Abstract
1. Earlier it had been found that during fat mobilization there was an increased blood flow in the adipose tissue and the tissue contained a vasodilator substance.
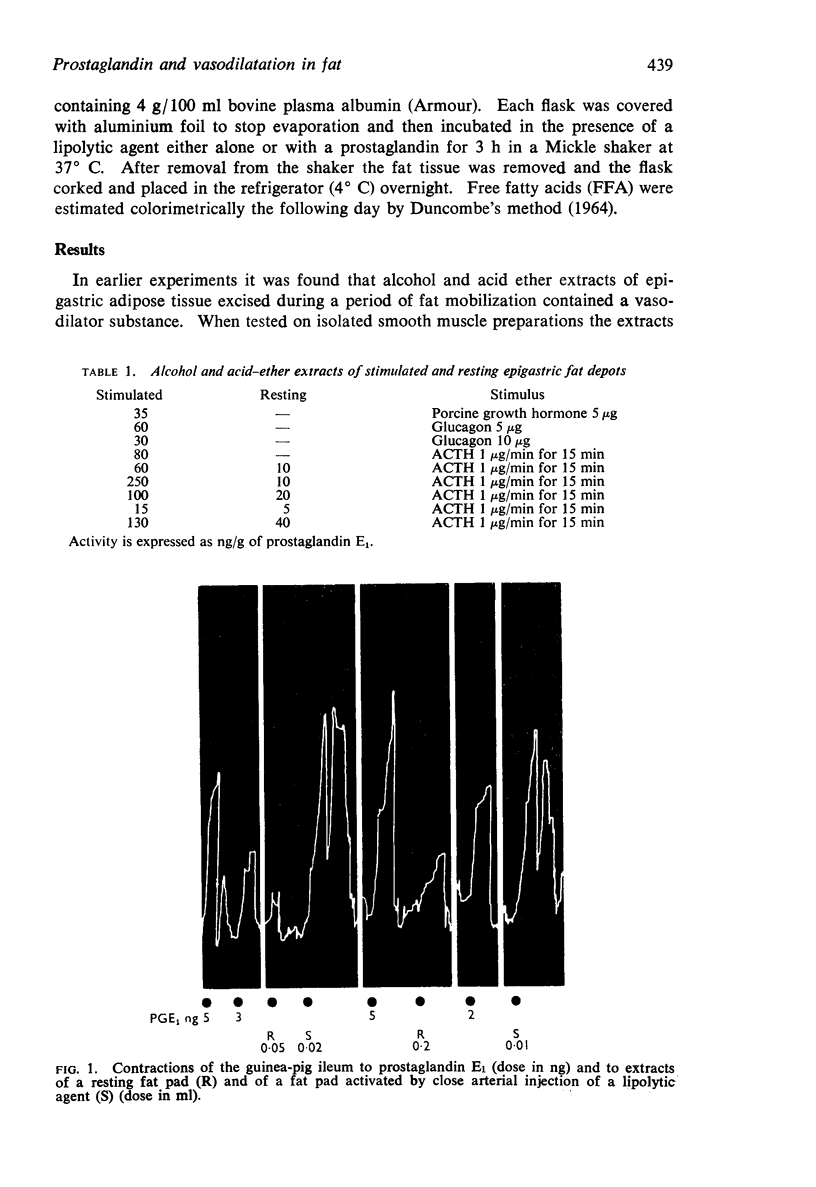
2. Extract of an activated fat pad contained 3 to 25 times as much activity as the contralateral resting fat pad.
3. The following findings suggest that the vasodilator substance is prostagladin E2:
(a) It caused contractions of the guinea-pig ileum which were not reduced by mepyramine, but were reduced by atropine.
