Abstract
1. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), acetylcholine (ACh), noradrenaline (NA), glutamate, D,L-homocysteic acid (DLH), glycine and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) were applied to single neurones in the brain stem of decerebrate cats by microiontophoresis. The abilities of D-lysergic acid diethylamide tartrate (LSD 25), methysergide maleate (UML 491) and 2-bromo-lysergic acid diethylamide (BOL 148) to antagonize the actions of these compounds were studied.
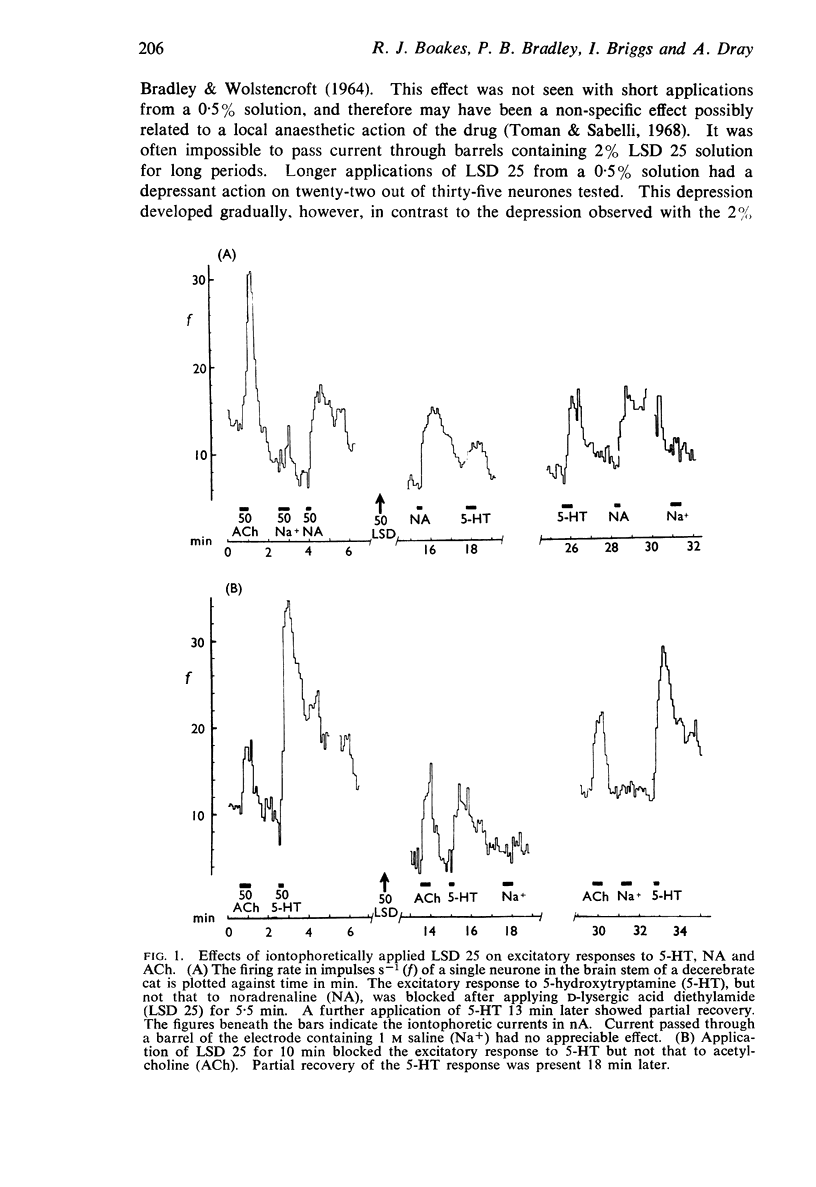
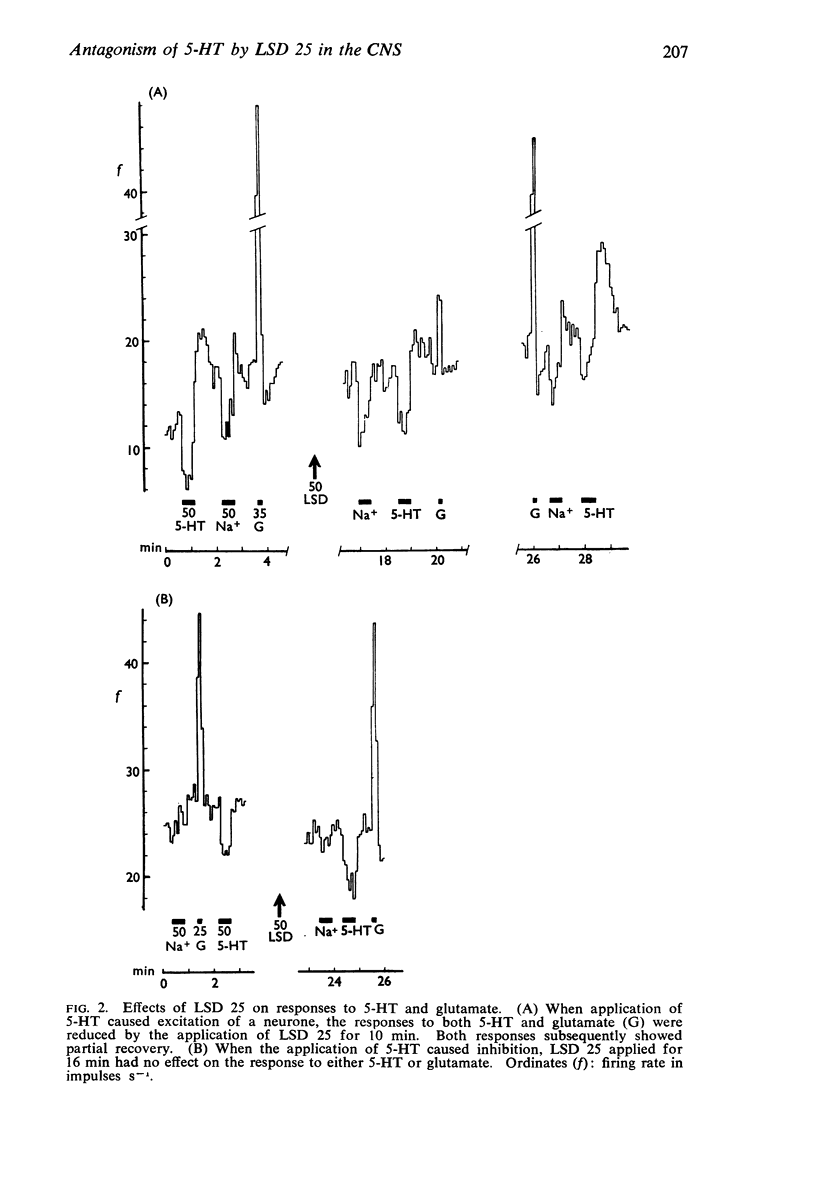
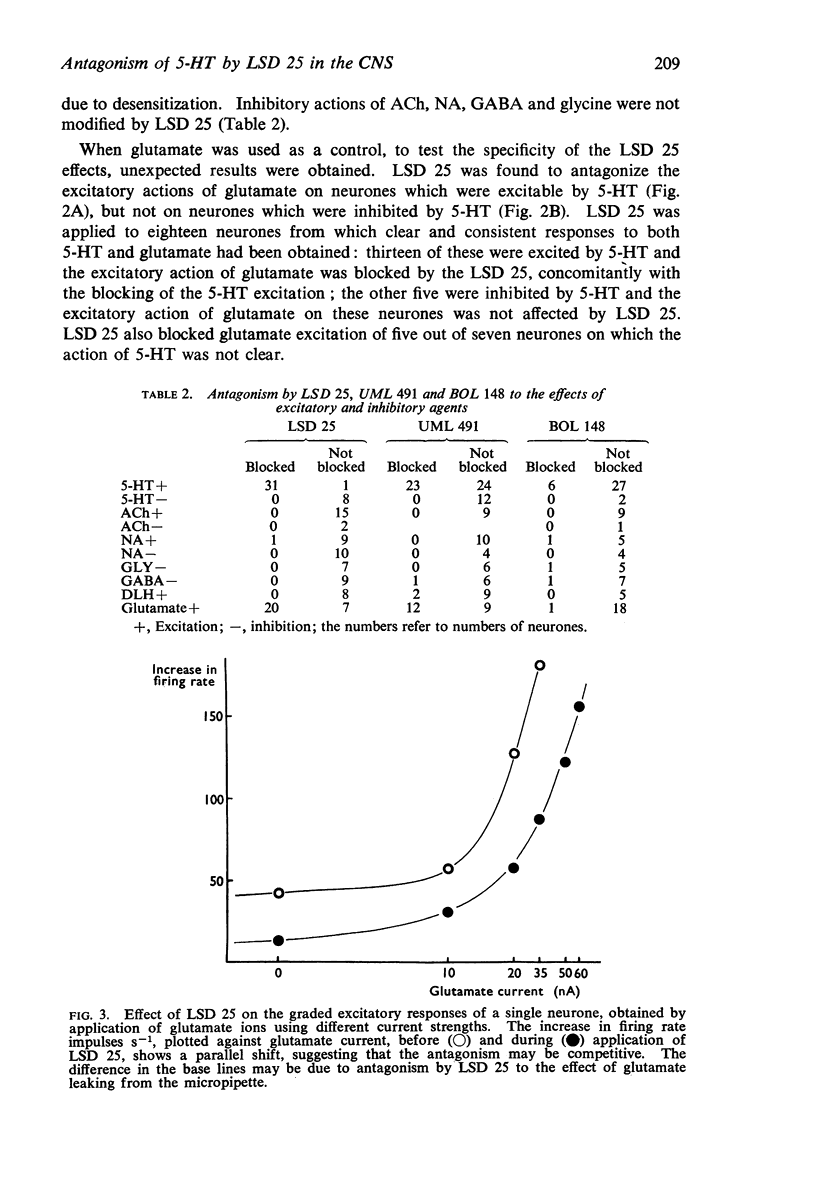
