Abstract
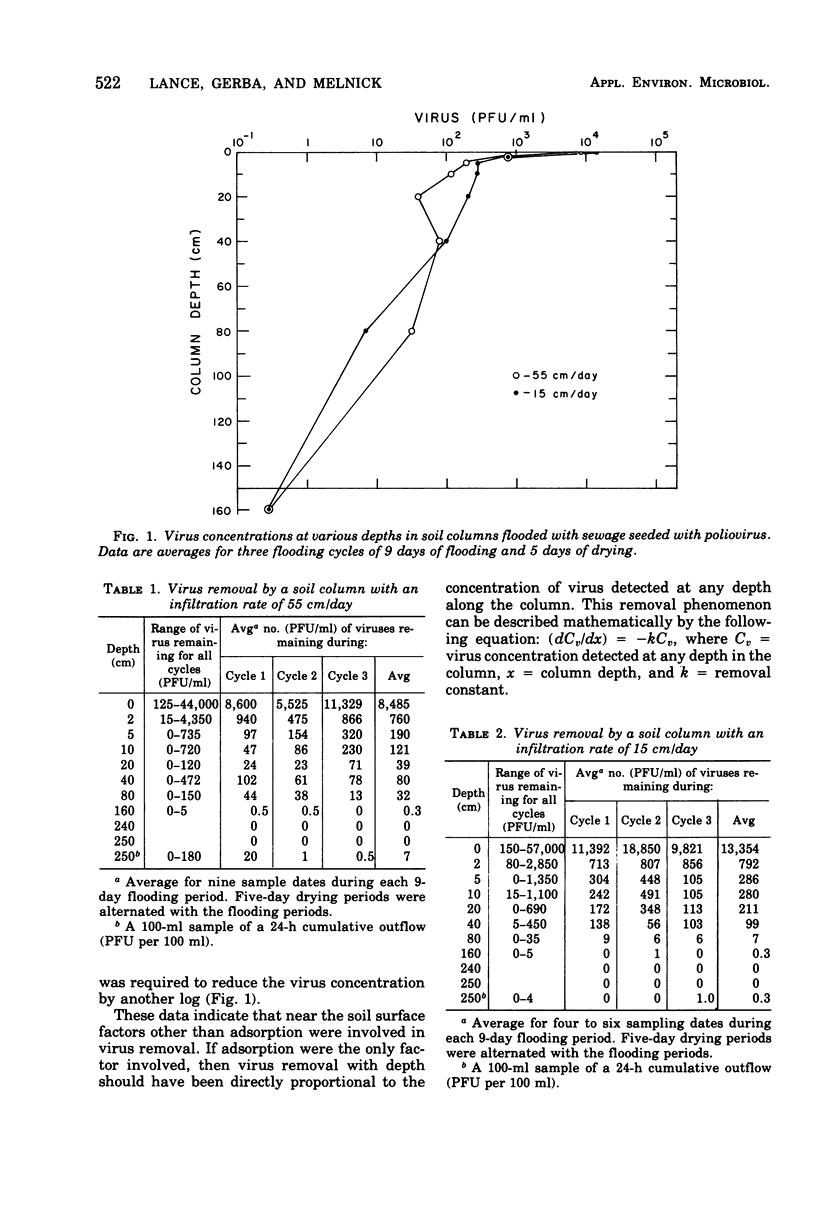
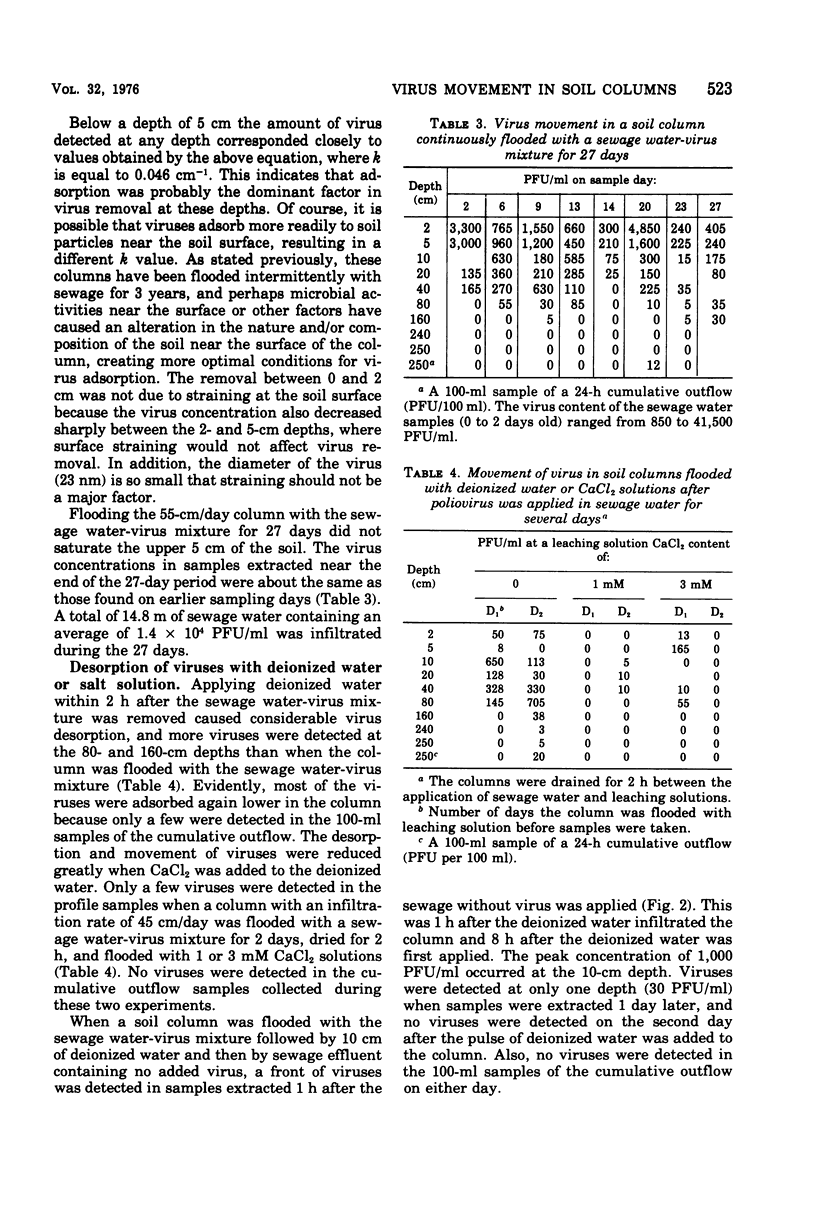
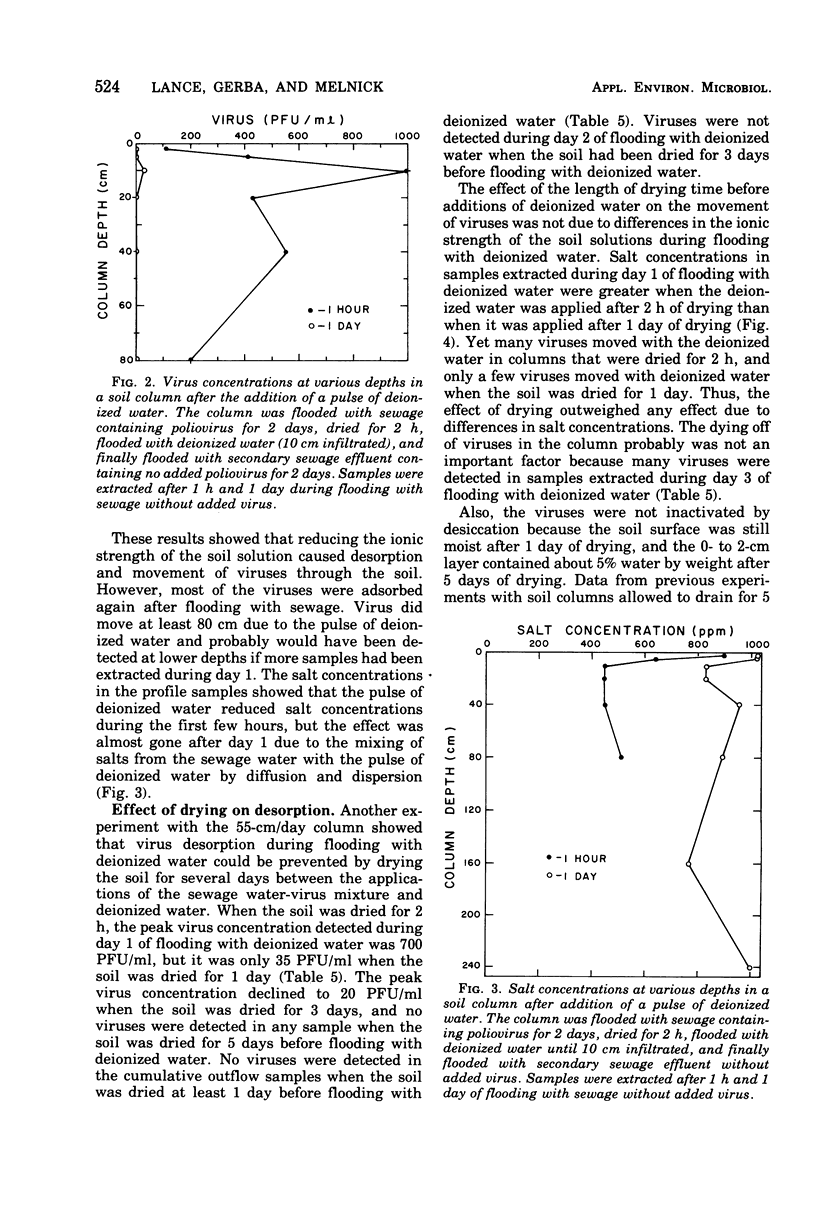
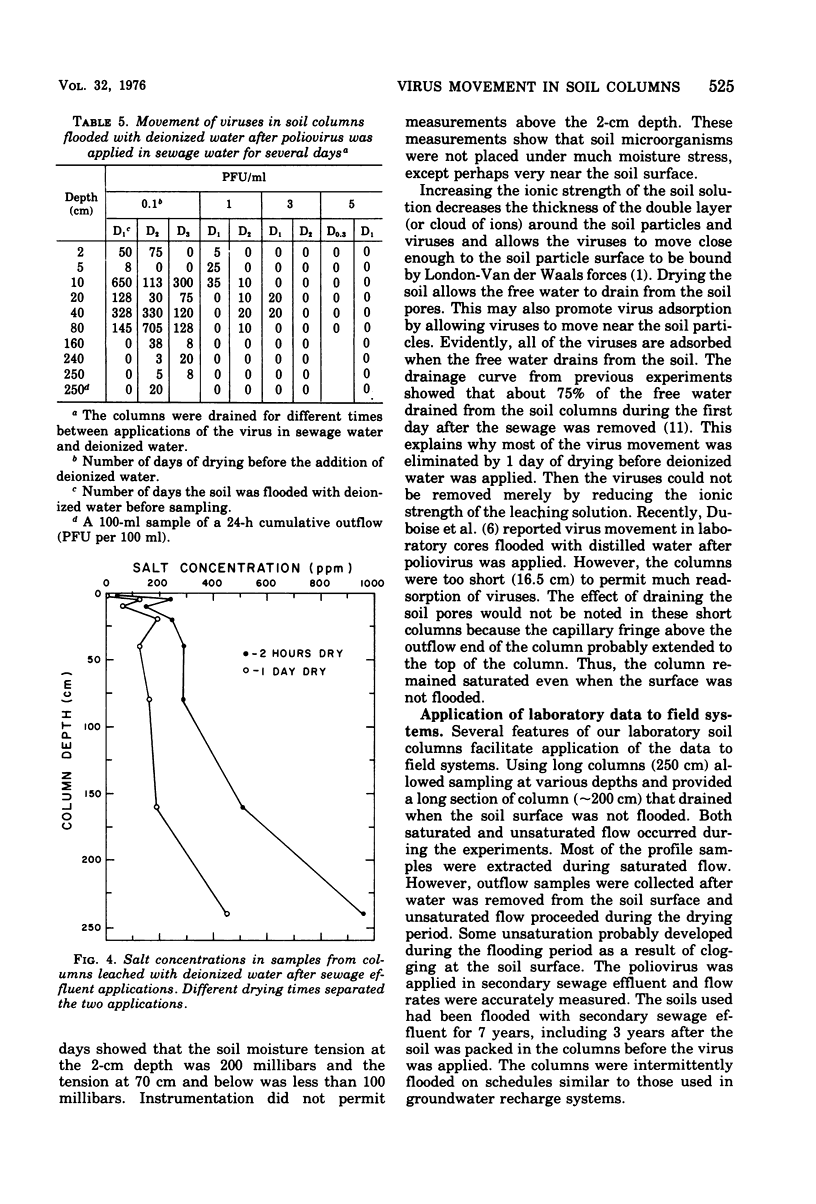
Secondary sewage effluent containing about 3 X 10(4) plaque-forming units of polio virus type 1 (LSc) per ml was passed through columns 250 cm in length packed with calcareous sand from an area in the Salt River bed used for ground-water recharge of secondary sewage effluent. Viruses were not detected in 1-ml samples extracted from the columns below the 160-cm level. However, viruses were detected in 5 of 43 100-ml samples of the column drainage water. Most of the viruses were adsorbed in the top 5 cm of soil. Virus removal was not affected by the infiltration rate, which varied between 15 and 55 cm/day. Flooding a column continuosly for 27 days with the sewage water virus mixture did not saturate the top few centimeters of soil with viruses and did not seem to affect virus movement. Flooding with deionized water caused virus desorption from the soil and increased their movement through the columns. Adding CaCl2 to the deionized water prevented most of the virus desorption. Adding a pulse of deionized water followed by sewage water started a virus front moving through the columns, but the viruses were readsorbed and none was detected in outflow samples. Drying the soil for 1 day between applying the virus and flooding with deionized water greatly reduced desorption, and drying for 5 days prevented desorption. Large reductions (99.99% or more) of virus would be expected after passage of secondary sewage effluent through 250 cm of the calcareous sand similar to that used in our laboratory columns unless heavy rains fell within 1 day after the application of sewage stopped. Such virus movement could be minimized by the proper management of flooding and drying cycles.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahling D. R., Berg G., Berman D. BGM, a continuous cell line more sensitive than primary rhesus and African green kidney cells for the recovery of viruses from water. Health Lab Sci. 1974 Oct;11(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboise S. M., Moore B. E., Sagik B. P. Poliovirus survival and movement in a sandy forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):536–543. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.536-543.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. G., Gerba C. P., Rice R. C., Bouwer H., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Virus and bacteria removal from wastewater by land treatment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):333–338. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.333-338.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Henderson M., Melnick J. L. Enterovirus concentration on cellulose membranes. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):476–480. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.476-480.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


