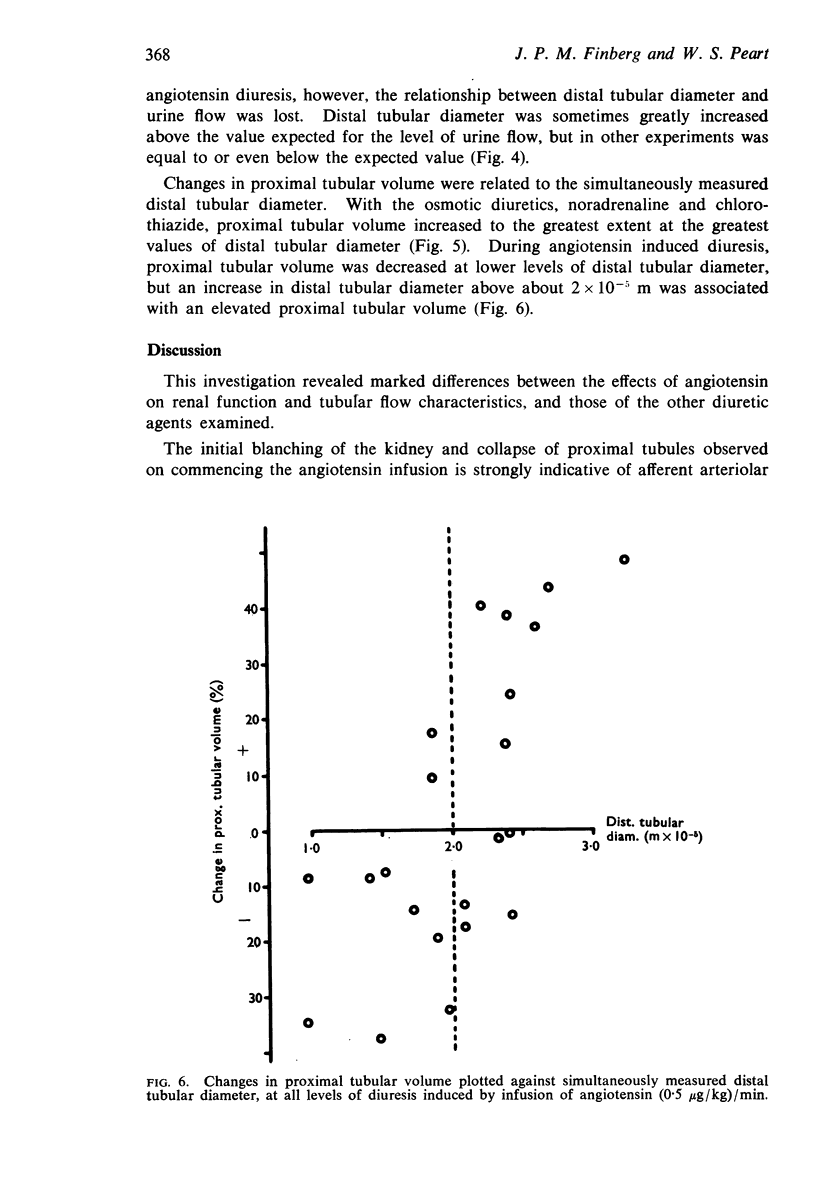
3. Marked changes were observed in superficial tubular calibre during a stable diuretic response to angiotensin. Where distal tubular diameter was normal for the rate of urine flow, proximal tubular volume was generally reduced. In a number of experiments, however, distal tubules were markedly dilated, and in these cases proximal tubular volume was also often increased. Angiotensin may therefore be capable of causing a degree of internal hydronephrosis in the rat kidney.