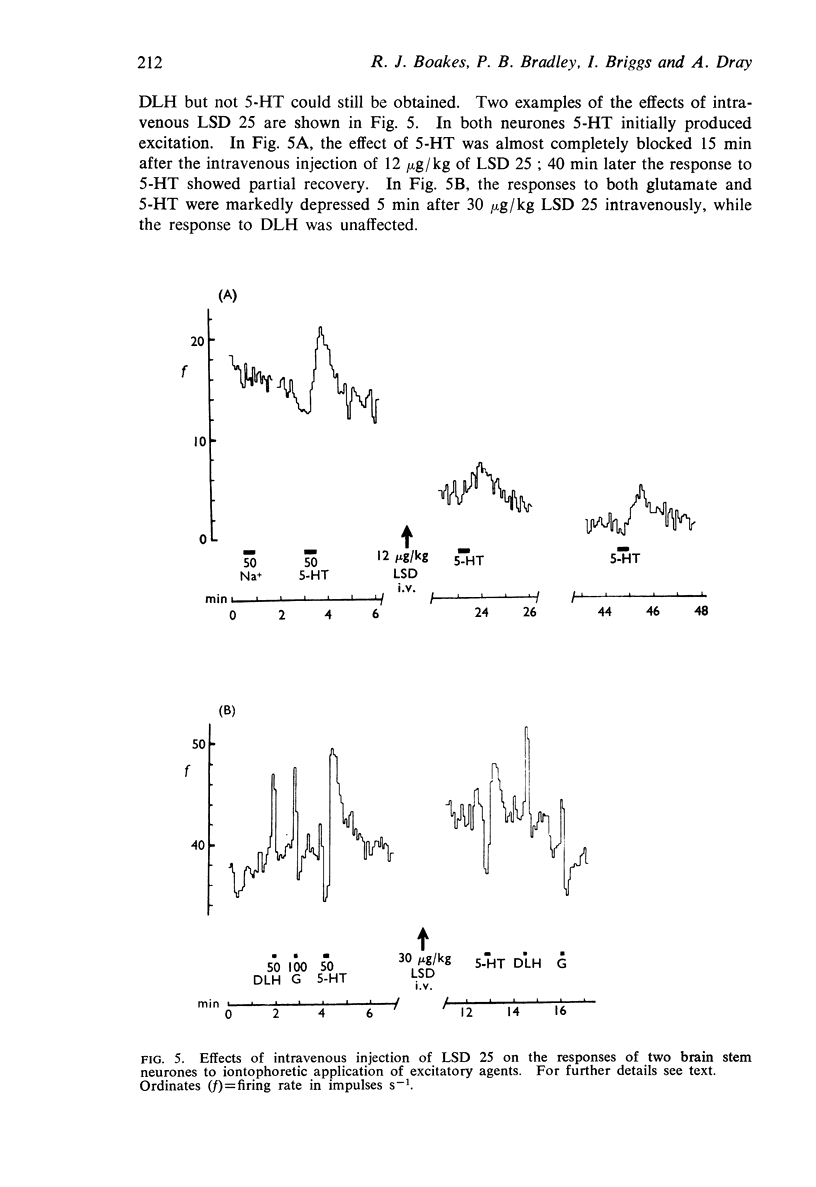
2. LSD 25 antagonized 5-HT excitation of single neurones when applied iontophoretically or administered intravenously. LSD 25 also antagonized glutamate excitation of neurones which could be excited by 5-HT. Inhibitory effects of 5-HT, the action of glutamate on neurones which