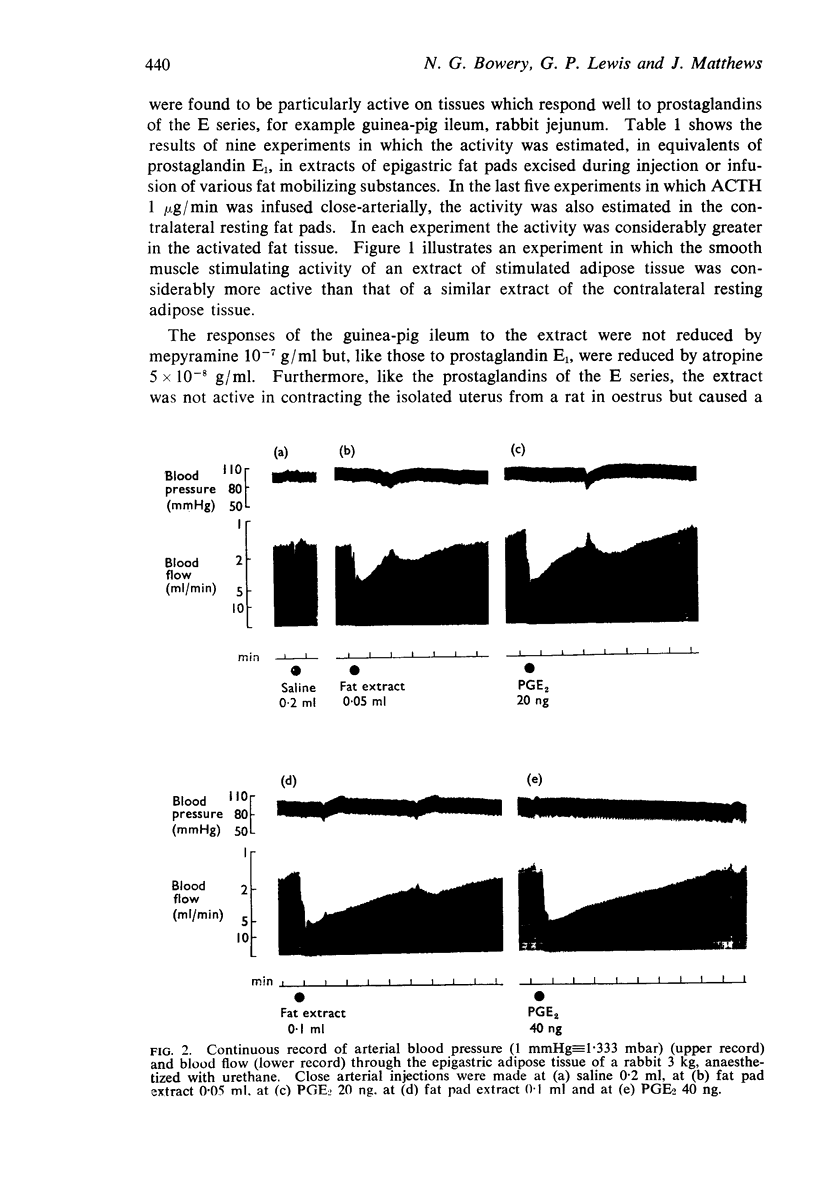
(b) It caused a prolonged vasodilator response when injected closearterially to the epigastric fat pad.
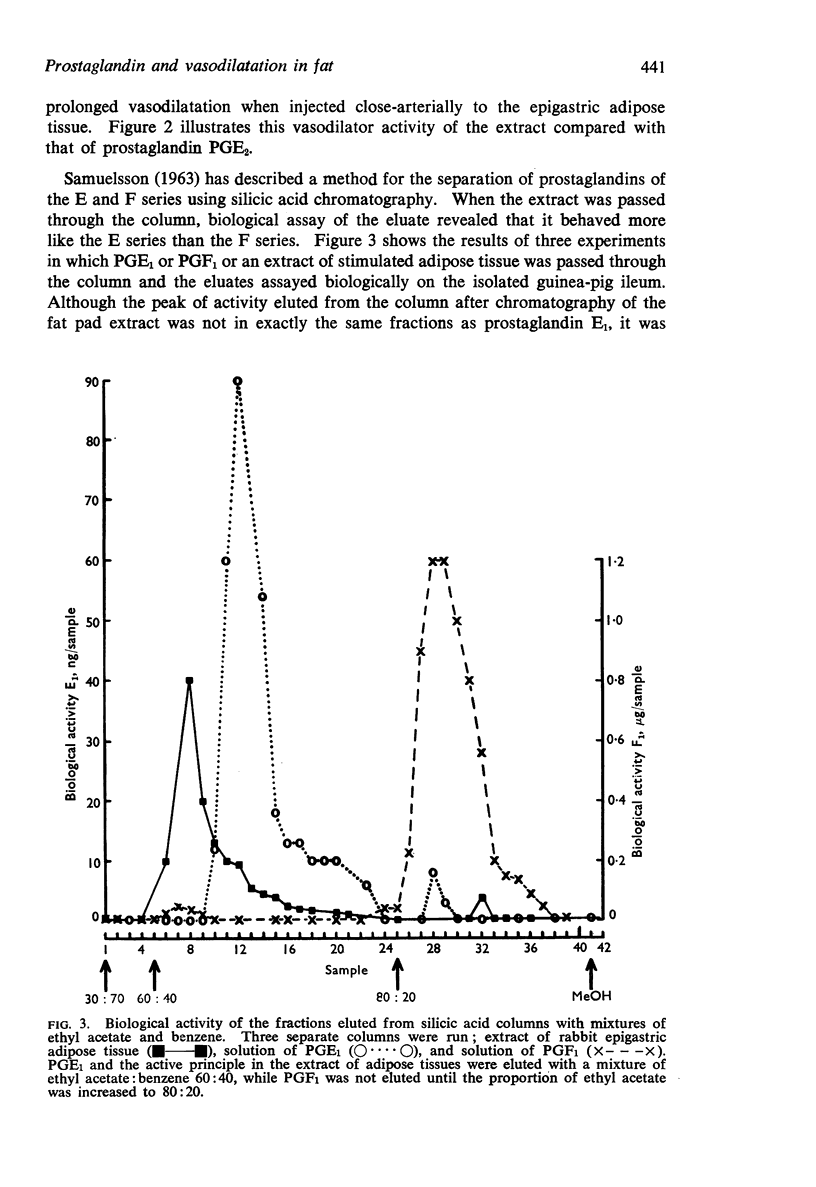
(c) It was eluted from a silicic acid column by a solvent system which