Abstract
1. The carrageenin foot test was established as a sensitive and reliable assay procedure for determining the anti-inflammatory activity of inflammatory exudates.
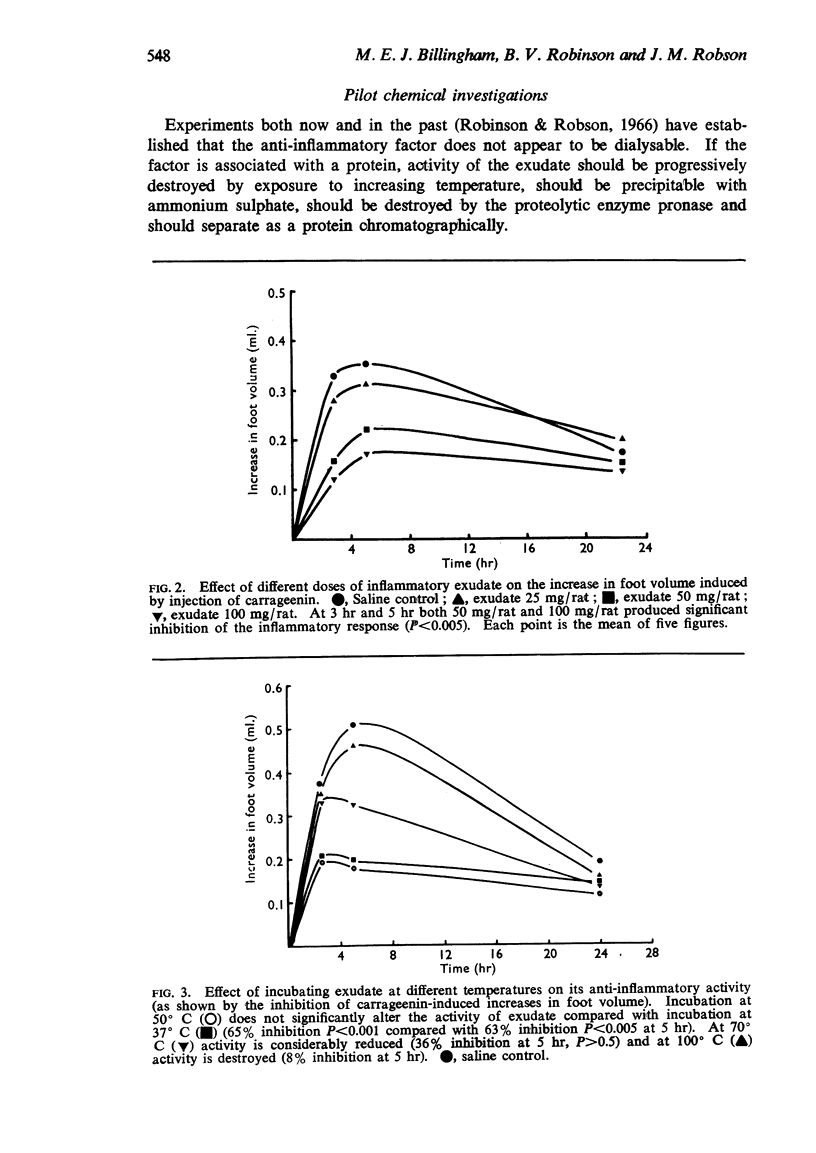
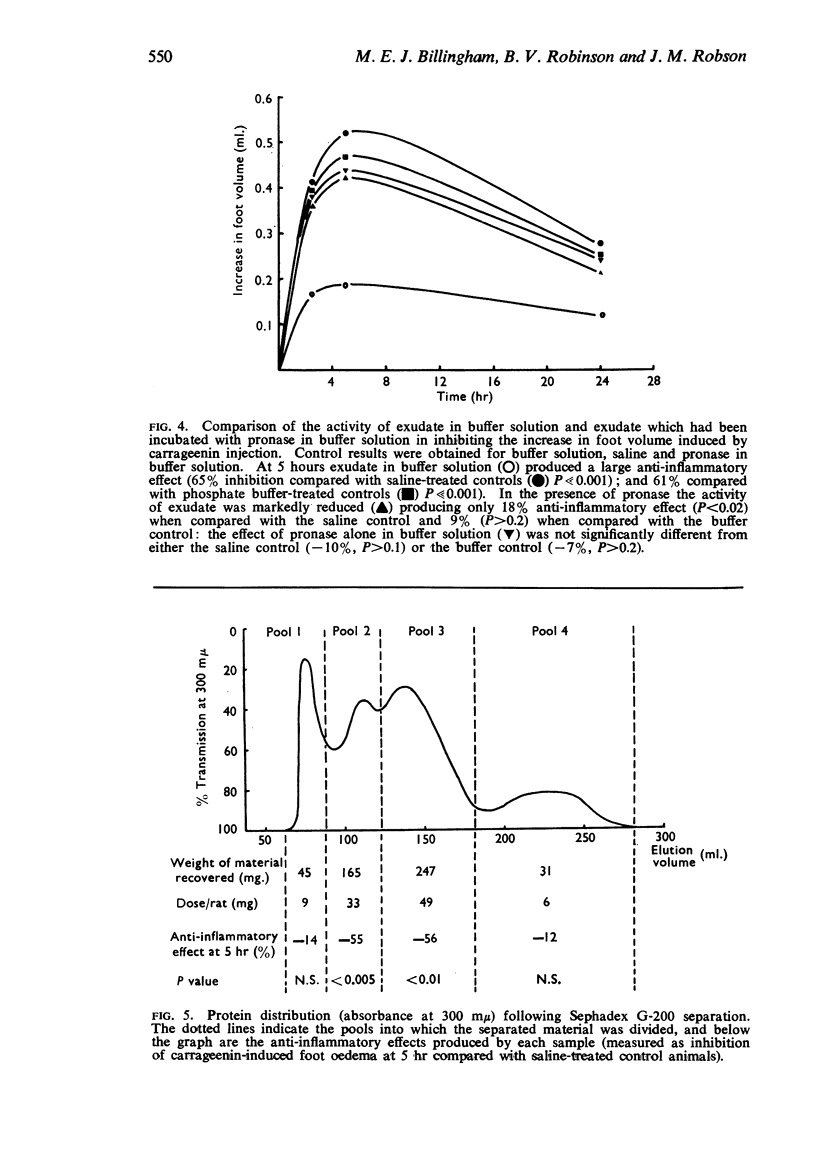