could be inhibited by 5-HT and the actions of all the other compounds tested were unaffected by LSD 25.
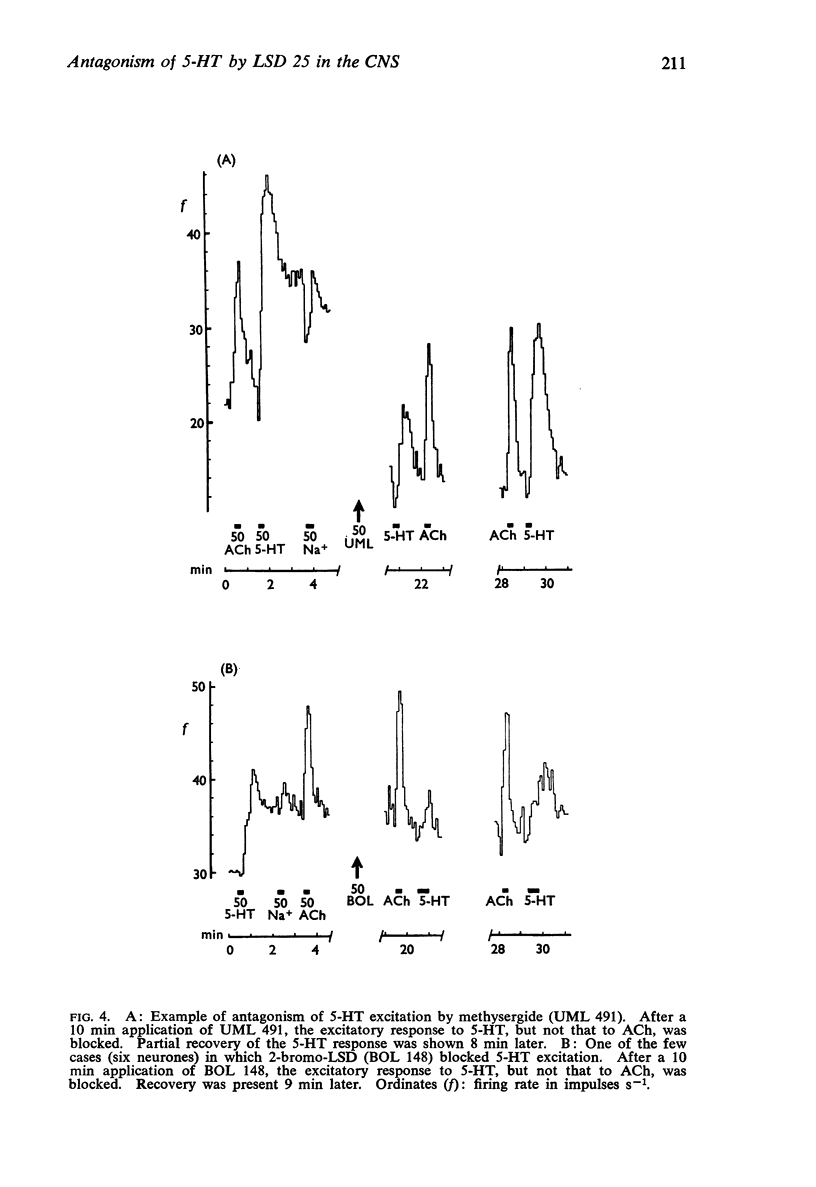
3. Iontophoretically applied UML 491 was also a specific antagonist to 5-HT and glutamate excitation but was less potent than LSD 25, and BOL 148 rarely exhibited antagonism.
