Abstract
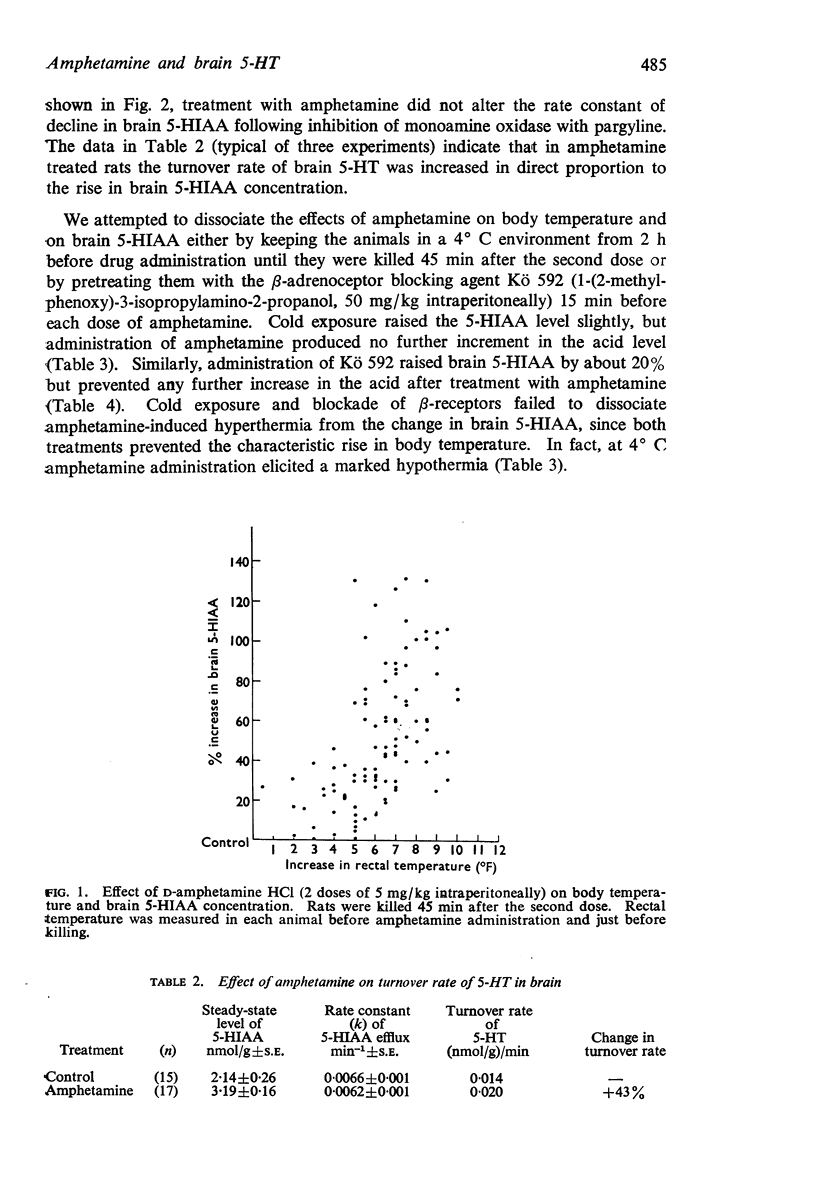
1. Administration of two doses of amphetamine HCl (5 mg/kg intraperitoneally) 45 min apart raised body temperature of rats by an average of 3·4° C and increased the turnover rate of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) by almost one-half.
2. Both effects were blocked by exposure to 4° C or by pretreatment with the β-blocker Kö 592 (1-(2-methylphenoxy)-3-isopropylamine-2-propanol), but not by the administration of the ganglionic blocker chlorisondamine combined with atropine.
