Abstract
1. The effects of central stimulant drugs injected intraperitoneally were examined on the release of acetylcholine (ACh) from the cerebral cortex of the anaesthetized rat. The effects of the drugs in increasing ACh release were approximately parallel to the increases produced in the electrical activity of the brain.
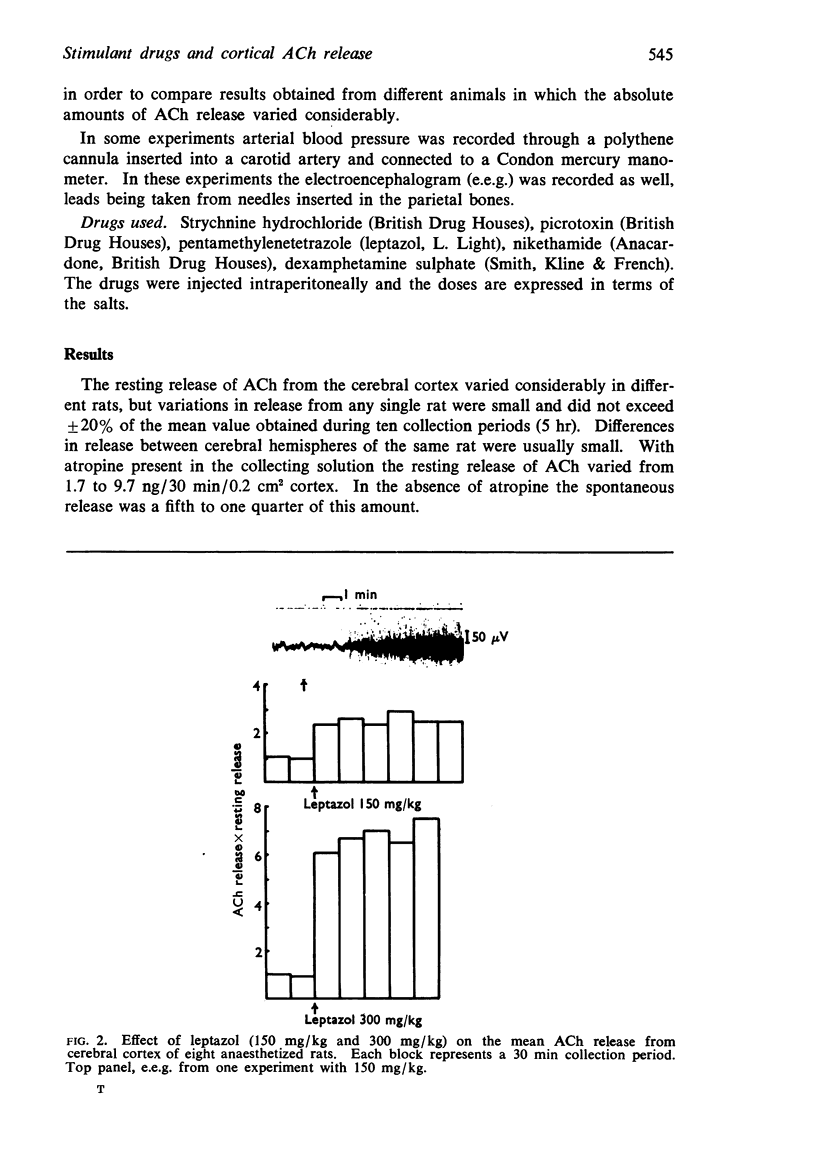
2. Leptazol in a dose of 150 mg/kg increased the release of ACh by 2.9 times the resting release and in a dose of 300 mg/kg by 7.5 times; on the e.e.g. the injection produced a large increase in the electrical activity.