is known to elute prostaglandins of the E series but not those of the F series.
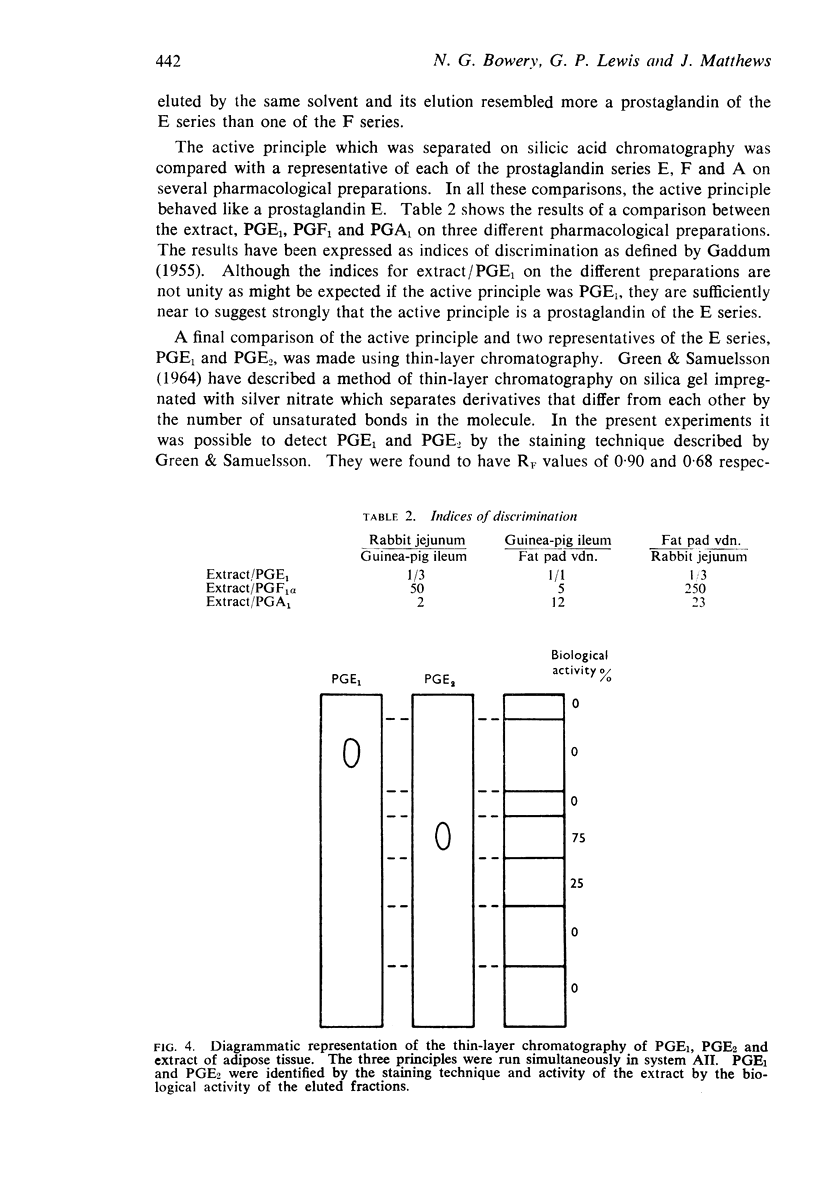
(d) Its indices of discrimination were similar to those of prostaglandin E's when assayed on three different pharmacological preparations.