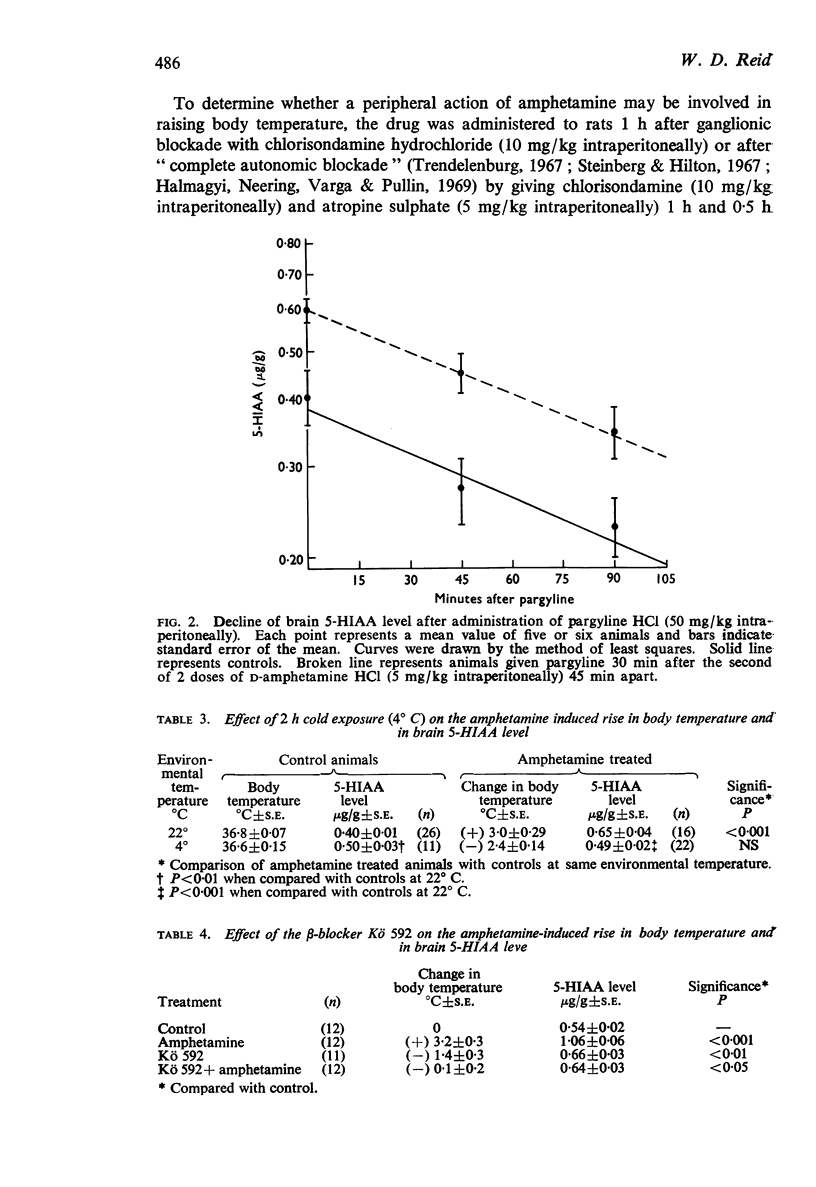
3. Since it has previously been shown that hyperthermia per se increases the turnover rate of brain 5-HT, and that amphetamine does not directly affect the uptake and release of 5-HT in brain slices, it is concluded that the amphetamine-induced increase in 5-HT turnover may be secondary to the rise in temperature produced by the drug.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOGDANSKI D. F., PLETSCHER A., BRODIE B. B., UNDENFRIEND S. Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKINGHAM S., MAYNERT E. W. THE RELEASE OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE, POTASSIUM AND AMINO ACIDS FROM PLATELETS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Mar;143:332–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The action of sympathomimetic amines in animals treated with reserpine. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):314–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beani L., Bianchi C., Santinoceto L., Marchetti P. The cerebral acetylcholine release in conscious rabbits with semi-permanently implanted epidural cups. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1968 Sep;7(5):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(68)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzinger T. H., Pratt A. W., Kitzinger C. THE THERMOSTATIC CONTROL OF HUMAN METABOLIC HEAT PRODUCTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 May;47(5):730–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Cheramy A., Feltz P., Glowinski J. Release of newly synthesized dopamine from dopamine-containing terminals in the striatum of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson A., Lindqvist M., Dahlström A., Fuxe K., Masuoka D. Effects of the amphetamine group on intraneuronal brain amines in vivo and in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Aug;17(8):521–523. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr L. A., Moore K. E. Norepinephrine: release from brain by d-amphetamine in vivo. Science. 1969 Apr 18;164(3877):322–323. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. A possible role played by central monoamine neurones in thermo-regulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Oct-Nov;71(2):224–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. On the mode of action of acetylcholine in evoking adrenal medullary secretion: increased uptake of calcium during the secretory response. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:385–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingell J. V., Owens M. L., Norvich M. R., Sulser F. On the role of norepinephrine biosynthesis in the central action of amphetamine. Life Sci. 1967 Jun 1;6(11):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfini E., Garattini S., Valzelli L. Activity of (+)-amphetamine at different environmental temperatures in three strains of mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 Dec;21(12):871–872. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessa G. L., Clay G. A., Brodie B. B. Evidence that hyperthermia produced by d-amphetamine is caused by a peripheral action of the drug. Life Sci. 1969 Feb 1;8(3):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Axelrod J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. IV. Effects of drugs on the disposition and metabolism of H3-norepinephrine and H3-dopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jul;153(1):30–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMSTEDT B., LUNDGREN G., SUNDWALL A. TREMORINE AND ATROPINE EFFECTS ON BRAIN ACETYLCHOLINE. Life Sci. 1963 Oct;10:731–736. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(63)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIEH A. C., CARLSON L. D., GRAY G. Role of the sympathetic nervous system in the control of chemical regulation of heat production. Am J Physiol. 1957 Aug;190(2):247–251. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.190.