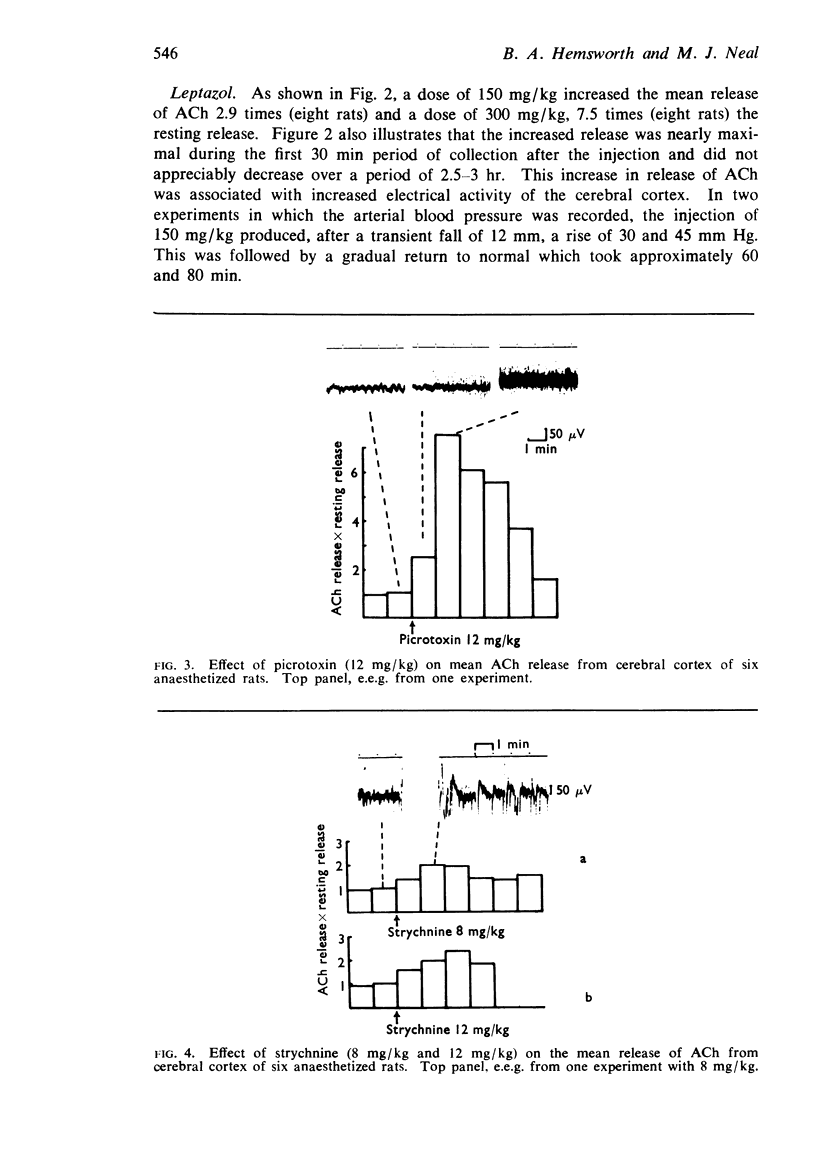
3. Picrotoxin in a dose of 12 mg/kg increased the release of ACh by 7.5 times and on the e.e.g. caused a large increase in activity.
4. Strychnine in doses of 8 mg/kg and 12 mg/kg increased the release of ACh by 2.0 and 2.4 times and produced a small increase in the activity of the e.e.g.
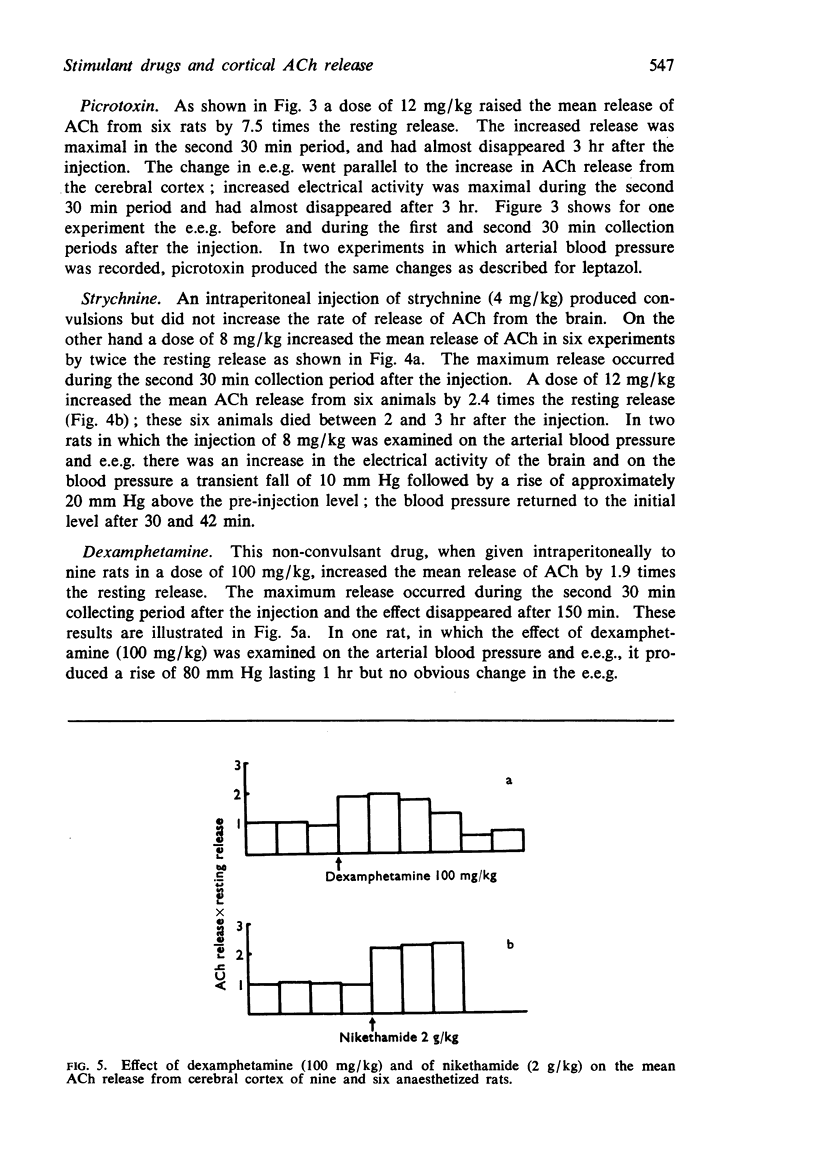
5. Dexamphetamine in a dose of 100 mg/kg increased the release of ACh by 1.9 times and had no appreciable effect on the e.e.g.
6. Nikethamide in a dose of 2 g/kg increased the release of ACh by 2.3 times and produced no appreciable change in the e.e.g.
7. Caffeine in a dose of 100 mg/kg produced no significant effect on the release of ACh.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY P. B., ELKES J. The effects of some drugs on the electrical activity of the brain. Brain. 1957 Mar;80(1):77–117. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beleslin D., Polak R. L., Sproull D. H. The effect of leptazol and strychnine on the acetylcholine release from the cat brain. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(2):308–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE M. R. A. Central nervous function and changes in brain metabolite concentration; characteristic glycogen increment patterns produced by convulsant drugs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1951 Mar;6(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1951.tb00613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesia G. G., Jasper H. H. Acetylcholine released from cerebral cortex in relation to state of activation. Neurology. 1966 Nov;16(11):1053–1063. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.11.