2. Incubation alone at a temperature above 70° C or with pronase at 37° C destroyed the anti-inflammatory activity of exudate.
3. The anti-inflammatory component of exudate was partially precipitated by 50% ammonium sulphate.
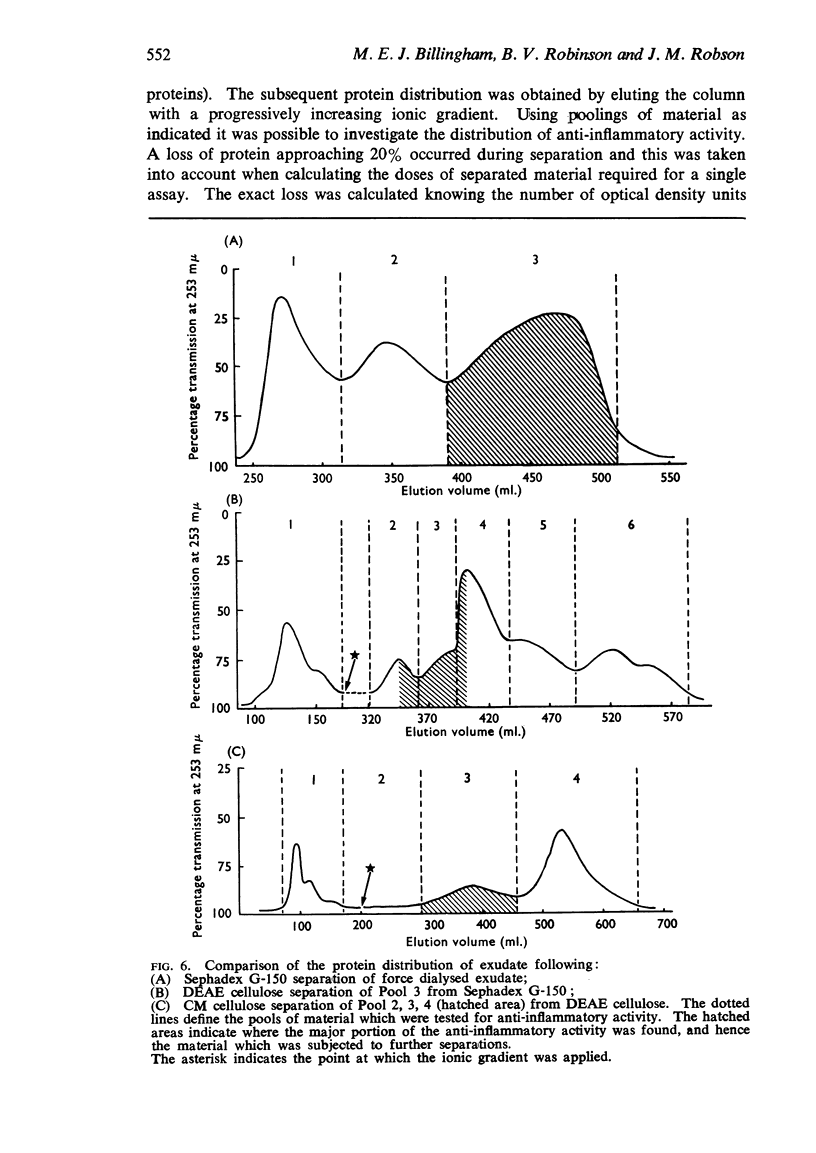
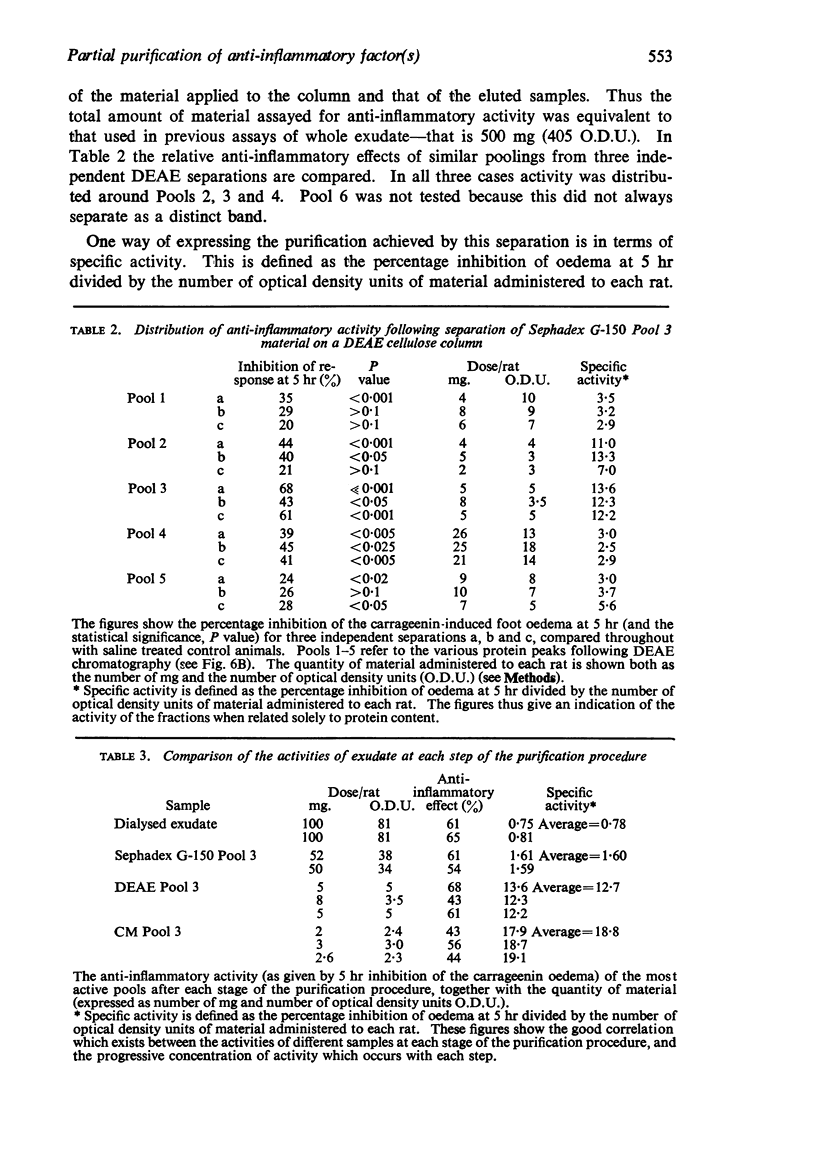
4. A partial purification process was devised using Sephadex G-150 gel filtration and DEAE and CM cellulose ion exchange chromatography to obtain at least a 24 fold purification.