4. It is suggested that antagonism to 5-HT and glutamate excitation of brain stem neurones may be the basis of the psychotomimetic action of LSD 25. It is also suggested that there may be similarities in the mechanisms by which 5-HT and glutamate produce excitation where they act on the same neurone.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIN A. H., CRAWFORD T. B., GADDUM J. H. The distribution of substance P and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the central nervous system of the dog. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):596–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM F. E., COSTA E., SALMOIRAGHI G. C. ANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL RABBIT OLFACTORY BULB NEURON RESPONSES TO THE MICROELECTROPHORESIS OF ACETYLCHOLINE, NOREPINEPHRINE AND SEROTONIN SYNERGISTS AND ANTAGONISTS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Oct;146:16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., ELKES J. The effects of some drugs on the electrical activity of the brain. Brain. 1957 Mar;80(1):77–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., KEY B. J. The effect of drugs on arousal responses produced by electrical stimulation of the reticular formation of the brain. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Feb;10(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., WOLSTENCROFT J. H. ACTIONS OF DRUGS ON SINGLE NEURONES IN THE BRAIN-STEM. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:15–18. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Straughan D. W. Micro-electrophoretic studies of neurones in the cat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(2):341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boakes R. J., Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Dray A. Antagonism by LSD to effects of 5-HT on single neurones. Brain Res. 1969 Oct;15(2):529–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boakes R. J., Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Dray A. Effects of lysergic acid derivatives on 5-hydroxytryptamine excitation of brain stem neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;38(2):453P–454P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Candy J. M. Iontophoretic release of acetylcholine, noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and D-lysergic acid diethylamide from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Dhawan B. N., Wolstencroft J. H. Pharmacological properties of cholinoceptive neurones in the medulla and pons of the cat. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):658–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B. Synaptic transmission in the central nervous system and its relevance for drug action. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1968;11:1–56. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Comer M. S., Costa E., Dlabac A. The role of brain serotonin in the mechanism of the central action of reserpine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 May;152(2):340–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Reid W. D. Serotonin in brain: functional considerations. Adv Pharmacol. 1968;6(Pt B Suppl):97–113. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERLETTI A., ROTHLIN E. Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in mental diseases and its antagonism to lysergic acid derivatives. Nature. 1955 Oct 22;176(4486):785–786. doi: 10.1038/176785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., DAVIS R. Pharmacological studies upon neurones of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Apr;18:217–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PERRIN D. D., WATKINS J. C. The excitation of spinal neurones by the ionophoretic application of agents which chelate calcium. J Neurochem. 1960 Aug;6:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T. N., Breese G. R., Kopin I. J. Serotonin release from brain slices by electrical stimulation: regional differences and effect of LSD. Science. 1967 Sep 22;157(3795):1461–1463. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3795.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Crawford J. M. Central synaptic transmission--microelectrophoretic studies. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1969;9:209–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz P. M., Ngai S. H., Costa E. Factors modulating brain serotonin turnover. Adv Pharmacol. 1968;6(Pt B):75–92. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN D. X., GIARMAN N. J. LSD-25 and the status and level of brain serotonin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Jan 13;96:98–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb50105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDHOFF A. J., ABRAMS B. Effect of glutamic acid and glutamine on the pyretogenic action of lysergic acid diethylamide. J Clin Exp Psychopathol Q Rev Psychiatry Neurol. 1960 Jan-Mar;21:7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. IV. DISTRIBUTION OF MONOAMINE NERVE TERMINALS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965:SUPPL 247–247:37+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H., FERRER S., CASTELLS C., LESEVRE N., LUSCHNAT K. Action de la diéthylamide de l'acide d'lysergique (LSD 25) sur les fonctions psychiques et l'eléctroencéphalogramme. Confin Neurol. 