(e) On thin-layer chromatography it behaved more like prostaglandin E2 than E1.
4. Neither prostaglandin E1 nor prostaglandin E2 inhibited the release of free fatty acids from the rabbit epigastric fat pad by ACTH1-24.
5. It seems likely that prostaglandin E2 is responsible for the vasodilatation accompanying fat mobilization from adipose tissue.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGSTROEM S., CARLSON L. A., OROE L. EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDINS ON CATECHOLAMINE INDUCED CHANGES IN THE FREE FATTY ACIDS OF PLASMA AND IN BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE DOG. PROSTAGLANDIN AND RELATED FACTORS 22. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Jan-Feb;60:170–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb02880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Ekelund L. G., Orö L. Cardiovascular and metabolic response to infusions of prostaglandin E1 and to simultaneous infusions of noradrenaline and prostaglandin E1 in man. Prostaglandin and related factors 35. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Aug;64(4):332–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A. Influence of the nutritional state on the inhibition of lipolysis in adipose tissue by Prostaglandin E1 and nicotinic acid. Prostaglandin and related factors 46. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Dec;65(4):383–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Carlson L. A., Orö L. Effect of different doses of prostaglandin E on free fatty acids of plasma, blood glucose and heart rate in the nonanesthetized dog. Prostaglandin and related factors 53. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jun;67(2):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Ekelund L. G., Orö L. Clinical and metabolic effects of different doses of prostaglandin E1 in man. Prostaglandin and related factors. Acta Med Scand. 1968 May;183(5):423–430. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNCOMBE W. G. THE COLORIMETRIC MICRO-DETERMINATION OF NON-ESTERIFIED FATTY ACIDS IN PLASMA. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Feb;9:122–125. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZBAUER M., VOGT M. Functional changes produced in the adrenal cortex of the rat by administration or by release of corticotrophin. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):449–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Mattews J. The mechanism of functional vasodilatation in rabbit epigastric adipose tissue. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):15–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Matthews J. The mobilization of free fatty acids from rabbit adipose tissue in situ. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):564–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Staehelin M. Adrenal responses to corticotrophin in the presence of an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1968 Aug;58(4):619–629. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0580619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E., Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M. Efflux of prostaglandin from adrenal glands stimulated with acetylcholine. Nature. 1966 Apr 16;210(5033):273–274. doi: 10.1038/210273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E., Kucharski J. Prostaglandin: release from the rat phrenic nerve--diaphragm preparation. Science. 1965 Sep 17;149(3690):1390–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3690.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from cerebral cortex of anesthetized cats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):125–134. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMUELSSON B. ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF PROSTAGLANDINS FROM HUMAN SEMINAL PLASMA. 18. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3229–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG D., VAUGHAN M., NESTEL P. J., BERGSTROM S. Effects of prostaglandin E opposing those of catecholamines on blood pressure and on triglyceride breakdown in adipose tissue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Jul;12:764–766. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Ramwell P. W. Release of prostaglandin from rat epididymal fat pad on nervous and hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1498–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Barthe P., Desaulles P. A. On the mechanism of the adrenal gland response to adrenocorticotrophic hormone in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Sep;50(1):55–64. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0500055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