5. Measurements of 11-hydroxycorticosteroid levels indicated that steroids were not involved in the mechanism by which the exudate produced its anti-inflammatory effects.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENITZ K. F., HALL L. M. THE CARRAGEENIN-INDUCED ABSCESS AS A NEW TEST FOR ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF STEROIDS AND NONSTEROIDS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Jul 1;144:185–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CYGIELMAN S., ROBSON J. M. THE EFFECT OF IRRITANT SUBSTANCES ON THE DEPOSITION OF GRANULATION TISSUE IN THE COTTON PELLET TEST. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1963 Dec;15:794–797. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1963.tb12882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARCY D. A. RESPONSE OF A SERUM GLYCOPROTEIN TO TISSUE INJURY AND NECROSIS. I. THE RESPONSE TO NECROSIS, HYPERPLASIA AND TUMOUR GROWTH. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:281–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPASQUALE G., GIRERD R. J. Anti-inflammatory properties of lyophilized inflammatory exudates. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1155–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPASQUALE G., GIRERD R. J., BEACH V. L., STEINETZ B. G. ANTIPHLOGISTIC ACTION OF GRANULOMA POUCH EXUDATES IN INTACT OR ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS. Am J Physiol. 1963 Dec;205:1080–1082. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.6.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn E. M., Bowman B. J., Koslowske T. C. The systemic response to inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):27–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90291-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. M., SPENCER P. S. A modified plethysmographic apparatus for recording volume changes in the rat paw. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962 Jul;14:464–466. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1962.tb11125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck J. C., Jacob R. A. The chemistry of dermal necrosis. Lab Invest. 1966 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jori A., Bernardi D. Presence of a general irritation and inhibition of a local inflammation. Med Pharmacol Exp Int J Exp Med. 1966;14(5):500–506. doi: 10.1159/000135825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADEN C., BLACKWELL R. Q., FOSDICK L. S. Anti-inflammatory effects of counterirritants. Am J Physiol. 1958 Dec;195(3):712–718. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.195.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHardy-Young S., Harris P. W., Lessof M. H., Lyne C. Singledose dexamethasone suppression test for Cushing's Syndrome. Br Med J. 1967 Jun 17;2(5554):740–744. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5554.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINDANI T. H. Recovery of an anti-inflammatory fraction from inflammatory exudate. Indian J Med Res. 1956 Oct;44(4):673–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON B. V., ROBSON J. M. PRODUCTION OF AN ANTI-INFLAMMATORY SUBSTANCE AT A SITE OF INFLAMMATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:420–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. V., Robson J. M. Further studies on the anti-inflammatory factor found at a site of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Feb;26(2):372–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcione E. J., Bogden A. E. Hepatic synthesis of alpha 2 (acute phase)-globulin of rat plasma. Science. 1966 Jul 29;153(3735):547–548. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3735.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., RISLEY E. A., NUSS G. W. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiiflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:544–547. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