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halmagyi D. F., Neering I. R., Varga D., Pullin J. Sustained complete autonomic blockade. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):271–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. C. Evidence that the central action of amphetamine is mediated via catecholamines. Psychopharmacologia. 1966;9(1):78–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00427706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himms-Hagen J. Sympathetic regulation of metabolism. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):367–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVERTY R., SHARMAN D. F. MODIFICATION BY DRUGS OF THE METABOLISM OF 3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLETHYLAMINE, NORADRENALINE AND 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE IN THE BRAIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Jun;24:759–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCAMAN R. E., MCCAMAN M. W., HUNT J. M., SMITH M. S. MICRODETERMINATION OF MONOAMINE OXIDASE AND 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN DECARBOXYLASE ACTIVITIES IN NERVOUS TISSUES. J Neurochem. 1965 Jan;12:15–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb10246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEAN J. R., MCCARTNEY M. Effect of D-amphetamine on rat brain noradrenaline and serotonin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 May;107:77–79. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morpurgo C., Theobald W. Pharmacological modifications on the amphetamine-induced hyperthermia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Feb;2(4):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAASONEN M. K., VOGT M. The effect of drugs on the amounts of substance P and 5-hydroxytryptamine in mammalian brain. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):617–626. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPEU G. EFFECT OF 'TREMORINE' AND SOME ANTI-PARKINSON'S DISEASE DRUGS ON ACETYLCHOLINE IN THE RAT'S BRAIN. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:895–895. doi: 10.1038/200895a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLETSCHER A., BARTHOLINI G., BRUDERER H., BURKARD W. P., GEY K. F. CHLORINATED ARYLALKYLAMINES AFFECTING THE CEREBRAL METABOLISM OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1964 Sep;145:344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletscher A., Bartholini G. Drug-induced changes of uptake and metabolism of 5-hydroxytryptamine by brain slices. Med Pharmacol Exp Int J Exp Med. 1967;16(5):432–440. doi: 10.1159/000137024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON J. A., WOODS E. F. Release of norepinephrine from the isolated heart. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):149–151. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid W. D., Volicer L., Smookler H., Beaven M. A., Brodie B. B. Brain amines and temperature regulation. Pharmacology. 1968;1(6):329–344. doi: 10.1159/000135983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M., Hilton J. G. Effect of sympathectomy and adrenalectomy upon ganglion blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 May;156(2):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valzelli L., Dolfini E., Tansella M., Garattini S. Activity of centrally acting drugs on amphetamine metabolism. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;20(8):595–599. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1968.tb09819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volicer L., Reid W. D. Effect of drugs on turnover rate of heart norepinephrine. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Jan;8(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A., Koe B. K., Tenen S. S. Antiamphetamine effects following inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Mar;151(3):339–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