1953;13(2):102–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIARMAN N. J., FREEDMAN D. X. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF THE ACTIONS OF PSYCHOTOMIMETIC DRUGS. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Mar;17:1–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFF H., ARNOLD O. H. Die Therapie der Schizophrenie. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1954 May 21;66(20):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp N. A., Fuxe K., Dahlström A. Demonstration and mapping of central neurons containing dopamine, noradrenaline, and 5-hydroxytryptamine and their reactions to psychopharmaca. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):727–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli L., Tebècis A. K., Filias N. Effects of glycine, beta-alanine and GABA, and their interaction with strychnine, on brain stem neurones. Brain Res. 1969 Nov;16(1):293–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISBELL H., MINER E. J., LOGAN C. R. Relationships of psychotomimetic to anti-serotonin potencies of congeners of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25). Psychopharmacologia. 1959;1:20–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00408108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Sobieszek A., Straughan D. W. Noradrenaline sensitive cells in cat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Dec;8(6):549–566. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. The responses of cortical neurones to monoamines under differing anaesthetic conditions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):261–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):32–41. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEY B. J. EFFECT OF LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE ON POTENTIALS EVOKED IN THE SPECIFIC SENSORY PATHWAYS. Br Med Bull. 1965 Jan;21:30–35. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEY B. J. The effect of drugs on discrimination and sensory generalisation of auditory stimuli in cats. Psychopharmacologia. 1961;2:352–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00404123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., PHILLIS J. W. Actions of certain amines on cerebral cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:471–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai N., Yamamoto C. Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, LSD and related compounds on electrical activities evoked in vitro in thin sections from the superior colliculus. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Sep;8(5):437–449. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostowski W., Giacalone E., Garattini S., Valzelli L. Electrical stimulation of midbrain raphe: biochemical, behavioral and bioelectrical effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Aug;7(2):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAELSON I. A., WHITTAKER V. P. The distribution of hydroxytryptamine in brain fractions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Jun;11:505–506. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Tebecis A. K. The responses of thalamic neurons to iontophoretically applied monoamines. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):715–745. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Tebècis A. K., York D. H. The inhibitory action of monoamines on lateral geniculate neurones. J Physiol. 1967 Jun;190(3):563–581. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosecrans J. A., Lovell R. A., Freedman D. X. Effects of lysergic acid diethylamide on the metabolism of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Oct;16(10):2011–2021. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW E., WOOLLEY D. W. Some serotoninlike activities of lysergic acid diethylamide. Science. 1956 Jul 20;124(3212):121–122. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3212.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satinsky D. Pharmacological responsiveness of lateral geniculate nucleus neurons. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 Sep;6(5):387–397. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerdt A. K., Stewart A. H., Himwich H. E. An electrographic study of d-lysergic acid diethylamide and nine congeners. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Mar;151(3):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWAROG B. M., PAGE I. H. Serotonin content of some mammalian tissues and urine and a method for its determination. Am J Physiol. 1953 Oct;175(1):157–161. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.175.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Satoh M., Yamatsu K., Kimura K., Nakama M. Central effects of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophane on tetrabenazine pretreated rabbits with special reference to the possible role of catecholamine and serotonin in the brain. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 May;7(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toman J. E., Sabelli H. C. Neuropharmacology of earthworm giant fibers. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 Nov;7(6):543–556. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIEHER L. M., DE ROBERTIS E. Subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Jun;12:596–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