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B., Mitchell J. F. The central release of acetylcholine during stimulation of the visual pathway. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIEBEL G., BONVALLET M., HUVE P., DELL P. Analyse neurophysiologique de l'action centrale de la d-amphétamine (maxiton). Sem Hop. 1954 May 6;30(30):1880–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOLLY E. R., STEINHAUS J. E. The effect of drugs injected into limited portions of the cerebral circulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Mar;116(3):273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANAI T., SZERB J. C. MESENCEPHALIC RETICULAR ACTIVATING SYSTEM AND CORTICAL ACETYLCHOLINE OUTPUT. Nature. 1965 Jan 2;205:80–82. doi: 10.1038/205080b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K. Chemical transmission and cortical arousal. Anesthesiology. 1967 Jan-Feb;28(1):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGO V. G., SILVESTRINI B. Action of eserine and amphetamine on the electrical activity of the rabbit brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Jun;120(2):160–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Chong G. C. Acetylcholine release from the cerebral and cerebellar cortices: its role in cortical arousal. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1253–1255. doi: 10.1038/2071253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALLEK W., KUEHN A. Effects of drugs on spontaneous and activated EEG of cat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Jul 1;120:319–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUTE C. C., LEWIS P. R. CHOLINESTERASE-CONTAINING SYSTEMS OF THE BRAIN OF THE RAT. Nature. 1963 Sep 21;199:1160–1164. doi: 10.1038/1991160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