4. Prolongation of dye transit times, and the appearance of a concentrated lissamine green bolus in distal tubules, was suggestive of a decreased superficial nephron flow rate, indicating that the diuretic effect of angiotensin may take place only through deeper nephrons.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONTING S. L., CANADY M. R., HAWKINS N. M. ANGIOTENSIN AND RENAL NA-K ACTIVATED ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE. (STUDIES ON NA-K ACTIVATED ATPASE, VIII). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:427–429. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. VARIATIONS IN PLASMA RENIN CONCENTRATION IN SEVERAL PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PATHOLOGICAL STATES. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:201–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., PEART W. S. The effect of angiotension on urine flow and electrolyte excretion in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci. 1962 Feb;22:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. D., Gottschalk C. W., Leyssac P. P. Proximal luminal volume and fluid reabsorption in the rat kidney. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Nov;74(3):440–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough M. A. Dose-dependent opposite effects of angiotensin on renal sodium excretion. Lancet. 1965 Nov 13;2(7420):987–988. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92845-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough M. A., Jones N. F., Marsden C. D. Effect of angiotensin on renal function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1153–1157. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., Malvin R. L. Renal extraction of PAH, GFR, and UNaV in the rat during infusion of angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):554–558. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., Regoli D., Roch-Ramel F., Peters G. Prerequisites for the natriuretic effect of val-5-angiotensin II amide in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1133–1138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Landon J., Peart W. S. The radioimmunoassay of angiotensin II. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Jul 1;173(1032):327–338. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Bennett C. M., Berliner R. W. The relationship between glomerular filtration rate and sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1358–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI105828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Lever A. F., Davies D. L., Robertson J. I. Renin and angiotensin. A survey of some aspects. Postgrad Med J. 1966 Mar;42(485):153–176. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.42.485.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEBONO E., LEEGDE J., MOTTRAM F. R., PICKERING G. W., BROWN J. J., KEEN H., PEART W. S., SANDERSON P. H. THE ACTION OF ANGIOTENSIN IN MAN. Clin Sci. 1963 Aug;25:123–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEXTER D., STONER H. B. The role of the adrenal medulla in water diuresis in rats. J Physiol. 1952 Dec;118(4):486–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Friedler R. M. The effects of combined renal vasodilatation and pressor agents on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):542–551. doi: 10.1172/JCI105368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg J. P., Peart W. S. Function of smooth muscle of the rat renal pelvis--response of the isolated pelvis muscle to angiotensin and some other substances. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of pressures in proximal and distal tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney during osmotic diuresis. Am J Physiol. 1957 May;189(2):323–328. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of pressures in proximal tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney and their relation to ureteral and renal venous pressures. Am J Physiol. 1956 May;185(2):430–439. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.2.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN A. F., SIM M. F. Diuresis in rats: effects of sympathomimetic and sympathetic blocking agents. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Dec;17:464–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertz K. H., Mangos J. A., Braun G., Pagel H. D. On the glomerular tubular balance in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Sep 15;285(4):360–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00363236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYROVSKY A. A new method for the determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1956 Sep-Oct;1(5):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(56)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. K., Dougles J. B. The effect of angiotensin on renal carbonic anhydrase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 5;151(2):520–522. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Nagel W., Schnermann J., Thurau K. Zur Frage einer direkten Angiotensinwirkung auf die Natriumresorption im proximalen Tubulus und in der Henleschen Schleife der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;292(2):118–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Thurau K. Micropuncture studies on the filtration rate of single superficial and juxtamedullary glomeruli in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(2):162–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00362733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. M., Aynedjian H. S., Bank N. Effect of acute hypertension on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1696–1709. doi: 10.1172/JCI105860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEYSSAC P. P. SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PROXIMAL TUBULAR WALL RELATED TO REABSORPTION DURING LUMINAL OCCLUSION FOLLOWING INTERRUPTION OF GLOMERULAR FILTRATION. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:36–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lameijer L. D., Soghikian K., de Graeff J. The effect of angiotensin on renal sodium excretion: studies in normal dogs and in dogs with experimental renal artery stenosis. Clin Sci. 1966 Jun;30(3):529–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laragh J. H., Cannon P. J., Bentzel C. J., Sicinski A. M., Meltzer J. I. ANGIOTENSIN II, NOREPINEPHRINE, AND RENAL TRANSPORT OF ELECTROLYTES AND WATER IN NORMAL MAN AND IN CIRRHOSIS WITH ASCITES. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42(7):1179–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI104803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowitz H. D., Stumpe K. O., Ochwadt B. Micropuncture study of the action of angiotensin-II on tubular sodium and water reabsorption in the rat. Nephron. 1969;6(3):173–187. doi: 10.1159/000179727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvin R. L., Vander A. J. Effects of angiotensin infusion on renal function in the unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Nov;213(5):1205–1208. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.5.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee R. D., Locke W. Effect of angiotensin amide on sodium isotope flux and short-circuit current of isolated frog skin. Endocrinology. 1967 Dec;81(6):1301–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-6-1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIJENSOHN C. M. Accion de la hipertensina o angiotonina en la hipertension arterial humana; su efecto sobre el rifión: modificaciones hemodinámicas de la diuresis y de la excreción del sodio. II. Sem Med. 1957 Aug 8;111(6):268–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS G. Renal tubular effect of val-5-angiotensin II amide in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:771–775. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr, Brunner F. P., Seldin D. W. Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance. I. Effect of aortic constriction and elevated ureteropelvic pressure on glomerular filtration rate, fractional reabsorption, transit time, and tubular size in the proximal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):590–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINHAUSEN M., IRAVANI I., SCHUBERT G. E., TAUGNER R., BRAUN A., VON EGIDY, ROHMANN F. P., TAUGNER G. AUFLICHTMIKROSKOPIE UND HISTOLOGIE DER TUBULUSDIMENSIONEN BEI VERSCHIEDENEN DIURESEZUSTAENDEN. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1963 Aug 8;336:503–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THURAU K., WOBER E. [On the localization of autoregulative resistance changes in the kidneys. Micropuncture measurements of the pressure in the tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney in changes of arterial pressure]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1962;274:553–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Liebau G., Fischbach H., Schnermann J. Balance between tubular flow rate and net fluid reabsorption in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. II. Reabsorptive characteristics during constriction of the renal artery. Pflugers Arch. 1968;304(4):297–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00587706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]